Vapor-phase growth and characterization of Mo1−xWxS2 (0 ≤ x ≤ 1) atomic layers on 2-inch sapphire substrates
Abstract
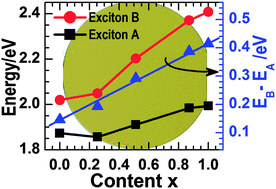
Atomically thin Mo1−xWxS2 (0 ≤ x ≤ 1) ternary compounds have been grown on 2-inch c-plane sapphire substrates with high uniformity by sulfurizing thin Mo1−xWx layers that were deposited at room temperature using a co-sputtering technique. Atomic force microscopy (AFM), Raman scattering, and optical absorbance spectroscopy (OAS) studies reveal that the Mo1−xWxS2 films consist of crystallites of two-to-four monolayers in thickness. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) shows that the core levels of Mo3d and W4f shift to lower binding energies while that of S2p shifts to higher ones with the increase in W compositions, which can be related to the larger electron affinity of W (0.8163 eV) than that of Mo (0.7473 eV). OAS has also shown that the direct bandgap of Mo1−xWxS2 is tuned from 1.85 to 1.99 eV by increasing x from 0 to 1. Both E12g and A1g phonon modes of the Mo1−xWxS2 films exhibit a two-mode behavior. The bandgap tuning and the two-mode phonon behaviors are typically the same as those recently observed in monolayer Mo1−xWxS2 obtained by mechanical exfoliation, thus shedding light on the bottom-up growth of large-scale two-dimensional Mo1−xWxS2 ternary alloys.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...