Pathway-based Bayesian inference of drug–disease interactions†
Abstract
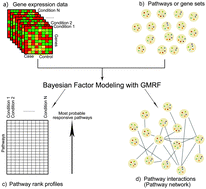
Drug treatments often perturb the activities of certain pathways, sets of functionally related genes. Examining pathways/gene sets that are responsive to drug treatments instead of a simple list of regulated genes can advance our understanding about such cellular processes after perturbations. In general, pathways do not work in isolation and their connections can cause secondary effects. To address this, we present a new method to better identify pathway responsiveness to drug treatments and simultaneously to determine between-pathway interactions. Firstly, we developed a Bayesian matrix factorisation of gene expression data together with known gene–pathway memberships to identify pathways perturbed by drugs. Secondly, in order to determine the interactions between pathways, we implemented a Gaussian Markov Random Field (GMRF) under the matrix factorization framework. Assuming a Gaussian distribution of pathway responsiveness, we calculated the correlations between pathways. We applied the combination of the Bayesian factor model and the GMRF to analyse gene expression data of 1169 drugs with 236 known pathways, 66 of which were disease-related pathways. Our model yielded a significantly higher average precision than the existing methods for identifying pathway responsiveness to drugs that affected multiple pathways. This implies the advantage of the between-pathway interactions and confirms our assumption that pathways are not independent, an aspect that has been commonly overlooked in the existing methods. Additionally, we demonstrate four case studies illustrating that the between-pathway network enhances the performance of pathway identification and provides insights into disease comorbidity, drug repositioning, and tissue-specific comparative analysis of drug treatments.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...