Graphene oxide for cellulose hydrolysis: how it works as a highly active catalyst?†
Abstract
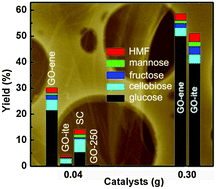
Graphene oxide (GO-ene), the two-dimensional carbon lattice decorated by abundant oxygen functionalities, is demonstrated as an efficient green catalyst towards selective hydrolysis of cellulose to glucose. The synergy of its carboxylic/phenolic groups and its layered, soft structure rendered GO-ene superior hydrolytic activity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...