Multi-stage structured catalyst system for post-treatment of GHGs emitted from industrial processes
Choji
Fukuhara
*a,
Hiroto
Naiki
a,
Hiroshi
Akama
a,
Yuki
Yamada
a,
Priyanka
Verma
 b and
Ryo
Watanabe
b and
Ryo
Watanabe
 *a
*a
aDepartment of Applied Chemistry and Biochemical Engineering, Graduate School of Engineering, Shizuoka University, 3-5-1 Johoku, Chuo-ku, Hamamatsu, Shizuoka 432-8561, Japan. E-mail: watanabe.ryo@shizuoka.ac.jp
bDepartment of Chemistry, Indian Institute of Technology Delhi, Hauz Khas, New Delhi, 110016, India
First published on 12th November 2025
Abstract
This study proposes a new approach for reducing CO2 emissions from industrial processes and contributing to sustainable environmental development. The primary focus is on post-processing emitted CO2 and constructing a coupled catalytic reaction system for CO2 conversion. This coupled reaction system consists of three reactors: the 1st reactor for the methanation of CO2, the 2nd reactor for the dry reforming of CH4 (DRM), and the 3rd reactor for solid carbon capture. The constructed system enabled the continuous production of synthesis gas (H2 + CO) even at a higher gas flow rate of 2 L min−1 while recovering >30% of the introduced CO2 as solid carbon. Furthermore, in this system, we have demonstrated that the quantity of H2 lower than the stoichiometric ratio of the methanation reaction (H2/CO2 = 4.0) is advantageous for system operation. Significantly improved DRM and carbon capture performance were achieved under these conditions. The obtained results indicate the potential of this system in the efficient treatment of CO2 from industrial emissions using a lower stoichiometric ratio of H2, which has significant implications for environmental conservation and energy reduction. Additionally, the thermodynamic evaluation indicated that reducing the amount of supplied H2 should have a beneficial impact on the exergy efficiency of the reaction system. The captured carbon has elongated fiber-like morphology with potential utilization as a functional material. We expect that the coupled reaction system designed in this study can serve as an innovative technology, contributing towards realizing a carbon-neutral society.
1. Introduction
In response to climate change, the Paris Agreement has set a long-term goal of limiting the average global temperature rise to 2 °C or preferably 1.5 °C above pre-industrial levels.1,2 Achieving a carbon-neutral society is essential to meeting this objective. Accordingly, research and development efforts are actively underway to advance technologies for the reduction, recovery, and utilization of greenhouse gases (GHGs). One representative method for CO2 recovery involves the separation and concentration of CO2 using amine-based absorption solutions.3–11 The recovered CO2 can be either converted into alternative fuels or chemical feedstocks through carbon capture and utilization (CCU), or stored underground through carbon capture and storage (CCS).Among the various CCU strategies, CO2 methanation (eqn (1)) is a well-known approach. First discovered by Sabatier et al. in 1902, it has since been referred to as the Sabatier reaction.12–14 The development of active catalysts for this reaction has mainly focused on tuning the catalyst support, with Ni- and Ru-based systems being widely employed.15–23 Numerous review articles have explored different catalyst supports and reaction conditions to improve performance.24–27
Industrial exhaust gases typically contain not only CO2 but also various impurities such as air, water vapor, and nitrogen oxides.28,29 Consequently, methanation-based CO2 utilization generally requires separation and purification facilities. In particular, the presence of oxygen in the feed gas can lead to combustion of hydrogen or methane, thereby reducing CH4 yield and potentially causing catalyst degradation due to oxidation.
However, in our previous study, we demonstrated that the presence of oxygen (1–15 vol%) accelerates the methanation rate without leading to CH4 combustion. This occurs because the combustion of H2 and O2 is significantly faster than the methanation reaction, and O2 is rapidly consumed at the reaction inlet via H2 combustion before CH4 is produced. The substantial thermal energy generated at the inlet propagates into the catalyst bed, eliminating the need for external heating. This phenomenon, known as auto-methanation, enables the reaction to proceed even under ambient temperature and atmospheric pressure conditions.30–34
| CO2 + 4H2 → CH4 + 2H2O ΔH0298 = −164.9 kJ mol−1 | (1) |
After converting CO2 from industrial exhaust gases via methanation, the resulting CH4 can be introduced into existing infrastructure as city gas. However, simply combusting this CH4 to regenerate CO2 would not contribute to achieving true carbon neutrality. Instead, it is preferable to convert CO2-derived CH2 into valuable substances for use as chemical feedstocks. One such pathway is the dry reforming of methane (DRM, eqn (2)), which produces synthesis gases (H2 and CO) through the reaction of CH4 with CO2, thereby aligning with the goal of carbon valorization.
Various studies have investigated DRM, including comprehensive reviews by Abbas, Wang, and Zhang.35–37 Among the catalysts employed for DRM, Ni-based systems are widely used due to their low cost and industrial applicability.38–41 We have also developed a honeycomb-shaped Ni/Al2O3 catalyst tailored for DRM, which enables large-scale gas processing and efficient thermal energy management.42 This catalyst demonstrates high heat transfer efficiency and low pressure drop, contributing to excellent reforming performance. Moreover, owing to its electroless plating-based fabrication, the electronic state of the Ni component is modified in a way that enhances resistance to carbon deposition.42
| CO2 + CH4 → 2CO + 2H2 ΔH0298 = 247.6 kJ mol−1 | (2) |
Furthermore, we have constructed a coupled reaction system that integrates both the DRM stage and the carbon capture stage, enabling the simultaneous conversion of CO2 and CH4.43,44 This system facilitates the production of synthesis gas while capturing solid carbon, as described in eqn (3)–(5). While carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies, primarily focused on geological storage, have been regarded as promising strategies for achieving a decarbonized society,45–49 they face significant limitations. These include the requirement for secure geological formations, large-scale infrastructure for liquid CO2 injection, and the need for long-term monitoring to prevent leakage. In contrast, our reaction system captures CO2 as solid carbon, thereby overcoming many of these challenges while simultaneously yielding valuable synthesis gas. In summary, the conversion of industrial CO2 emissions into useful chemical products, coupled with their fixation as solid carbon, offers a viable pathway to accelerate the realization of a carbon-neutral society.
| 2CO → C + CO2 ΔH0298 = −172.0 kJ mol−1 | (3) |
| CO + H2 → C + H2O ΔH0298 = −131.3 kJ mol−1 | (4) |
| CH4 → C + 2H2 ΔH0298 = 75.0 kJ mol−1 | (5) |
In this study, we further advanced the previously developed reaction system, comprising DRM and carbon capture stages, by incorporating an initial methanation stage. As a result, the newly constructed system consists of sequential methanation → DRM → carbon capture stages. This novel multi-stage catalytic reaction system enables the production of synthesis gas from CO2 as the feedstock while simultaneously capturing solid carbon. It is specifically designed for the treatment of industrial exhaust gases. The operational characteristics of the system were evaluated under laboratory conditions simulating large-scale CO2 processing.
