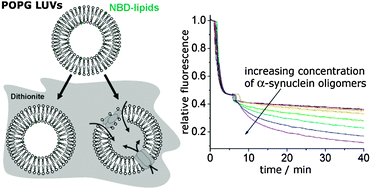
Interactions of oligomeric aggregates of the intrinsically disordered protein α-synuclein with lipid membranes appear to play an important role in the development of Parkinson's disease. The permeabilization of cellular membranes by oligomers has been proposed to result in neuronal death. The detailed mechanisms by which α-synuclein oligomers permeabilize lipid bilayers remain unknown. Two different mechanisms are conceivable. Oligomers may either insert into membranes forming pores through which small molecules can cross the membrane or their interaction with the membrane may disorder the lipid packing, giving rise to membrane defects. Here we show, using kinetic leakage measurements, that α-synuclein oligomer induced impairment of membrane integrity is not limited to the formation of permanent membrane spanning pores. Fast membrane permeabilization could be observed in a fraction of the large unilamellar vesicles. We have also observed, for the first time, that α-synuclein oligomers cause an enhanced lipid flip-flop. In neuronal cells, most of the α-synuclein is not expected to be present in an oligomeric form, but as monomers. In our in vitro experiments, we find that membrane bound monomeric α-synuclein can only delay the onset of oligomer-induced membrane permeabilization, implying that α-synuclein monomers cannot counteract oligomer toxicity.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...