Development of a microwave-assisted extraction method and isotopic validation of mercury species in soils and sediments†
Abstract
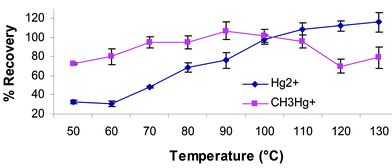
An efficient and rapid closed vessel microwave-assisted extraction method based on an acidic extractant has been developed to determine inorganic mercury and methylmercury in soils and sediments. Parameters optimized during this study were nitric acid concentration, amount of sample, extraction temperature and irradiation time. The results suggest that the nitric acid concentration and the irradiation temperature are statistically significant both for extraction efficiency and for stability of mercury species. A processed topsoil (Hg < 0.01 ng g−1) spiked with inorganic mercury and methylmercury and SRM 2711 (spiked with methylmercury) were used during the method development. The sample preparation was optimized in a closed-vessel system by heating 1.0 g of sample in 10.0 ml of 4.0 mol l−1 HNO3 for 10 min at 100 °C with magnetic stirring. Analyses of the extracts were carried out by using three types of instruments, Direct Mercury Analyzer-80 (DMA-80), inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (ICP-MS) and high-performance liquid chromatograph coupled with inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (HPLC-ICP-MS). The results obtained from each of these detection techniques agreed significantly at the 95% confidence level. The method was validated by the analyses of two types of specifically prepared reference soil samples and four certified reference materials (BCR 580, SRM 2704, SRM 2709 and SRM 1941a). The inorganic mercury and methylmercury concentrations found were in good agreement at the 95% confidence level with the certified or “made-to” value. The method was also validated using EPA Method 6800 as a diagnostic tool to check whether interconversion of inorganic mercury to methylmercury or vice versa took place during or after extraction; the amount of such interconversions was found to be statistically negligible. The method is in the process of consideration and adopted by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA) as a primary mercury species extraction protocol from soils and sediments in EPA draft Method 3200.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...