Photochemical regulation of the activity of an endonuclease BamHI using an azobenzene moiety incorporated site-selectively into the dimer interface
Abstract
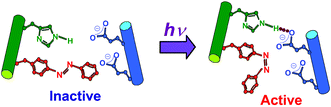
Endonuclease BamHI mutants having an azophenylalanine residue in the dimer interface (azoAla-BamHI) were synthesized; while the activity was almost suppressed using trans-azoAla-BamHI, the cis-isomer generated with photoirradiation recovered its intrinsic activity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...