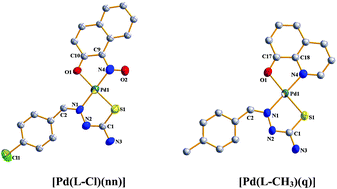
The reaction of a 1 : 1 mixture of 4-R-benzaldehyde thiosemicarbazone [denoted in general as HL–R; where H stands for the dissociable acidic proton and R (R = OCH3, CH3, H, Cl and NO2) for the substituent] and 1-nitroso-2-naphthol (abbreviated as Hnn), with an equivalent quantity of Na2[PdCl4] in ethanolic medium affords a group of mixed-ligand complexes of the type [Pd(L–R)(nn)]. A similar reaction of a mixture of HL–R and quinolin-8-ol (Hq) with Na2[PdCl4] affords another family of mixed-ligand complexes of the type [Pd(L–R)(q)]. Crystal structures of [Pd(L–Cl)(nn)], [Pd(L–CH3)(q)] and [Pd(L–Cl)(q)] have been determined. In all the complexes the thiosemicarbazones are coordinated to the metal center, via dissociation of the acidic proton, as monoanionic bidentate N,S-donors forming five-membered chelate rings. In the [Pd(L–R)(nn)] complexes, the 1-nitroso-2-naphtholate anion is coordinated as a N,O-donor forming a five-membered chelate ring. Similarly in the [Pd(L–R)(q)] complexes, the quinolin-8-olate anion is bound to the metal center in the N,O-mode forming a five-membered chelate ring. All the [Pd(L–R)(nn)] and [Pd(L–R)(q)] complexes show characteristic 1H NMR signals, and in dichloromethane solution they all display intense absorptions in the visible and ultraviolet regions. Catalytic activities of the [Pd(L–R)(nn)] and [Pd(L–R)(q)] complexes have been examined towards some C–C and C–N coupling reactions, where both were found to show notable catalytic efficiency.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...