The constructed system efficiently converts CO2 into synthesis gas and solid carbon while operating with sub-stoichiometric amounts of H2. Furthermore, we assessed the thermodynamic performance of the system using exergy efficiency as an indicator and confirmed its effectiveness as a promising technology for achieving a carbon-neutral society.
2. Experimental
2.1 Multi-stage structured catalytic reaction system
The reaction experiments were conducted using a fixed-bed circulating reactor. A three-zone electric furnace (Asahi Rika Seisakusho Co., Ltd) equipped with independent PID controllers was employed to control the reaction temperature. The multi-stage reaction system consisted of three sequential zones housed within the furnace, as illustrated in Fig. 1.The first-stage reactor (1st reactor) served as the methanation zone and was equipped with a rigid glass reaction tube (thickness: 1.5 mm, inner diameter: 8 mm, and length: 750 mm), in which two parallel spiral-structured Ru/CeO2 catalysts were installed. The second-stage reactor (2nd reactor), denoted as the DRM zone, utilized a quartz glass reaction tube (same dimensions) loaded with six consecutive spiral Ni/CeO2–Al2O3 catalysts. The third-stage reactor (3rd reactor), dedicated to carbon capture, employed a Pyrex glass tube (thickness: 1.5 mm, inner diameter: 30 mm, and length: 700 mm), containing five tubular Fe–Co–K catalysts arranged in series.
The total gas flow rate was varied from 1.0 to 3.0 L min−1 while maintaining a fixed O2 concentration of 3 vol%. The feed gas composition was set at 20 vol% CO2 with H2/CO2 ratios ranging from 2 to 4, and N2 as the balance.
Prior to the reaction, catalyst pretreatment was conducted via H2 reduction at a flow rate of 200 mL min−1. The 1st reactor was reduced at 200 °C for 1 h, while the 2nd and 3rd reactors were reduced at 600 °C for 1 h. After reduction, external heating of the 1st reactor was discontinued, and the reactor was allowed to cool to room temperature (25 °C), followed by thermal insulation with alkaline earth silicate (AES) wool. The operating temperatures for the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd reactors were subsequently maintained at 25 °C, 700 °C, and 470 °C, respectively. All reactors were heated and cooled under N2 circulation.
For the initial 1 h of the reaction, gas was supplied only to the 1st and 2nd reactors to evaluate methanation and DRM performances. Subsequently, the valve (SV) was opened, and the reforming gas was introduced into the 3rd reactor for 5 h to perform carbon capture. After this stage, the valve (SV#2) was closed, and gas flow was limited again to the 1st and 2nd reactors in order to evaluate catalyst degradation.
The outlet gas compositions from each reactor were analyzed using a microgas chromatograph equipped with a thermal conductivity detector (TCD) (Agilent 490 Micro GC). The detected products under all operating conditions included CO2, CH4, CO, H2O, and solid carbon, with no other by-products observed. Notably, all of the supplied O2 was completely consumed by the catalyst in the 1st reactor.
To prevent the transfer of water vapor into the downstream reactors, cold traps maintained at approximately 0 °C were installed after both the methanation and DRM zones. The amount of water was quantified based on the condensed water collected in the traps and was found to be broadly consistent with the amount estimated from the hydrogen balance. These traps effectively removed H2O while allowing CH4, CO2, and H2 to pass through. Gas analysis after the DRM stage revealed no signs of excess H2 or CO formation, nor elevated H2/CO ratios, indicating that steam methane reforming (SMR) did not occur under the applied conditions.
The CO2 and CH4 conversion rates and CH4 selectivity were calculated using the following equations (eqn (6)–(8)), with carbon atoms as the reference:
| CO2 conv. (%) = (1 − [CO2]out/[CO2]in) × 100 | (6) |
| CH4 conv. (%) = (1 − [CH4]out/[CH4]in) × 100 | (7) |
| CH4 sel. (%) = ([CH4]out/total C-containing products) × 100 | (8) |
The carbon capture rate (CCR) was calculated by dividing the quantity of captured solid carbon by the total amount of CO2 fed, as defined in eqn (9):
| CCR (%) = (amount of captured solid carbon (mol))/(total moles of CO2 in feed (mol h−1) × capture time (h)) × 100 | (9) |
2.2 Preparation of the structured catalyst
The spiral-type Ru/CeO2 catalyst used in the methanation zone was prepared as follows. First, a Ru/CeO2 granular catalyst was synthesized via the impregnation method using cerium oxide (CeO2) powder as the support and ruthenium nitrate (Ru(NO3)3) as the metal precursor. CeO2 powder (particle size: 6.8 nm, BET surface area: 126 m2 g−1, JRC-CEO-2, Catalysis Society of Japan) was suspended in 50 mL of distilled water and stirred for 12 h at room temperature. Subsequently, ruthenium nitrate solution (50 g L−1, Tanaka Kikinzoku Kogyo Co., Ltd) was added to the suspension and stirred for an additional 2 h. The resulting mixture was evaporated to dryness at 80 °C to obtain Ru/CeO2 powder with 10 wt% Ru loading, which was then calcined at 500 °C for 3 h in air to yield the Ru/CeO2 granular catalyst. The spiral-type catalyst for the 1st reactor was prepared by depositing the Ru/CeO2 granular catalyst onto a metallic substrate using the wash-coat method. A porous metal substrate (Cellmet, Toyama Sumitomo Denko Co., Ltd) with a thickness of 1 mm, a width of 7 mm, and a length of 100 mm was coiled into a spiral shape with 3.5 turns (1260°). The formed substrate was treated with 0.8 N NaOH solution and immersed in a catalyst slurry, followed by repeated hot air drying until 900 mg of catalyst was coated per substrate. Two spiral-type Ru/CeO2 catalysts were thus prepared. The spiral-type Ni/CeO2–Al2O3 catalyst used in the DRM zone (2nd reactor) was prepared using six porous metal substrates (Cellmet, Toyama Sumitomo Denko Co., Ltd; thickness: 1 mm, width: 7 mm, and length: 55 mm), each coiled once (360°) and treated with 0.8 N NaOH solution. The substrates were coated with an alumina–ceria sol prepared from aluminum-triisopropoxide (12 g), nitric acid (6 mL), formaldehyde (4 mL), cerium ammonium nitrate (3.28 g), and distilled water (80 mL), with a Ce![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Al molar ratio of 1
