One-pot controllable synthesis of oligo(carbonate-ether) triol using a Zn-Co-DMC catalyst: the special role of trimesic acid as an initiation-transfer agent†
Abstract
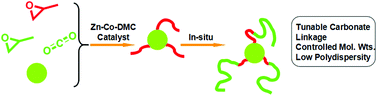
A one-pot synthesis of oligo(carbonate-ether) triol was realized by the copolymerization of CO2 and propylene oxide (PO) using a zinc-cobalt double metal cyanide (Zn-Co-DMC) catalyst in the presence of 1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylic (trimesic) acid (TMA). The catalytic activity ranged from 0.3 to 1.0 kg g−1 DMC under various copolymerization conditions. The structure of the oligo(carbonate-ether) triol was clearly confirmed, providing sound evidence for the special role played by the TMA, i.e., that it acted as an initiation-transfer agent. In the first stage the TMA initiated PO homo-polymerization to afford oligo-ether triol via a core-first approach in the presence of Zn-Co-DMC. After all of the TMA was consumed, the in situ formed oligo-ether triol acted as new chain transfer agent to participate in the copolymerization, forming carbonate-ether segments and therefore the oligo(carbonate-ether) triol. Since every molecule of TMA participated in initiation and propagation steps, the molecular weight of the triol depended on the amount of TMA used rather than the amount of Zn-Co-DMC. Consequently, the number average molecular weight (Mn) of the oligo(carbonate-ether) triol could be well controlled from 1400 to 3800 g mol−1 with a relatively narrow polydispersity index (PDI) (1.15–1.45), and its carbonate unit content (CU) could be adjusted between 20% and 54%.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...