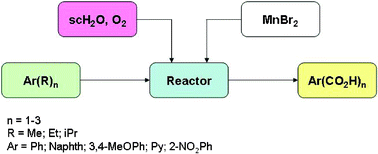
A variety of different alkylaromatic compounds having a range of alkyl groups (methyl, ethyl and isopropyl), varying aromatic groups (benzene, naphthalene and pyridine), and largely different ring electron densities (toluene and 3,4-dimethoxytoluene) have been successfully oxidized selectively to aromatic aldehyde and carboxylic acids in sub- and supercriticalwater using a continuous reactor under a wide range of experimental conditions. The estimated difference in initial reactivities of these substrates is approximately 10 000. Selected yields include toluene → benzoic acid (83%), isopropylbenzene → benzoic acid (46%), ethylbenzene → benzoic acid (68%), 2,6-dimethylnaphthalene → 2,6-naphthalenedicarboxylic acid (25%; co-oxidized with p-xylene) and 3,4-dimethoxytoluene → 3,4-dimethoxybenzoic acid (60%). 2-Nitrotoluene gave very poor yields, consistent with previous attempts to oxidize this substance homogeneously. For the first time, the reactivities and carboxylic acid yields of all three isomers of methylpyridine (picoline) have been determined. The initial reactivities are 3-isomer > 2-isomer > 4-isomer, the thermal decarboxylation rates are 2-isomer ≫ 3-isomer > 4-isomer, and the best yields are 3-isomer > 4-isomer > 2-isomer, with maximum yields of 50, 33, and 18 mol% respectively.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...