Two-dimensional array of particles originating from dipole–dipole interaction as evidenced by potential curve measurements at vertical oil/water interfaces
Abstract
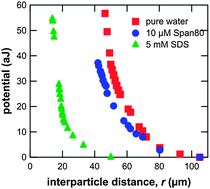
We propose a new method to evaluate the interaction potential energy between the particles adsorbed at an oil/water interface as a function of interparticle distance. The method is based on the measurement of the interparticle distance at a vertical oil/water interface, at which the gravitational force is naturally applied to compress the particle monolayer in the in-plane direction. We verified the method by examining whether we obtained the same potential curve upon varying the gravitational acceleration by tilting the interface. The present method is applicable in the force range from ∼0.1 to ∼100 pN, determined by the effective weight of the particles at the interface. The method gives a rather simple procedure to estimate a long range interaction among the particles adsorbed at oil/water interfaces. We applied this method to polystyrene particles at the decane/aqueous surfactant solution interface, and obtained the interparticle potential curves. All the potential curves obtained by the present method indicated that the interparticle repulsion is due to the electrical dipole–dipole interaction based on the negative charge of the particles. The mechanism of the dipole–dipole interaction is further discussed on the basis of the effects of surfactants.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...