Microfluidic devices for label-free and non-instrumented quantitation of unamplified nucleic acids by flow distance measurement†
Abstract
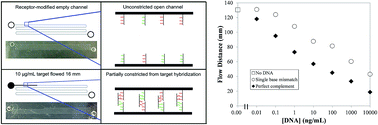
Timely biomarker quantitation has potential to improve human health but current methods have disadvantages either in terms of cost and complexity for benchtop instruments, or reduced performance in quantitation and/or multiplexing for point-of-care systems. We previously developed microfluidic devices wherein visually observed flow distances correlated with a model analyte's concentration (Chatterjee et al., Anal. Chem., 2012, 84, 7057). Here, we significantly expand over this prior result to demonstrate the measurement of unamplified DNA analogues of microRNAs (miRNAs), biomarkers whose levels can be altered in disease states. We have developed a method for covalently attaching nucleic acid receptors on poly(dimethylsiloxane) microchannel surfaces by silane and cross-linker treatments. We found a flow distance dependence on target concentrations from 10 μg mL−1 to 10 pg mL−1 for DNA in both buffer and synthetic urine. Moreover, flow time in addition to flow distance is correlated with target concentration. We also observed longer flow distances for single-base mismatches compared to the target sequence at the same concentration, indicating that our approach can be used to detect point mutations. Finally, experiments with DNA analogues of miRNA biomarkers for kidney disease (mir-200c-3p) and prostate cancer (mir-107) in synthetic urine showed the ability to detect these analytes near clinically relevant levels. Our results demonstrate that these novel microfluidic assays offer a simple route to sensitive, amplification-free nucleic acid quantitation, with strong potential for point-of-care application.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...