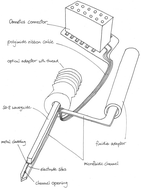
In optogenetics, neurons are genetically modified to become sensitive to light and thus, they can be stimulated or inhibited by light of certain wavelengths. In this work, we describe the fabrication of a polymer-based shaft electrode as a tool for optogenetics. This device can conduct light as well as fluids to a target brain region and record electrical neural signals from the same part of the tissue simultaneously. It is intended to facilitate optogenetic in vivo experiments with those novel multimodal neural probes or polymer optrodes. We used microsystems technology to integrate an SU-8 based waveguide and fluidic channel into a polyimide-based electrode shaft to allow simultaneous optical stimulation, fluid delivery, and electrophysiological recording in awake behaving animals. In a first acute proof-of-concept experiment in genetically modified mice, our device recorded single unit activity that was modulated by laser light transmitted into the tissue via the integrated waveguide.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...