A multi-channel device for high-density target-selective stimulation and long-term monitoring of cells and subcellular features in C. elegans†
Abstract
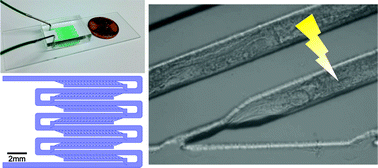
Selective cell ablation can be used to identify neuronal functions in multicellular model organisms such as Caenorhabditis elegans. The optogenetic tool KillerRed facilitates selective ablation by enabling light-activated damage of cell or subcellular components in a temporally and spatially precise manner. However, the use of KillerRed requires stimulating (5 min–1 h), culturing (~24 h) and imaging (often repeatedly) a large number of individual animals. Current manual manipulation methods are limited by their time-consuming, labor-intensive nature, and their usage of anesthetics. To facilitate large-scale selective ablation, culturing, and repetitive imaging, we developed a densely-packed multi-channel device and used it to perform high-throughput neuronal ablation on KillerRed-expressing animals. The ability to load worms in identical locations with high loading efficiency allows us to ablate selected neurons in multiple worms simultaneously. Our device also enables continuous observation of animals for 24 h following KillerRed activation, and allows the animals to be recovered for behavioural assays. We expect this multi-channel device to facilitate a broad range of long-term imaging and selective illumination experiments in neuroscience.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...