High amounts of broccoli in pasta-like products: nutritional evaluation and sensory acceptability
Abstract
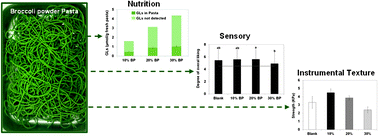
Pasta and noodles were enriched with concentrations of broccoli powder (BP) up to 30% (v/v). To ensure the benefits from the broccoli nutrients, their leakage during cooking should be prevented. Such leakage is determined by the microstructure. In a previous study we have shown that the microstructure can change dramatically in such broccoli-enriched products. In this article we investigated the amount of nutrients retained within the product. As a representative of nutrients we have chosen glucosinolates (GLs). Therefore, we have investigated the concentration of these phytochemicals in dried and cooked pasta and noodles. We have found that glucosinolates present in the pasta and noodles increase linearly with the volume fraction of BP up to 20%. At 30% BP the retained amount of GLs was equal to that of 20% BP and did not increase further. Therefore incorporation of 30% BP does not lead to additional health benefits over incorporation of 20% BP. We conclude that the nutritional function of our pasta-like products can be improved by enrichment up to 20% broccoli. This value is much higher than that found in common commercial products (which is a few percent). In this article we also briefly address the sensory acceptability of such products. Up to 20% broccoli the products turned out to remain acceptable. Combining this with our results on texture analysis we conclude that the GLs release, sensory acceptability and textural properties are related via the microstructure.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...