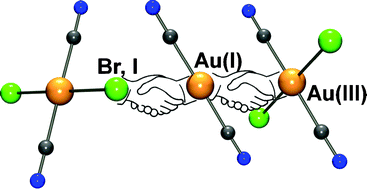
The salts K[AuCl2(CN)2]·H2O (1), K[AuBr2(CN)2]·2H2O (2) and K[AuI2(CN)2]·⅓H2O (3) were synthesized and structurally characterized. Compound 1 crystallizes as a network of square planar [AuCl2(CN)2]− anions separated by K+ cations. However, 2 and 3 feature 2-D sheets built by the aggregation of [AuX2(CN)2]− anions via weak, intermolecular X⋯X interactions. The mixed anion double salts K3[Au(CN)2]2[AuBr2(CN)2]·H2O (4) and K5[Au(CN)2]4[AuI2(CN)2]·2H2O (5) were also synthesized by cocrystallization of K[Au(CN)2] and the respective K[AuX2(CN)2] salts. Similarly to 2 and 3, the [Au(CN)2]− and [AuX2(CN)2]− anions form 2-D sheets via weak, intermolecular AuI⋯X and AuI⋯AuI interactions. In the case of 5, a rare unsupported AuI⋯AuIII interaction of 3.5796(5) Å is also seen between the two anionic units. Despite the presence of Au(I) aurophilic interactions of 3.24–3.45 Å, neither 4 nor 5 exhibit any detectable emission at room temperature, suggesting that the presence of AuI⋯X or AuI⋯AuIII interactions may affect the emissive properties.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...