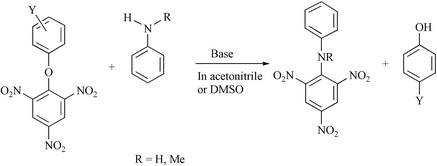
Rate data are reported for the reactions of a series of 3′- and 4′-substituted phenyl 2,4,6-trinitrophenyl ethers, 4, with aniline in acetonitrile, leading to 2,4,6-trinitrodiphenylamine. The main reaction flux occurs through a base catalysed pathway involving formation of a zwitterionic intermediate, equilibrium constant K1, and rate-limiting proton transfer to base, rate constant kAn. The effects of ring substituents on values of rate and equilibrium constants are discussed. In contrast the corresponding reactions in DMSO involve both uncatalysed and base catalysed pathways. Reactions of 4 with N-methylaniline are extremely slow, but values of rate constants for reaction of 4-nitrophenyl 2,4,6-trinitrophenyl ether were measured using 1H NMR spectroscopy. The value of the parameter K1kAn is lowered by a factor of 105 for N-methylaniline relative to aniline in both acetonitrile and in DMSO. This reduction is attributed to increased steric hindrance both in formation of the intermediate and to proton transfer.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...