Al molar ratio of 1![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 10. The coated substrates were calcined through a multi-step process at 500 °C for 60 min, 100 °C for 30 min, and 800 °C for 60 min to form a γ-alumina layer. Pd nuclei were deposited by alternately immersing each substrate 20 times in a Pd bath (PdCl2: 1.4 × 10−3 mol L−1, HCl: 5.7 × 10−3 mol L−1, 35 °C) and an Sn bath (SnCl2·2H2O: 1.1 × 10−3 mol L−1, HCl: 5.7 × 10−3 mol L−1, 35 °C). Electroless Ni plating was then conducted by immersing the Pd-seeded substrates in a plating bath (NiCl2·6H2O: 22.5 g L−1, NaBH4: 0.3 g L−1, NaOH: 10 g L−1, and ethylenediamine: 30 mL L−1) at 55 °C for 30 min. The tubular Fe–Co–K catalyst used in the carbon capture zone (3rd reactor) was prepared by first synthesizing an Fe–Co–K granular catalyst via the co-impregnation method. Iron(III) nitrate nonahydrate and cobalt(II) nitrate hexahydrate were dissolved in distilled water in a 20
10. The coated substrates were calcined through a multi-step process at 500 °C for 60 min, 100 °C for 30 min, and 800 °C for 60 min to form a γ-alumina layer. Pd nuclei were deposited by alternately immersing each substrate 20 times in a Pd bath (PdCl2: 1.4 × 10−3 mol L−1, HCl: 5.7 × 10−3 mol L−1, 35 °C) and an Sn bath (SnCl2·2H2O: 1.1 × 10−3 mol L−1, HCl: 5.7 × 10−3 mol L−1, 35 °C). Electroless Ni plating was then conducted by immersing the Pd-seeded substrates in a plating bath (NiCl2·6H2O: 22.5 g L−1, NaBH4: 0.3 g L−1, NaOH: 10 g L−1, and ethylenediamine: 30 mL L−1) at 55 °C for 30 min. The tubular Fe–Co–K catalyst used in the carbon capture zone (3rd reactor) was prepared by first synthesizing an Fe–Co–K granular catalyst via the co-impregnation method. Iron(III) nitrate nonahydrate and cobalt(II) nitrate hexahydrate were dissolved in distilled water in a 20![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 80 molar ratio, and potassium nitrate (10 wt% relative to total Fe and Co) was added. The mixture was stirred for 2 h and dried at 80 °C to obtain the precursor powder, which was then calcined at 600 °C for 3 h in air. The resulting powder was suspended in 2-propanol (98%, Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd) to form a slurry, which was coated onto the inner walls of stainless-steel tubes (JIS SUS304, inner diameter: 25 mm and length: 50 mm) previously treated with 0.8 M NaOH solution. Each tube was loaded with 100 mg of catalyst using the wash-coat method. This process was repeated to prepare five tubular Fe–Co–K catalysts for use in the 3rd reactor stage. Because Cl-containing precursors (PdCl2, SnCl2·2H2O, and NiCl2·6H2O) were used during the preparation of the Ni/CeO2–Al2O3 catalyst, the final catalysts were analyzed for residual Cl content. X-ray fluorescence (XRF) spectroscopy, with a detection limit of several tens of ppm, was employed for this purpose. The results showed that Cl levels in all as-prepared catalysts were below the detection limit, indicating that the washing, drying, and calcination steps effectively removed Cl introduced during synthesis. This confirmation was added to the manuscript to ensure that residual Cl did not influence the catalytic performance.
80 molar ratio, and potassium nitrate (10 wt% relative to total Fe and Co) was added. The mixture was stirred for 2 h and dried at 80 °C to obtain the precursor powder, which was then calcined at 600 °C for 3 h in air. The resulting powder was suspended in 2-propanol (98%, Wako Pure Chemical Industries, Ltd) to form a slurry, which was coated onto the inner walls of stainless-steel tubes (JIS SUS304, inner diameter: 25 mm and length: 50 mm) previously treated with 0.8 M NaOH solution. Each tube was loaded with 100 mg of catalyst using the wash-coat method. This process was repeated to prepare five tubular Fe–Co–K catalysts for use in the 3rd reactor stage. Because Cl-containing precursors (PdCl2, SnCl2·2H2O, and NiCl2·6H2O) were used during the preparation of the Ni/CeO2–Al2O3 catalyst, the final catalysts were analyzed for residual Cl content. X-ray fluorescence (XRF) spectroscopy, with a detection limit of several tens of ppm, was employed for this purpose. The results showed that Cl levels in all as-prepared catalysts were below the detection limit, indicating that the washing, drying, and calcination steps effectively removed Cl introduced during synthesis. This confirmation was added to the manuscript to ensure that residual Cl did not influence the catalytic performance.
2.3 Characterization of the catalyst and captured carbon
The physicochemical properties of the prepared catalysts and the carbonaceous products collected from the third reactor were comprehensively characterized using multiple analytical techniques. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM; JSM-IT700HR/LA, JEOL) was employed to examine the surface morphology and microstructure of the spiral-type catalysts and the deposited carbon. This technique enabled visualization of catalyst coating uniformity, metal particle dispersion, and the morphology of carbon species, including filamentous structures and agglomerated deposits. To complement the morphological observations, elemental analysis was performed using energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) on the same regions. This allowed for elemental mapping of key components such as Ru, Ni, Fe, Co, K, and Ce and confirmed the homogeneous distribution of active species on the structured catalyst supports.2.4 Evaluation of energy
Based on the reaction results, the standard exergy and physical exergy of each component were calculated using eqn (10) and (11), respectively, and the total exergy was obtained by summing these values. The standard exergy (ε0, in kJ min−1) was calculated according to the following equation:Standard exergy ε0 [kJ min−1]
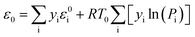 | (10) |
In formulaic form
| εp = ΔH − T0 × ΔS = ∫ from T0 to T of [yi × Cp,i]dT | (11) |
3. Results and discussion
3.1 Fundamental properties of the multi-stage catalytic reaction system (methanation, DRM, and carbon capture)
