Iodine speciation studies in commercially available seaweed by coupling different chromatographic techniques with UV and ICP-MS detection
Abstract
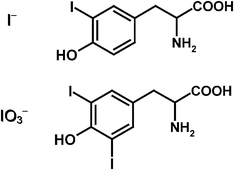
Speciation of iodine in commercially available commonly consumed seaweed samples was performed using a multidimensional chromatographic approach coupled with

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...