Experimental and theoretical investigations of the self-association of oxaliplatin†
Abstract
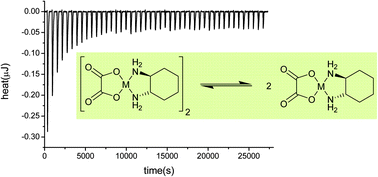
Self-aggregation in water of anti-cancer agents such as oxaliplatin (1) or its palladium-containing parent (2) is suspected to be the main reason for the exceptional resistance of concentrated infusions of these complexes to hydrolysis; this hypothesis, i.e. the self-association of metal chelates, was investigated in a systematic manner by experimental and theoretical means. 1H diffusion-ordered NMR spectroscopy (DOSY NMR) and UV-visible absorption titration were inconclusive as to the formation of a dimer of 1 in water or DMSO. Further isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) methods allowed the accurate determination of the enthalpy of formation of only the homodimer [2]2 and putative heterodimer [1·2] together with an estimation of the formation constants, which indicate that dimer formation is not a spontaneous process in solution, whereas electrospray ESI mass spectroscopy tends to suggest the contrary in the gas phase. A dispersion-corrected DFT method, i.e. DFT-D (BLYP-D3), was used to model the aggregation in solution (COSMO) and to investigate the assisting role of London force in the cohesion of bimolecular aggregates. The concordance of experimental and theoretical thermodynamic parameters was judged reasonably even though the treatment of solvation by conventional continuum models does not account for specific interactions of the solute with molecules of solvent; nonetheless these results outline the importance of dispersion, a.k.a. London force. The role of the latter was further stressed by computing the affinities of 1 and 2 for the lipophilic cavity of cucurbit[7]uril in modeled water (COSMO-RS), which were preliminarily determined experimentally by ITC methods using pure water as solvent. From our investigations carried out in pure water the connection between the notorious chemical stability of “concentrated” infusions of 1 in aqueous media and the formation of oligomers remains unsettled.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...