Schiff based injectable hydrogel for in situ pH-triggered delivery of doxorubicin for breast tumor treatment
Abstract
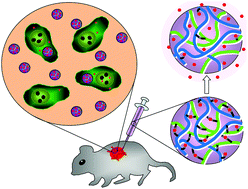
In this study, we report a facile approach to develop an injectable hydrogel with an in situ and pH sensitive drug delivery system for cancer treatment. The hydrogel was based on modified chitosan and alginate. We conjugated doxorubicin (DOX) to succinated chitosan (S-chi) via a Schiff base between a ketone group in the DOX and an amine group in the S-chi, which led to a pH sensitive release of DOX upon the stimulus of an acidic tumor microenvironment. Hydrogel formed in minutes while DOX conjugated S-chi was mixed with oxidized alginate. The hydrogel structure was characterized by cryo-imaging, FTIR and a rheology test. The DOX release profiles were tested in response to different pH values. The MTT assay showed a low toxicity of the hydrogel. The gel in turn inhibited the growth of tumor cells MCF-7 effectively when loaded with DOX. Finally, the DOX laden hydrogel was injected into the xenograft breast tumor model and significantly inhibited tumor growth.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...