Nitrogen-doped zinc oxide thin films biosensor for determination of uric acid
Abstract
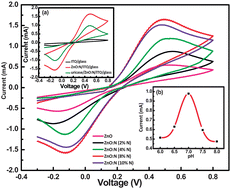
Nitrogen-doped zinc oxide thin films (ZnO:N) have been realized as a potential matrix for the development of a uric acid biosensor. The correlation between the change in property of the ZnO film with N doping concentration and its biosensing response has been studied. The nitrogen dopant in a ZnO film alters its defects profile, thus improving the charge transfer characteristics and resulting in an enhanced peak oxidation current in the cyclic voltammogram in comparison to that of the pure ZnO film. The studies reveal that the bio-electrode based on the nitrogen-doped ZnO thin film matrix exhibits better sensitivity (1.1 mA mM−1 cm−2) with linearity over a wide range (0.05 mM to 1.0 mM) of uric acid concentration. A comparatively low value (0.10 mM) of the Michaelis–Menten constant (Km) indicates high affinity of the immobilized uricase towards uric acid. The proposed ZnO:N thin films matrix-based uric acid-biosensor has good reproducibility, a long shelf-life (20 weeks) and high selectivity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...