The bioinspired construction of an ordered carbon nitride array for photocatalytic mediated enzymatic reduction†
Abstract
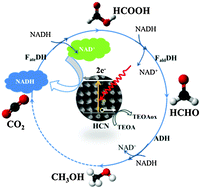
A carbon nitride array (CNA) material has been constructed using a sacrificial diatom template. A regular carbon nitride nanorod array could be replicated from the periodic and regular nanochannel array of the template. The directional charge transport properties and high light harvesting capability of the CNA gives much better performance in splitting water to give hydrogen than its bulk counterpart. Furthermore, by combining with a rhodium complex as a mediator, the nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) cofactor of many enzymes could be photocatalytically regenerated by the CNA. The rate of the in situ NADH regeneration is high enough to reverse the biological pathway of the three dehydrogenase enzymes, which then leads to the sustainable conversion of formaldehyde to methanol and also the reduction of carbon dioxide into methanol.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...