Retracted Article: p-Chloranil modified carbon nanotubes paste electrode as a voltammetric sensor for the simultaneous determination of methyldopa and uric acid†
Abstract
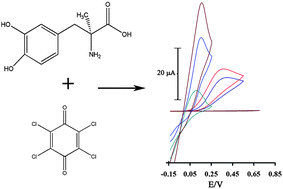
In this study, a multiwalled carbon nanotubes modified electrode (prepared by incorporating p-chloranil as a mediator) was used as a voltammetric sensor for the determination of methyldopa (MDOP) in the presence of uric acid (UA). The results indicate that the electrode is efficient in terms of its electrocatalytic activity for the oxidation of MDOP, leading to an overpotential reduced by more than 250 mV. Using square wave voltammetry (SWV), we could measure MDOP and UA in one mixture independently from each other by a potential difference of about 355 mV. The peak current was linearly dependent on MDOP concentration in the range of 0.5–165.5 μmol L−1, with a detection limit of 0.2 μmol L−1. The proposed method was also used for the determination of MDOP in urine, drug and serum samples using the standard addition method.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...