Fig. 2(a) shows a high-resolution TEM image of the RuO2/CeO2 (as-made) catalyst, where well-defined lattice fringes corresponding to CeO2 (111) (d ≈ 0.31 nm) and RuO2 (101) (d ≈ 0.22 nm) planes are clearly visible. The RuO2 nanoparticles are dispersed over the CeO2 crystallites and form quasi-epitaxial interfaces between the CeO2 (111) and RuO2 (101) planes, suggesting partial lattice matching at the oxide–oxide boundary. The corresponding STEM-EDX elemental mapping images (Fig. 2(b–d)) confirm the spatial distribution of each element. Cerium (cyan) is homogeneously distributed throughout the support, while ruthenium (green) is mainly localized in the outer regions of the CeO2 particles. Oxygen (red) is uniformly distributed, consistent with the coexistence of CeO2 and RuO2 phases. These observations indicate that RuO2 nanoparticles are finely dispersed and quasi-epitaxially anchored on the CeO2 surface, resulting in intimate oxide–oxide interfaces that can facilitate interfacial redox processes. Fig. 3 presents high-resolution TEM images of the oxidized NiO/γ-Al2O3 and Co3O4/(Co,Fe)3O4 catalysts. In the NiO/γ-Al2O3 sample (Fig. 2(a)), finely dispersed NiO nanocrystals are clearly observed on the alumina support. Lattice fringes with an interplanar spacing of approximately 0.24 nm correspond to the NiO (111) plane of the face-centered-cubic (fcc) structure, confirming the formation of crystalline NiO domains after calcination. The surrounding γ-Al2O3 matrix shows weak, short-range ordering with diffuse contrast, typical of its defective spinel structure. The intimate contact between NiO and γ-Al2O3 suggests partial structural accommodation at the interface, which facilitates the formation of finely dispersed NiO nanoparticles that can be readily reduced to metallic Ni under hydrogen treatment. Fig. 3(b) shows the HRTEM image of the Fe–Co–K catalyst after calcination. Well-defined lattice fringes with spacings of 0.29 nm and 0.24 nm are assigned to the (220) and (311) planes, respectively, of the spinel-type Co3O4 or (Co,Fe)3O4 phase. These reflections are characteristic of mixed Co–Fe spinel oxides, indicating that Fe3+ ions are partially incorporated into the Co3O4 lattice to form a solid solution. The uniform periodicity and sharp contrast imply high crystallinity of the spinel domains, whereas K species are not visible in the TEM images due to their amorphous and highly dispersed nature. Such a well-developed oxide microstructure provides thermally stable precursors for the subsequent formation of active metallic Co–Fe nanoparticles under reduction conditions. The corresponding Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) patterns of the RuO2/CeO2, NiO/γ-Al2O3, and Fe–Co–K samples are shown in Fig. S1–S3, respectively.Based on these structural observations, the catalytic properties of the multi-reactor system were subsequently evaluated under fixed-bed conditions to clarify the relationship between the oxide structure and reaction performance. The fundamental characteristics of the constructed system were investigated by fixing the feed gas composition in the methanation zone (i.e., the 1st reactor) at an H2/CO2 ratio of 4.0, corresponding to the stoichiometric conditions. Subsequent investigations focused on the characteristics of the products obtained from the methanation reaction, dry reforming reaction, and solid carbon capture. Fig. 4 presents the variations in the quantities of initially supplied CO2 and H2 gases and their corresponding changes across the methanation, DRM, and carbon capture zones ((a) and (b)). It also shows the production profiles of CH4, CO, solid carbon (C), and H2O in each reaction zone ((c)–(f)). In the methanation zone (1st reactor), despite the high flow rate with a total gas throughput of 2 L min−1 (corresponding to a gas contact time of 0.23 s), CO2 and H2 were efficiently converted to CH4. Under these conditions, the CO2 conversion rate reached 70.2%, and CH4 selectivity was 95.5%. Notably, even under auto-methanation conditions without external heating (i.e., at room temperature),30–34 the spiral-shaped structured catalyst exhibited superior performance. In the DRM zone (2nd reactor), the CO2 conversion increased to 96.3%, accompanied by the formation of CO and H2. Despite a short contact time of 0.38 s, further CO2 consumption was observed. In the carbon capture zone (3rd reactor), although a slight increase in CO2 was observed, attributed to the disproportionation reaction (2CO → C + CO2), a significant amount of solid carbon was successfully captured. Through this integrated catalytic reaction process, approximately 85.9% of the initially supplied CO2 was converted into valuable products, including CH4, CO, and solid carbon. Additionally, although the amount of H2 generated was lower than that in the methanation stage, around 40% was still recovered. These results demonstrate that efficient CO2 conversion was achieved even under high-flow-rate conditions (2 L min−1), and one of the key contributing factors may be the use of the spiral-shaped structured catalyst.
 | ||
| Fig. 4 Materials flow ((a) CO2, (b) H2, (c) CO, (d) CH4, (e) C, and (f) H2O) at H2/CO2 = 4.0, O2: 3 vol%. | ||
The spiral-shaped catalyst promotes vortex (swirling) gas flow under high-flow conditions, which thins the gas-phase boundary layer on the catalyst surface. When the swirl number, defined using eqn (12), exceeds 0.5, a swirling flow is established, inducing forced recirculation over the catalyst surface. This enhances the contact efficiency between the reactant gases and the catalyst active sites, thereby accelerating the reaction rate and promoting conversion.48 Under the conditions applied in this study, the swirl number was calculated to be 0.56, indicating that such swirling flow was indeed generated.
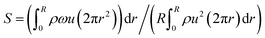 | (12) |
Fig. 5 shows the reaction characteristics—specifically, the conversion rates, gas composition, and kinetic behavior in the DRM and carbon capture zones over a 7-hour period. During the first hour, the gas produced from the methanation zone (R-1: outlet of the 1st reactor) was directed exclusively to the DRM zone (2nd reactor). Thereafter, a valve was switched on to connect the DRM zone (R-2: outlet of the 2nd reactor) to the carbon capture zone (3rd reactor). After 6 hours of combined operation, the valve was switched again to isolate the DRM zone. In other words, the data from the period following the first hour reflect the performance of the DRM zone (as presented in Fig. 4), while the data after 6 hours reflect the behavior of the carbon capture zone (R-3: outlet of the 3rd reactor). The reforming temperature was maintained at 700 °C, and the temperature of the carbon capture zone was 470 °C.
In Fig. 5(a), the CO2 and CH4 conversions are calculated from the concentrations measured at R-1, which corresponds to the inlet of the DRM zone. This approach ensures that the downstream conversion trends observed during DRM-only operation (0–1 h and after 6 h) and during DRM + carbon capture operation (1–6 h) can be directly compared under identical inlet conditions. In contrast, the gas composition in Fig. 5(b) and the H2/CO ratio in Fig. 5(c) are measured at R-2 during DRM-only operation and at R-3 during DRM + carbon capture operation, as indicated in the figure. This explicit separation of calculation basis (R-1) and composition measurement points (R-2 and R-3) clarifies the data origin for each parameter.
