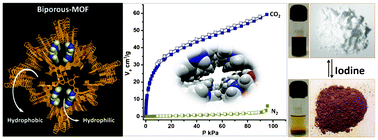
A new three-dimensional (3D) bi-porous metal–organic framework (MOF), {[(Me2NH2)2]·[Cd3(5-tbip)4]·2DMF}n (1) (5-tbipH2: 5-tert-butylisophthalic acid) has been synthesized. The 5-tbip ligand containing a hydrophobic t-butyl group and hydrophilic carboxylate groups is used to synthesize the bi-porous framework. This 3D MOF contains two types of channels, a wide mouth hydrophilic channel of dimension 7.448 × 7.676 Å2 and a narrow mouth hydrophobic channel of dimension 2.33 × 1.926 Å2. Hydrophilic channels are lined with the orderly arranged dimethyl ammonium (DMA) cations which neutralize the anionic 3D framework. The guest-free form of the MOF (1′) showed interesting CO2 selectivity over other gases such as N2, CH4, and H2. Since the effective pore size of the desolvated compound 1′ (∼0.6 nm: from the pore size distribution curve of CO2 adsorption measurement) is much more than the kinetic diameter of all measured gases (CO2 = 3.3 Å, CH4 = 3.76 Å, N2 = 3.64 Å and H2 = 2.8 Å), selective capture of CO2 by 1′ could be ascribed to the strong electrostatic interaction of CO2 with the framework. Compound 1′ also shows reversible iodine uptake (1′ ⊂ 4I2: based on the sample weight measurements and TGA data) with visible color change of the compound. Interestingly, the iodine-loaded MOF showed ∼76 times increase in electrical conductivity compared to 1′.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...