Development and validation of a cryogen-free automatic gas chromatograph system (GC-MS/FID) for online measurements of volatile organic compounds
Abstract
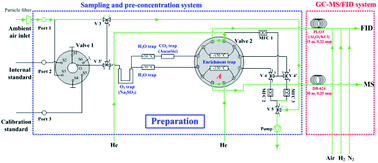
An automatic gas chromatograph system equipped with a mass spectrometer and a flame ionization detector (GC-MS/FID) was developed for online measurements of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in the atmosphere. This system consisted of a custom-built cryogen-free cooling device that can create an ultra-low temperature of −165 °C, a two-channel sampling and pre-concentration system, and a commercial GC-MS/FID. One channel in the sampling and pre-concentration system was designated to trap C2–C5 hydrocarbons, whereas the other was designed to trap other VOC species. The newly developed GC-MS/FID system was then employed to measure VOCs in ambient air, and its observation data were compared with those from three well-established techniques, including an offline GC-MS/FID coupled with canister sampling, a proton transfer reaction-mass spectrometer (PTR-MS), and an online gas chromatograph system equipped with an FID and a photo ionization detector (GC-FID/PID). The online and offline GC-MS/FID measurements for alkanes, acetylene, C2–C3 alkenes, C6–C8 aromatics, and halocarbons showed good agreement. In addition, the online GC-MS/FID measurements for C6–C9 aromatics, acetone, and methacrolein + methylvinylketone (MACR + MVK) agreed well with the PTR-MS observations. Mixing ratios of C2–C7 alkanes, C3–C5 alkenes, and C6–C8 aromatics also showed good agreement between the online GC-MS/FID and GC-FID/PID techniques. These inter-comparison results demonstrated the accuracy of online GC-MS/FID measurements for C2–C12 NMHCs, C3–C4 carbonyls, and halocarbons.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...