Combinatorial fluorescence energy transfer molecular beacons for probing nucleic acid sequences†
Abstract
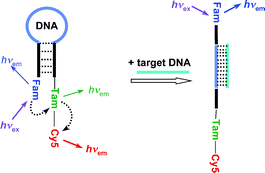
We report the design, synthesis, and characterization of molecular beacons (MB) consisting of three distinct fluorophores, 6-carboxyfluorescein (Fam), N,N,N′,N′-tetramethyl-6-carboxyrhodamine (Tam), and Cyanine-5 (Cy5). The primary light absorber/energy donor (Fam) is located on one terminus of the MB, whereas the primary energy acceptor/secondary donor (Tam) and secondary acceptor (Cy5) are located at the other terminus of the MB. In the absence of target DNA or RNA, the MB exists in the stem-closed form. Excitation of Fam initiates an energy transfer cascade from Fam to Tam and further to Cy5 generating unique fluorescence signatures defined as the ratio of the emission from each of the three fluorophores. This energy transfer cascade was investigated in detail by steady-state and time-resolved fluorescence spectroscopy, as well as fluorescence depolarization studies. In the presence of the complementary target DNA, the MB opened efficiently and hybridized with the target separating Fam and Tam by a large distance, so that energy transfer from Fam to Tam was blocked in the stem-open form. This opening of the MB generates a “bar code” fluorescence signature, which is different from the signature of the stem-closed MB. The fluorescence signature of this combinatorial fluorescence energy transfer MB can be tuned by variation of the spacer length between the individual fluorophores.
- This article is part of the themed collection: In honour of George Simms Hammond

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...