Palladium catalyzed carbonylative annulation of the C(sp2)–H bond of N,1-diaryl-1H-tetrazol-5-amines and N,4-diaryl-4H-triazol-3-amines to quinazolinones†
Abstract
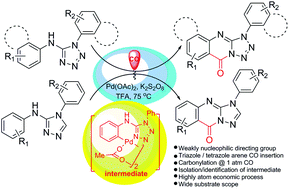
Pd(II) catalyzed direct C–H carbonylative annulation of N,1-diaryl-1H-tetrazol-5-amines and N,4-diaryl-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-amines gave the corresponding triazole and tetrazole fused quinazolinones in good yields. This methodology offers a convenient method for the synthesis of these important heterocyclic scaffolds in a highly atom economical process. On the mechanistic aspect weakly nucleophilic triazole and tetrazole moieties function as both directing as well as intramolecular nucleophiles. The catalytically active C–H activated intermediate dimeric Pd complex was isolated and characterized which on exposure to CO gas gave the corresponding tetrazole fused quinazolinone derivative. On the basis of isolation of the intermediate and observed kinetic isotope effects, a mechanism has been proposed for the C–H activated direct carbonylative annulation reaction.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Synthetic methodology in OBC


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...