Synthesis of β-cyclodextrin conjugated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for selective binding and detection of cholesterol crystals†
Abstract
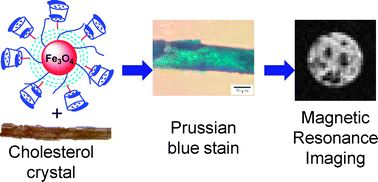
Water-soluble, β-cyclodextrin conjugated superparamagnetic nanoparticles have been constructed. These particles showed selective binding to cholesterol crystals, which opens the door for the detection of cholesterol crystal-related diseases such as atherosclerosis by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...