Activation of Si–Si and Si–H bonds at Pt: a catalytic hydrogenolysis of silicon–silicon bonds†
Abstract
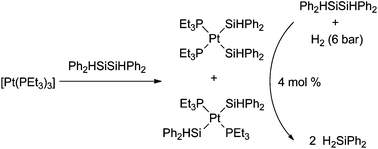
The activation of Ph2HSiSiHPh2 and Me3SiSiMe3 at [Pt(PEt3)3] (1) yielded the products of oxidative addition. The formation of [Pt(SiHPh2)2(PEt3)2] (2) as a mixture of the cis and trans isomers appears to proceed quantitatively, whereas a conversion to give cis-[Pt(SiMe3)2(PEt3)2] (3) was not complete. Treatment of 1 with one equivalent of H2SiPh2 led to cis-and trans-[Pt(H)(SiHPh2)(PEt3)2] (cis-4, trans-4) together with the dinuclear complex [(Et3P)2(H)Pt(μ-SiPh2)(μ–η2-HSiPh2)Pt(PEt3)] (5). In contrast, HSiMe3 reacts with [Pt(PEt3)3] to yield cis-[Pt(H)(SiMe3)(PEt3)2] (7) exclusively. Catalytic reactions of dihydrogen with the disilanes Ph2HSiSiHPh2 or Me3SiSiMe3 in the presence of catalytic amounts of [Pt(PEt3)3] (1) led to the products of hydrogenolysis, H2SiPh2 and HSiMe3. The conversion of Me3SiSiMe3 is much slower and needs higher temperature to proceed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...