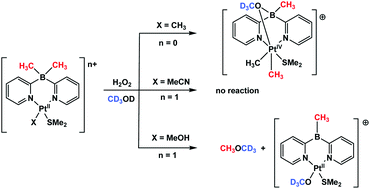
New dimethyldi(2-pyridyl)borato (dmdpb) platinum(II) complexes, (dmdpb)PtIIMe(SMe2) (1), (dmdpb)PtII(L)(SMe2)+, L = MeOH (2), MeCN (3), supported by dimethylsulfide ligand and featuring one (1) or no hydrocarbyls at the metal (2, 3) were prepared and their oxidation with hydrogen peroxide was studied. Both complex 1 bearing the formal charge of +1 on the metal and the methanol complex 2 capable of losing the proton of the methanol ligand to form the methoxide derivative 4 charged similarly to 1, are reactive towards H2O2. However, the cationic complex 3 with a formal charge of +2 on the metal does not react with H2O2. The oxidation of the monomethyl platinum(II) complex 1 leads to the B-to-Pt methyl transfer and formation of a robust dimethyl PtIV species 5 which does not undergo C–O reductive elimination up to 100 °C. By contrast, oxidation of 2 in methanol-d4 leads to quantitative formation of dimethyl ether-d3, CD3OCH3. It was presumed that the latter reaction involves the B-to-Pt methyl transfer and formation of a highly reactive cationic monomethyl PtIV species whose methyl group carbon atom can accept nucleophilic attack by the methanol-d4 solvent to form dimethyl ether-d3.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...