Accessing 4-oxy-substituted isoquinolinones via C–H activation and regioselective migratory insertion with electronically biased ynol ethers†
Abstract
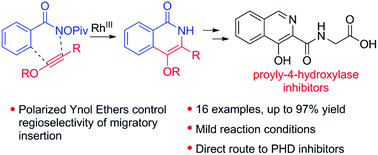
The rhodium-catalyzed C–H activation and annulation with ynol ethers to directly provide 4-oxy substituted isoquinolinones is reported. The polarized nature of ynol ethers provides an electronic bias for controlling the regioselectivity of the migratory insertion process. While the highly reactive nature of ynol ethers presents a challenge, mild conditions were found to provide product in moderate to good yield. Utility was demonstrated by application in the synthesis of a prolyl-4-hydroxylase inhibitor framework.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...