Edible oleogels based on water soluble food polymers: preparation, characterization and potential application
Abstract
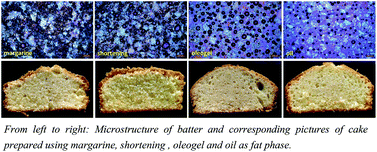
Oil structuring using food-approved polymers is an emerging strategy and holds significant promise in the area of food and nutrition. In the current study, edible oleogels (containing >97 wt% of sunflower oil) were prepared using a combination of water soluble food polymers (methylcellulose and xanthan gum) and further evaluated for potential application as a shortening alternative. Microstructure studies (including cryo-SEM) and rheology measurements were conducted to gain more insights into the properties of these new types of oleogels. In addition, the functionality of oleogel as a shortening alternative was studied in terms of batter properties and the texture analysis of cakes and compared to the reference batches made using either oil, commercial shortening or cake margarine. Interestingly, while the batter properties (air incorporation, rheology and microstructure) of the oleogel batch were more close to the oil batch, the textural properties of cakes were significantly better than oil and resembled more to the cakes prepared using shortening and margarine.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...