Nanoalloying bulk-immiscible iridium and palladium inhibits hydride formation and promotes catalytic performances†
Abstract
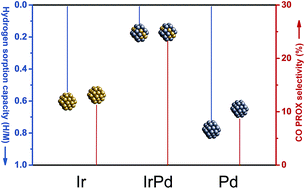
The hydrogen sorption properties of oxide-supported Ir–Pd nanoalloys have been determined for the first time, and correlated with their catalytic behavior. The addition of Ir to Pd suppresses hydride formation and leads to improved catalytic performances with respect to pure metals in the preferential oxidation of CO in H2 excess (PROX).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...