To complement these time-series data, Fig. 6 presents the outlet gas compositions at R-1, R-2, and R-3 under the same operating conditions, enabling a direct visual comparison of changes in the major components (CH4, H2, CO, CO2, and inert gas) and the distribution of products at each stage. Initially, the feed gas consists mainly of H2 and CO2 at an H2/CO2 ratio of 4.0 (stoichiometric for methanation), with no CH4 or CO present. After the methanation stage (R-1), H2 and CO2 are largely converted to CH4, with a CO2 conversion of 70.2% and a CH4 selectivity of 95.5%, while a small amount of CO is formed as a byproduct. Condensed water is removed before analysis. At the DRM outlet (R-2), CH4 is almost completely consumed, CO2 conversion increases to 96.3%, and CO and H2 contents increase markedly—reflecting the strong progression of the endothermic DRM reaction within a short contact time (0.38 s).
 | ||
| Fig. 6 Outlet gas compositions at each stage: the methanation zone, DRM zone, and carbon capture zone. Bars show CH4, H2, CO, CO2, and inert gas; the CCR is indicated for the carbon capture zone. | ||
We analyzed the actual reaction pathway in the DRM reactor by evaluating the incremental molar changes (Δ, outlet–inlet, DRM basis) of H2 and CO. As shown in Fig. S4, ΔH2 is plotted against ΔCO together with the stoichiometric reference lines for DRM (ΔH2/ΔCO = 1) and SMR (ΔH2/ΔCO = 3). The experimental data fall close to the DRM line, and a regression constrained through the origin gave ΔH2/ΔCO = 0.79. This clearly demonstrates that the stoichiometry of the observed reaction is consistent with DRM, while SMR can be ruled out within the experimental uncertainty. The elevated H2/CO ratios observed at the outlet are therefore not indicative of SMR, but rather a consequence of H2 carry-over from the upstream methanation zone. As shown in Fig. 4, a significant amount of unreacted H2 remained after the methanation stage, which was transported into the DRM reactor. Moreover, the inter-stage cold traps effectively removed water vapor, suggesting that the influence of residual H2O on side reactions such as SMR was minimal under the present conditions. The outlet gas composition is thus consistent with DRM predominance, and no evidence supports SMR under our conditions.
Finally, at the carbon capture outlet (R-3), CO decreases significantly via the disproportionation reaction (2CO → C + CO2), resulting in solid carbon capture with a carbon capture rate (CCR) of 28.2% and a corresponding increase in CO2. This sequential change in outlet composition quantitatively illustrates the dominant role of R-1 (methanation) in CH4 formation, R-2 (DRM) in syngas (H2 + CO) production, and R-3 (carbon capture) in solid carbon fixation. By explicitly linking conversions to R-1 and gas compositions to R-2 and R-3 and by adding Fig. 6 for side-by-side outlet comparison, the relationship between the operating sequence, measurement location, and reactor performance is made unambiguous. The results demonstrate that catalyst activity and product composition in the DRM zone were stable during the first hour. However, upon connecting the carbon capture zone, a significant decrease in CO2 conversion was observed. This decline was attributed to the introduction of reforming gas into the carbon capture zone, where the CO disproportionation reaction (eqn (3)) and the reduction of CO to carbon (eqn (4)) proceeded, resulting in the formation of solid carbon. Indeed, the CO concentration dropped from approximately 20% during the first hour to around 7% after the valve switch, while the CO2 concentration increased from ∼1% to ∼6%. After the valve was switched back to isolate the DRM zone at the 6-hour mark, the CO2 conversion was found to have decreased by approximately 10%, and the CH4 conversion increased by about 10% compared to the initial value of ∼88%. These changes indicate that the catalyst underwent slight deactivation and that the CH4-rich feed promoted methane decomposition. Under stoichiometric methanation conditions (H2/CO2 = 4.0), the resulting gas supplied to the DRM zone contained a considerable excess of CH4 relative to CO2, favoring the decomposition of CH4. This result suggests that a lower H2/CO2 ratio is more suitable and that the amount of H2 required in the methanation zone can be reduced.
Fig. 7 shows representative images of the solid carbon captured in this experiment. Although variations in the amount of carbon deposition were observed across the different catalyst regions (A–E), a substantial quantity of solid carbon was collected in all sections. The carbon capture rate (CCR) was calculated using eqn (9), based on the total weight of carbon captured across all regions (A + B + C + D + E), and was determined to be 28.2%. These results demonstrate that the coupled multi-stage reaction system developed in this study is capable of capturing a significant amount of solid carbon from CO2, thereby contributing to the realization of carbon neutrality.
Building upon the system-level performance trends described above, we undertook a detailed assessment of the operational robustness of the downstream segment—specifically, the coupled dry reforming (2nd reactor) and solid carbon capture (3rd reactor) stages—through extended-duration reuse experiments. This downstream stability assessment was driven by the recognition that, during CO2 capture in the 3rd reactor, a portion of the active Fe–Co–K catalyst species becomes incorporated into the deposited carbon. Over extended operation, this incorporation could lead to gradual depletion of active metals, thereby reducing carbon capture efficiency and potentially altering the composition of the gas returned to the DRM stage. To replicate realistic operating conditions, the DRM and carbon-capture reactors were run in the same continuous series configuration as used in the tests shown in Fig. 5, ensuring that the DRM outlet stream fed directly into the capture stage. The DRM stage was continuously monitored to determine whether interventions in the capture stage had any measurable effect on its performance. After an initial carbon-capture run (reuse#1), the spent capture-stage catalyst was cored to reopen the blocked central flow path while deliberately retaining an approximately 2 mm-thick catalyst-containing carbon layer along the reactor wall. This approach was chosen to maintain catalytic functionality in the retained layer and to avoid full catalyst removal. No H2 reduction was performed to prevent gasification of the retained carbon. Mass measurements before and after coring (Table S1) showed a reduction from 3.70 g to 1.67 g, corresponding to the removal of 2.03 g of carbon. The reuse#1 catalyst was then evaluated under identical coupled DRM-capture conditions. Time profiles of CO2 conversion, CH4 conversion, and H2/CO ratio (Fig. S5), along with total captured carbon and spatial distribution (Fig. S6), were essentially indistinguishable from those of the fresh catalyst, with the CCR maintained at 35.4% compared to 37.0% for the fresh case. The negligible drop in performance is attributed to four factors: (i) preservation of active Fe–Co sites within the retained carbon layer, (ii) minimal active metal loss during the first coring step, (iii) improved gas flow distribution through the reopened central channel, and (iv) continued catalytic activity of nanoparticles embedded in the retained layer (Fig. S7).
Subsequently, the spent reuse#1 catalyst underwent a second coring operation to produce reuse#2. Mass measurements (Table S2) indicated a reduction from 5.07 g to 3.41 g, corresponding to 1.66 g of carbon removed. Performance data (Fig. S8–S10) showed that the CCR declined to 25.8%, accompanied by a progressive decrease in CO2 conversion over the capture period. This deterioration is consistent with cumulative metal loss and possible microstructural changes in the retained carbon layer.
