Fabrication and markedly enhanced white up-conversion emission of core–shell structured NaGdF4:Tm3+/Yb3+/Ho3+@SiO2
Abstract
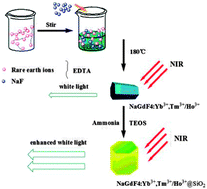
Core–shell structured NaGdF4:Yb3+/Tm3+/Ho3+@SiO2 microrods were successfully prepared via the Stöber sol–gel method by coating a layer of silica on the surface of NaGdF4:Yb3+/Tm3+/Ho3+ particles derived from a hydrothermal process. The phase, structure, morphology and up-conversion (UC) luminescence properties were characterized by various techniques. It is found that the products with core–shell structure exhibit bright UC emissions. Strong white light emission is generated by tuning the Tm/Ho molar ratio in the Tm/Ho co-doped system. The formation process of the core–shell sample has also been discussed. In particular, the white UC emission can be markedly enhanced by coating a silica layer onto the surface of the phosphors, showing great potential in display and lighting fields.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...