Facile synthesis of furfuryl ethyl ether in high yield via the reductive etherification of furfural in ethanol over Pd/C under mild conditions†
Abstract
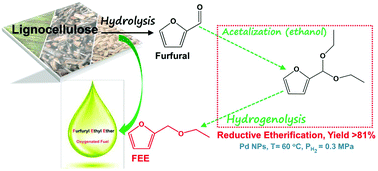
The one-pot synthesis of furfuryl ethyl ether (FEE) over Pd nanoparticles supported on TiO2, Al2O3, SiO2, and active carbon via the catalytic reductive etherification of furfural in ethanol was systematically studied. The Pd nanoparticles supported on SiO2, TiO2 and active carbon are all active for this novel process under mild reaction conditions, with Pd/C showing the highest selectivity to FEE. The effects of palladium loading, reaction temperature, and hydrogen pressure on the activity and selectivity of Pd/C have been investigated in detail. The results demonstrate that suitable Pd amount, low reaction temperature of about 60 °C, and low H2 pressure of about 0.3 MPa are favorable for the formation of the desired ether product. Under the optimized conditions, an unprecedented high yield of up to 81% of FEE was firstly obtained with the major by-products being furfuryl alcohol and 2-methyltetrahydrofuran. Compared with the conventional hydrogenation-etherification route via furfural alcohol as a reaction intermediate, the reductive etherification shows significant advantage in product yield because of its much lower reaction temperature that is required.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...