To quantify the extent of metal loss, TG-DTA analysis of carbon captured by a fresh catalyst (Fig. S11) was performed. The analysis revealed that 97.03% of the mass loss upon heating was due to carbon combustion, with the remaining 2.97% corresponding to catalyst metals. Using this value and the carbon removal data for positions A–D (Table S3), the total active metal loss over the two coring cycles was estimated at ∼110 mg (Table S4). This loss correlates with the performance decline observed in reuse#2. As a countermeasure, an Fe–Co–K mixed oxide equivalent to the estimated metal loss (∼110 mg) was prepared as a slurry in ∼1 mL of 2-propanol and uniformly applied to the retained carbon layer of the reuse#2 catalyst via a micropipette, followed by drying to yield the reuse#3 catalyst. The reuse#3 results (Fig. S12–S14) demonstrated that the CCR recovered to 34.9% and CO2-conversion behavior returned to the level of the fresh and reuse#1 catalysts. Throughout all reuse experiments, DRM performance remained within the trends shown in Fig. 5, confirming that capture-stage interventions did not adversely affect upstream DRM operation.
The three reactors in this system are connected in series under a unidirectional flow scheme, with each stage independently temperature-controlled and thermally insulated. Sampling points are denoted as R-1 (outlet of the 1st reactor, methanation), R-2 (outlet of the 2nd reactor, DRM), and R-3 (outlet of the 3rd reactor, carbon capture). Under the operating sequence for Fig. 5 (0–1 h: DRM only; 1–6 h: DRM + carbon capture connected; >6 h: DRM re-isolated), gas composition measured at R-1 remained unchanged within GC uncertainty upon connecting the carbon-capture stage, with no indication of pressure build-up or temperature fluctuation. Similarly, DRM performance at 700 °C was unaffected whether the capture stage was connected (measurements at R-3) or disconnected (measurements at R-2), with no measurable changes in the temperature profile, CO2-conversion trend, or H2/CO ratio. These observations confirm physical and thermal independence between stages under the applied flow and insulation configuration.
At the same time, the series configuration imposes an intentional chemical sequential dependency: the composition at R-1 defines the DRM inlet, enabling CH4/CO2 reforming to syngas at R-2, and the CO-rich stream from DRM feeds the carbon-capture stage, where the Boudouard reaction (2CO → C + CO2) deposits solid carbon at R-3. This deliberate combination of physical independence and chemical coupling ensures that downstream stages do not disturb upstream performance while enabling the overall process to achieve high CO2 utilization through stepwise conversion to CH4, CO, and solid carbon.
Accordingly, in the following section, we investigate the effects of varying operating conditions to achieve more efficient CO2 conversion via methanation.
3.2 Improving the system efficiency by optimizing the H2/CO2 ratio
In the coupled system combining the methanation zone (1st reactor) and the DRM zone (2nd reactor), it is necessary to maintain a sufficient concentration of CO2 as the feedstock for DRM. Therefore, a lower H2/CO2 ratio in the methanation zone is preferable. As discussed in the previous section, operating under stoichiometric methanation conditions results in excessive CH4 formation, which can accelerate degradation of the DRM catalyst. The H2/CO2 ratio in the methanation feed significantly affects the performance of the coupled catalytic system. Accordingly, the optimal operating conditions were investigated by varying the H2/CO2 ratio in the methanation reactor.Fig. 8(a) presents the reaction characteristics in the methanation zone as a function of the H2/CO2 ratio, while Fig. 8(b) illustrates the resulting CO2/CH4 ratio in the gas composition entering the DRM zone. All experiments were conducted under auto-methanation conditions, i.e., without external heating. Even when the H2/CO2 ratio was below the stoichiometric value of 4.0, methanation proceeded with high conversion efficiency due to the exothermic nature of the reaction and the promotion of auto-methanation. Although CO2 conversion decreased with lower H2/CO2 ratios, the decline was smaller than that predicted by equilibrium. Specifically, at H2/CO2 = 4.0, the CO2 conversion reached approximately 70% of the equilibrium value, whereas at H2/CO2 = 2.0, the conversion remained at approximately 84% of the equilibrium value. These results indicate that a reduction in hydrogen supply does not severely compromise CH4 production efficiency and may compensate for the economic disadvantage of high hydrogen consumption in methanation.
As shown in Fig. 8(b), lowering the H2/CO2 ratio also resulted in a more favorable CO2/CH4 ratio in the feed gas entering the DRM zone. A higher CO2/CH4 ratio was achieved at lower H2/CO2 values, which is advantageous for DRM operation. Since DRM is often accompanied by carbon deposition, the H/C and O/C atomic ratios in the feed gas are important factors. In particular, a higher O/C ratio has been reported to suppress carbon deposition,50 thereby minimizing catalyst deactivation. The observed increase in the CO2/CH4 ratio achieved through lowering the H2/CO2 ratio contributes to this effect. At H2/CO2 ratios of 2.5 or lower, the CO2/CH4 ratio exceeded 1.2 (Fig. 8(b)), demonstrating the effectiveness of this strategy in suppressing carbon deposition and enhancing DRM catalyst stability.
Fig. 9 illustrates the reaction characteristics, specifically, CO2 and CH4 conversions, in the DRM zone when the H2/CO2 ratio in the methanation feed gas was varied from 2.0 to 3.5, along with those of the coupled reaction system after synthetic gas was introduced into the carbon capture zone following the first hour. During the initial hour, the CO2 conversion in the DRM zone remained stable regardless of the H2/CO2 ratio. Furthermore, the extent of the decrease in CO2 conversion after opening the connecting valve to the carbon capture zone showed no significant dependence on the H2/CO2 ratio, with nearly identical trends observed over the subsequent 5-hour period. However, for H2/CO2 ratios of 3.0 and 3.5, the CO2 conversions after reconnecting the DRM zone (post-capture) were lower than those observed during the initial hour, suggesting partial catalyst degradation. In contrast, for H2/CO2 ratios of 2.0 and 2.5, no observable degradation was detected, indicating that operation at lower H2/CO2 ratios is more favorable, as it enables sustained DRM activity while minimizing H2 consumption.
Fig. 10 shows the variation in the amount of carbon captured in the carbon capture zone as a function of the H2/CO2 ratio in the methanation feed. The amount of solid carbon collected was found to vary depending on this ratio, with H2/CO2 values between 2.5 and 3.0 yielding the highest carbon capture. These results indicate that effective CO2 fixation in the form of solid carbon can be achieved while maintaining lower hydrogen usage, thereby contributing to both catalyst longevity and system efficiency.
