Doping strategies to control A-centres in silicon: insights from hybrid density functional theory
Abstract
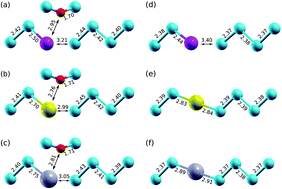
Hybrid density functional theory is used to gain insights into the interaction of intrinsic vacancies (V) and oxygen-vacancy pairs (VO, known as A-centres) with the dopants (D) germanium (Ge), tin (Sn), and lead (Pb) in silicon (Si). We determine the structures as well as binding and formation energies of the DVO and DV complexes. The results are discussed in terms of the density of states and in view of the potential of isovalent doping to control A-centres in Si. We argue that doping with Sn is the most efficient isovalent doping strategy to suppress A-centres by the formation of SnVO complexes, as these are charge neutral and strongly bound.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...