Phenazine antibiotic inspired discovery of potent bromophenazine antibacterial agents against Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis†
Abstract
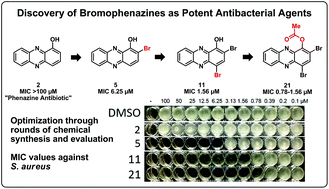
Nearly all clinically used antibiotics have been (1) discovered from microorganisms (2) using phenotype screens to identify inhibitors of bacterial growth. The effectiveness of these antibiotics is attributed to their endogenous roles as bacterial warfare agents against competing microorganisms. Unfortunately, every class of clinically used antibiotic has been met with drug resistant bacteria. In fact, the emergence of resistant bacterial infections coupled to the dismal pipeline of new antibacterial agents has resulted in a global health care crisis. There is an urgent need for innovative antibacterial strategies and treatment options to effectively combat drug resistant bacterial pathogens. Here, we describe the implementation of a Pseudomonas competition strategy, using redox-active phenazines, to identify novel antibacterial leads against Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis. In this report, we describe the chemical synthesis and evaluation of a diverse 27-membered phenazine library. Using this microbial warfare inspired approach, we have identified several bromophenazines with potent antibacterial activities against S. aureus and S. epidermidis. The most potent bromophenazine analogue from this focused library demonstrated a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 0.78–1.56 μM, or 0.31–0.62 μg mL−1, against S. aureus and S. epidermidis and proved to be 32- to 64-fold more potent than the phenazine antibiotic pyocyanin in head-to-head MIC experiments. In addition to the discovery of potent antibacterial agents against S. aureus and S. epidermidis, we also report a detailed structure–activity relationship for this class of bromophenazine small molecules.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...