3.3 Assessment of system performance from the perspective of energy
In the previous section, it was demonstrated that reducing the amount of supplied H2 enhances the functionality of both the DRM and carbon-capture zones. In this section, we evaluate the effect of varying H2 supply on each reaction zone from a thermodynamic standpoint, using exergy analysis.Fig. 11 presents the exergy levels of the outlet gases from each reaction zone, with the exergy of the feed gas to the methanation zone taken as the reference. Since methanation is an exothermic reaction, it releases heat into the surroundings, leading to a significant decrease in exergy, particularly due to the consumption of high-exergy H2. This effect was especially pronounced at an H2/CO2 ratio of 4.0 (stoichiometric), where the exergy loss reached 101.8 kJ h−1. In contrast, when the H2/CO2 ratio was reduced to 2.0, the exergy loss was mitigated to approximately 63.2 kJ h−1, nearly half the loss observed under stoichiometric conditions. These results underscore the thermodynamic advantage of operating at lower H2/CO2 ratios in the methanation zone.
In contrast, the DRM reaction is endothermic, absorbing heat from the surroundings and thereby increasing the exergy of the system. In other words, the exergy losses incurred during methanation are partially recovered through integration with the DRM zone. Under all tested conditions, the exergy in the DRM zone increased, with particularly favorable values observed at H2/CO2 ratios of 2.0 and 2.5, where the exergy change was positive. The third-stage carbon-capture zone exhibited relatively small exergy changes, but the final exergy remained positive. The exergy values of the generated synthesis gas (CO + H2) and solid carbon were 510 kJ mol−1 and 275 kJ mol−1, respectively, contributing substantially to the high exergy content of the products.
However, when the H2/CO2 ratio was 3.0 or higher, the total system exergy became negative, despite partial recovery in the DRM zone. This indicates that excess H2 supply is thermodynamically unfavorable in this integrated system. In contrast, reducing the H2 feed improves the overall energetic efficiency. Moreover, minimizing the use of costly H2 directly contributes to reducing operational costs, highlighting the advantages of this coupled reaction system from both thermodynamic and economic perspectives.
When the measured external energy inputs are explicitly included in the calculation (as shown in the extended evaluation in Fig. S15), the overall exergy balance of the system decreases substantially compared to the values shown in Fig. 11. Under these expanded boundaries, the net exergy for all H2/CO2 ratios shifts downward, and in many cases, including those previously favorable (e.g., ratios of 2.0 or 2.5), the total balance moves close to zero or becomes distinctly negative. This indicates that, while internal heat integration between the exothermic methanation/CO disproportionation and the endothermic DRM can partially offset thermal demands, it cannot by itself compensate for the impact of the external energy inputs. From a practical standpoint, this result has important implications for the feasibility of the process. A negative net exergy under realistic operating boundaries means that, if powered by conventional energy sources, the process would consume more useful energy than is embodied in its outputs. Therefore, to render the process both energetically and environmentally sustainable, it is essential to pair the integrated reactor system with renewable, low-carbon energy sources. In addition, the endothermic DRM stage and any auxiliary heating requirements offer opportunities for waste heat utilization. By coupling the system with industrial processes that generate low-to medium-grade heat (e.g., metallurgy, cement production, and chemical manufacturing), part of the thermal demand can be met without additional primary energy consumption. Such integration could significantly reduce the external exergy input, shifting the overall balance toward neutrality or positivity. Thermal storage technologies could further smooth the intermittency of both renewable electricity and waste heat availability, enabling continuous operation without resorting to fossil-derived backup. Furthermore, process optimization can target minimizing unnecessary external energy input—both to reduce direct operational costs and to limit the upstream energy burden. Strategies include designing catalysts to perform efficiently under low-external-energy conditions, optimizing flow distribution to reduce energy losses and integrating real-time control systems that dynamically adjust operating conditions in response to renewable energy availability. By combining these engineering measures with renewable energy supply and waste heat utilization, the system can maintain a net-positive exergy balance even under the expanded accounting framework, enabling sustainable and efficient long-term operation.
3.4 Physicochemical properties of captured carbon
Fig. 12 shows an SEM image illustrating the morphology of the solid carbon captured in the carbon-capture zone (3rd reactor), along with elemental analysis data obtained by EDX. Despite the active involvement of Fe and Co in carbon fiber growth, the majority of the catalyst remained physically intact throughout the reaction. No significant pressure drop or reactor clogging was observed during over 5 hours of operation, suggesting that the catalyst structure was maintained and that metal leaching was minimal. While a small amount of metal was detected in the carbon product, the catalyst exhibited stable performance over the entire duration of the experiment. Elemental iron (Fe) was observed at the tips of the carbon structures, suggesting that the carbon grew via a tip-growth mechanism. As previously reported,42,51–58 the growth of solid carbon over Fe-based catalysts proceeds through a carbide-mediated, diffusion–precipitation pathway. CO first adsorbs and dissociates on metallic Fe sites to yield surface C and O; the O is scavenged via CO formation, while the nascent C dissolves into the Fe lattice, producing a carburized phase that evolves toward Fe3C (cementite) under CO-rich conditions.51–53 Because Fe3C is metastable at the relevant temperatures, it periodically decomposes, releasing carbon that migrates through or along the metal particle and precipitates as sp2 carbon at the particle–gas interface.54,55 Repetition of this dissolve–transport–precipitate cycle drives filament nucleation and elongation. In the tip-growth mode, sustained carbon precipitation at the particle–filament interface lifts the particle away from the substrate so that it resides at the fiber tip—exactly the morphology we observed by SEM/EDX, with Fe (and Co) signals concentrated at fiber termini.50,56The relative rates of the elementary steps—CO dissociation, bulk/surface diffusion of carbon in Fe, Fe3C formation/decomposition, and sp2 precipitation—are strongly sensitive to temperature (via C solubility and diffusivity in Fe), particle size, and alloying.52,57 Alloying Fe with Co increases the solubility and mobility of carbon in the metallic phase and can stabilize specific carbide domains, which accelerates filament growth and narrows the diameter distribution; this is consistent with our elemental maps showing Fe/Co co-localization at tips.53,57 Gas-phase composition also modulates the steady state: higher CO chemical potential favors carburization and Boudouard-assisted carbon supply, whereas added H2 promotes surface cleaning and shifts the carbide–metal equilibrium, thereby tuning the balance between nucleation and etching.54,58 These factors together rationalize why long fibers preferentially form near the reactor inlet where CO activity is higher and residence time is longer in our system.
Although tip-growth dominates under our conditions, base-growth can occur when particles remain strongly anchored (e.g., by partial encapsulation or favorable wetting), leading to nucleation beneath the particle while the metal stays at the filament base.50,55 The coexistence of tip- and base-growth modes is therefore expected across spatially heterogeneous microenvironments in the bed. Taken together, the SEM/EDX evidence of Fe/Co at fiber tips, the persistence of activity over multi-hour operation, and the known carbide-mediated mechanism from the literature support the view that carbon formation here proceeds predominantly via an Fe(–Co) carbide diffusion–precipitation pathway, with Co acting synergistically to facilitate carbon transport and precipitation.50–58
The detection of fine Fe species in the SEM and EDX analyses supports this reaction pathway. However, it is also possible that some fiber-shaped carbon was generated via a base-growth mechanism, initiated beneath the deposited carbon layer by nucleating carbon atoms.
