Tailoring surface plasmons of high-density gold nanostar assemblies on metal films for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy†
Abstract
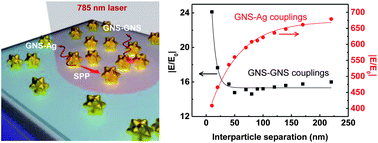
Plasmonic systems based on metal nanoparticles on a metal film have generated great interest for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) chemical sensors. In this study, we describe the fabrication of ultrasensitive SERS substrates based on high-density gold nanostar assemblies on silver films with tailored surface plasmons, where multiple field enhancements from particle–film and interparticle plasmon couplings and lightening rod effects of sharp tips of nanostars contribute to the enormous Raman enhancements. We show that the interplay between interparticle and particle–film plasmon couplings of high-density gold nanostars (GNSs) on metal and dielectric films as a function of interparticle separation can be tailored to provide maximum SERS effects. We observe that the SERS enhancement factor (EF) of GNSs on a metal film as a function of interparticle separation follows a broken power law function, where the EF increases with the interparticle separation for the strong interparticle coupling range below an interparticle separation of ∼0.8 times the GNS size, but decreases for the weak interparticle coupling range (for an interparticle separation of >0.8 times the GNS size). Finally, we demonstrate the use of tailored plasmonic substrates as ultrasensitive SERS chemical sensors with an attomole level of detection capability of 2,4-dinitrotoluene, a model compound of nitroaromatic explosives.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...