Rapid amplification/detection of nucleic acid targets utilizing a HDA/thin film biosensor
Abstract
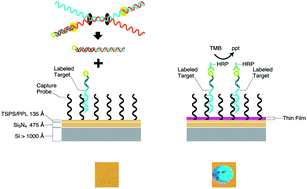
Thin film biosensors exploit a flat, optically coated silicon-based surface whereupon formation of nucleic acid hybrids are enzymatically transduced in a molecular thin film that can be detected by the unaided human eye under white light. While the limit of sensitivity for detection of nucleic acid targets is at sub-attomole levels (60 000 copies) many clinical specimens containing bacterial pathogens have much lower levels of analyte present. Herein, we describe a platform, termed HDA/thin film biosensor, which performs helicase-dependant nucleic acid amplification on a thin film biosensor surface to improve the limit of sensitivity to 10 copies of the mecA gene present in methicillin-resistant strains of Staphylococcus. As double-stranded DNA is unwound by helicase it was either bound by solution-phase DNA primers to be copied by DNA polymerase or hybridized to surface immobilized probe on the thin film biosensor surface to be detected. Herein, we show that amplification reactions on the thin film biosensor are equivalent to in standard thin wall tubes, with detection at the limit of sensitivity of the assay occurring after 30 minutes of incubation time. Further we validate the approach by detecting the presence of the mecA gene in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) from positive blood culture aliquots with high specificity (signal/noise ratio of 105).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...