Synthesis, characterization and electrochemiluminescent properties of cyclometalated platinum(ii) complexes with substituted 2-phenylpyridine ligands†
Abstract
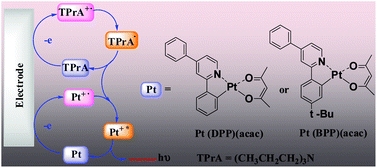
Two neutral cyclometalated platinum(II) complexes, Pt(DPP)(acac) and Pt(BPP)(acac) (DPP = 2,4-diphenylpyridine, BPP = 2-(4-tert-butylphenyl)-4-phenylpyridine, acac = acetylacetone), have been synthesized and characterized by 1H NMR spectroscopy, mass spectrometry, elemental analyses and by X-ray crystallography for Pt(DPP)(acac). Electrogenerated chemiluminescence (ECL) of the two complexes in the absence or presence of coreactant tri-n-propylamine (TPrA) in different solvents (CH3CN, CH2Cl2, DMF, CH3CN/H2O (V, 50 : 50)) has been studied. The ECL spectra are identical to their own PL spectra, indicating that ECL processes lead to the same metal-to-ligand charge-transfer (3MLCT) excited state that is generated by light excitation. The ECL potentials of Pt(DPP)(acac) and Pt(BPP)(acac)/TPrA in CH3CN and CH3CN/H2O solution were at ∼0.75 V vs. SCE, and significantly negatively shifted by about 0.6 V compared to that of the Ru(bpy)32+/TPrA system. The ECL quantum efficiencies of the complexes are comparable to that of the Ru(bpy)32+/TPrA system. The significant increase of the ECL signal in the coreactant system is due to the formation of the strongly reducing intermediate TPrA˙. It is noteworthy that the ECL efficiencies of the synthesized compounds are much higher than that of the tridentate polypyridyl ligands.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...