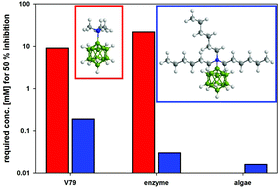
Representatives of N,N,N-trialkylammoniododecaborates, which are anions in a new class of ionic liquids, were tested for their hazard potential. As biological test systems, toxicity against V79 mammalian cells, reproduction inhibition of Scenedesmus vacuolatus algae, and inhibition of acetylcholinesterase were studied. EC50 values for the toxicity against V79 cells range between 9.1 mM for the trimethylammonio derivative and 0.19 mM for the trihexyl derivative. Reproduction inhibition of S. vacuolatus range between over 3 mM for the trimethylammonio derivative down to 0.016 mM for the trihexyl derivative. Fifty percent inhibition of acetylcholinesterase was caused by 21.9 mM of the trimethylammonio derivative, as compared to 0.03 mM for the hexyl derivative The data demonstrate that increasing hydrophobicity leads to higher toxicity and inhibition for straight alkyl chains. All tested ABs are able to induce leakage in liposomes and the capability for triggering it strongly increases with the length of the alkyl chain and consequently with lipophilicity. The leakage experiments could be an indicator for toxic tendencies in vitro but they allow no quantitative prediction of EC50 values. For branched chains and for derivatives with mixed substitution, a prediction of the toxic potential is not simple. The new class of ionic liquids is in general no more toxic than the ionic liquids presently in industrial applications.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...