Speciation analysis of antimony in water samples via combined nano-sized TiO2 colloid Preconcentration and AFS analysis
Abstract
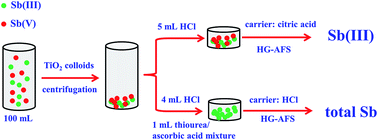
A method for the speciation of Sb(III) and Sb(V) in water samples was developed using nano-sized TiO2 colloids as adsorbent and hydride generation atomic fluorescence spectrometry (HG-AFS) as a determination technique. The adsorption efficiency for Sb(III) and Sb(V) exceeded 98.0% within a short time when the pH was 6.0. Two carrier acid solutions, citric acid (1%) for Sb(III) and HCl (2%) for total Sb, were used. After the determinations of Sb(III) and total Sb, Sb(V) could be calculated by their difference. The effects of certain conditions on the ratio of Sb(III)/Sb(V) and the presence of coexisting ions were studied. The enrichment factor for both Sb(III) and total Sb was 20. The detection limits of this method were 10 ng L−1 for Sb(III) and 13 ng L−1 for total Sb. The relative standard deviations (n = 6) were 6.7% for Sb(III) and 4.4% for total Sb, demonstrating good analytical precision. The accuracy of the proposed method was validated with an environmental water sample certified reference material (GSB 07-1376-2001) with a Sb(III) concentration of 1.24 ± 0.26 mg L−1. The obtained Sb(III) concentration was 1.22 ± 0.03 mg L−1, which was in good agreement with the certified value. The developed method was simple, fast and sensitive without any filtration or desorption steps and provided low detection limits for Sb(III) and Sb(V).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...