The relationship between classification of multi-domain proteins using an alignment-free approach and their functions: a case study with immunoglobulins†
Abstract
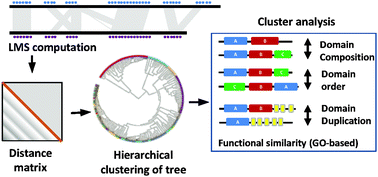
Establishing functional relationships between multi-domain protein sequences is a non-trivial task. Traditionally, delineating functional assignment and relationships of proteins requires domain assignments as a prerequisite. This process is sensitive to alignment quality and domain definitions. In multi-domain proteins due to multiple reasons, the quality of alignments is poor. We report the correspondence between the classification of proteins represented as full-length gene products and their functions. Our approach differs fundamentally from traditional methods in not performing the classification at the level of domains. Our method is based on an alignment free local matching scores (LMS) computation at the amino-acid sequence level followed by hierarchical clustering. As there are no gold standards for full-length protein sequence classification, we resorted to Gene Ontology and domain-architecture based similarity measures to assess our classification. The final clusters obtained using LMS show high functional and domain architectural similarities. Comparison of the current method with alignment based approaches at both domain and full-length protein showed superiority of the LMS scores. Using this method we have recreated objective relationships among different protein kinase sub-families and also classified immunoglobulin containing proteins where sub-family definitions do not exist currently. This method can be applied to any set of protein sequences and hence will be instrumental in analysis of large numbers of full-length protein sequences.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...