Selective, catalytic aerobic oxidation of alcohols using CuBr2 and bifunctional triazine-based ligands containing both a bipyridine and a TEMPO group†
Abstract
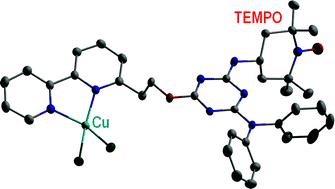
Three novel, bifunctional
* Corresponding authors
a Leiden Institute of Chemistry, Gorlaeus Laboratories, Leiden University, P. O. Box 9502, 2300 RA Leiden, The Netherlands
b Université Bordeaux 1, CNRS-CRPP, 115, avenue du Dr Schweitzer, 33600 Pessac, France
c ALS, Berkeley Lab, 1 Cyclotron Rd, MS2-400, Berkeley, CA 94720, USA
d Dipartimento di Chimica Generale ed Inorganica, Chimica Analitica, Chimica Fisica, Università degli Studi di Parma, Viale G. Usberti 17/A, 43100 Parma, Italy
Three novel, bifunctional

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Z. Lu, T. Ladrak, O. Roubeau, J. van der Toorn, S. J. Teat, C. Massera, P. Gamez and J. Reedijk, Dalton Trans., 2009, 3559 DOI: 10.1039/B820554J
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
