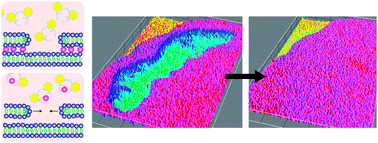
We describe an experimental system where we can generate, and subsequently close, multiple large membrane ruptures in supported double bilayers. We show in this study for the first time that large membrane pores (∼10–150 μm in size) in flat phospholipid vesicles can be reduced in size or completely closed by a pore edge tension driven area reduction mechanism. We can dynamically control the membrane tension of a flat giant unilamellar vesicle and its interplay with the surface adhesion to a solid support. Adhesion to the support surface causes increased membrane tension, which eventually relaxes by the formation of several pores in the membrane. We show that the tension propagation time τmax is exceptionally long in this system, which allows for simultaneous opening of multiple pores. The pores can be stabilized by Ca2+-mediated pinning sites in the interior of the flat giant unilamellar vesicle. After pore formation followed by pinning, we depleted Ca2+ ions resulting in removal of pinning and relaxation of membrane tension. This allows the pore to close, driven by the pore edge tension.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...