Elemental mapping showed spatial consistency between Fe and Co, indicating that both metals contributed catalytically to carbon growth. At capture locations C, E, and other regions, fiber-shaped solid carbon formed through such mechanisms was clearly observed. This type of carbon can serve as a functional material, with potential applications in fuel cell electrodes and other energy devices. Thus, the reaction system not only converts CO2 into solid carbon but also produces value-added materials.
Fig. 13 shows SEM images of solid carbon formed at varying gas inlet flow rates during methanation. Using an H2/CO2 ratio of 2.5, gas flow rates of 1.0 and 3.0 L min−1 were applied to assess the influence of residence time on carbon morphology. In both cases, long carbon fibers were observed at the front end of the reactor (inlet side). In contrast, the fibers captured at the rear stage were shorter, particularly at a flow rate of 1.0 L min−1, where fiber growth was less prominent. This suggests that carbon growth was more active in the front zone due to longer contact time between the feed gas and the catalyst. Carbon deposition reactions, such as CO disproportionation and CO reduction, likely occurred more rapidly in the front zone and diminished toward the rear, correlating with gas-phase compositional changes along the reactor length.
Fig. 14 presents the Raman spectrum of solid carbon captured in zone A under the same conditions as shown in Fig. 13. Two prominent peaks were observed: the D band (∼1380 cm−1), attributed to structural defects, and the G band (∼1580 cm−1), associated with graphitic ordering. The intensity ratio (ID/IG), an indicator of carbon crystallinity, was approximately 1.3, indicating low defect density and a relatively well-ordered graphitic structure. Compared to plasma-derived carbon (typically ID/IG > 1.5),59 the carbon obtained here exhibits greater graphitic character. A similarly low ID/IG ratio was observed across other sampling zones, suggesting spatially uniform conditions favorable for ordered carbon growth throughout the reactor. It should be noted that the D/G ratio in Raman analysis can depend on the excitation wavelength used. In this study, measurements were performed with a 532 nm laser, a commonly adopted wavelength for graphitic carbon characterization, enabling direct comparison with reported literature values.60,61 Additionally, in the low-frequency region below 500 cm−1, a distinct feature attributable to the radial breathing mode (RBM) was detected. This mode is characteristic of certain tubular or hollow nanostructures such as single-walled or multi-walled carbon nanotubes, suggesting that the captured carbon contains a fraction of nanotube-like graphitic domains alongside filamentous fibers.61
These results indicate that, even in the absence of external heating, the heat released by the upstream exothermic methanation and DRM reactions was sufficient to raise and sustain the carbon formation zone at 500–650 °C, the optimal temperature window for the development of well-ordered graphitic carbon. This is supported by the observed morphology and its spatial distribution under different flow conditions and compositions. The alignment of carbon filaments, the presence of Fe and Co nanoparticles, and the detection of RBM features collectively indicate a dynamic catalytic environment in which metal–support interactions, local gas-phase conditions, and nanostructure-specific growth pathways jointly govern nucleation and growth. The alignment of carbon filaments and the presence of Fe and Co nanoparticles indicate a dynamic catalytic environment in which metal–support interactions and local gas-phase conditions jointly govern nucleation and growth. From a materials perspective, the resulting carbon exhibits desirable properties for high-performance applications. The filamentous morphology, low defect density, crystalline ordering, and partial nanotube-like domains suggest potential in electrochemical devices such as supercapacitors, battery electrodes, and fuel cell components. Furthermore, the large surface area and mesoporous nature may be advantageous for gas adsorption or environmental remediation. The structural integrity of the carbon fibers during collection indicates strong adhesion to the catalyst surface and mechanical robustness, facilitating downstream processing and functionalization, which is critical for industrial applications.
The ability to generate structured carbon with controlled morphology from CO2 under autothermal conditions greatly enhances the value proposition of the multi-stage reactor system. The captured carbon thus functions not only as a CO2 sink but also as a resource for producing high-value functional materials. Tip-growth, primarily mediated by Fe and possibly assisted by Co nanoparticles, enabled the formation of crystalline carbon fibers. The observed spatial variation in fiber morphology reflects the influence of gas composition and flow dynamics. This system integrates catalytic control, thermal self-management, and reactor design to yield high-quality carbon materials while achieving CO2 mitigation. By coupling carbon capture with material synthesis, this approach offers a viable and technologically promising strategy for carbon-negative CO2 utilization.
4. Conclusions
A novel, multi-stage, catalytic reaction system was developed that directly converts industrial CO2 emissions into solid carbon while producing valuable chemical raw materials. The evaluation of the fundamental characteristics demonstrated that reducing the supplied H2 enhances the durability of the DRM catalyst and improves the functionality for carbon capture. Furthermore, the reduction in the supplied H2 significantly improves the exergy efficiency of this reaction system. These findings indicate that the challenges associated with the methanation, which undesirably requires a high H2 feed level, can be effectively addressed. The captured solid carbon grows in a fibrous structure, making it suitable for applications as a functional material. We hope that the constructed multi-stage reaction system will contribute to realizing a carbon-neutral society.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, Ryo Watanabe, upon reasonable request.Supplementary information is available. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d5se00847f.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by JST-ALCA-Next Program Grant Number JPMJAN24C2, Japan.References
- K. Akimoto, F. Sano, J. Oda, H. Kanaboshi and Y. Nakano, Climate change mitigation measures for global net-zero emissions and the roles of CO2 capture and utilization and direct air capture, Energy Clim. Change, 2021, 2, 100057 CrossRef.
- J. Rogelj, M. den Elzen, N. Höhne, T. Fransen, H. Fekete, H. Winkler, R. Schaeffer, F. Sha, K. Riahi and M. Meinshausen, Paris Agreement climate proposals need a boost to keep warming well below 2 °C, Nature, 2016, 534, 631–639 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Chen, S. Deng, H. Wei, B. Wang, J. Huang and G. Yu, Activated carbons and amine-modified materials for carbon dioxide capture-a review, Front. Environ. Sci. Eng., 2013, 7, 326–340 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. Hongqun, X. Zhenghe, F. Maohong, G. Rajender, S. Rachid B, B. Alan E and W. Ian, Progress in carbon dioxide separation and capture: A review, J. Environ. Sci., 2008, 20, 14–27 CrossRef.
- Y. Wu, J. Xu, K. Mumford, G. W. Stevens, W. Fei and Y. Wang, Recent advances in carbon dioxide capture and utilization with amines and ionic liquids, Green Chem. Eng., 2020, 1, 16–32 CrossRef.
- F. R. H. Abdeen, M. Mel, M. S. Jami, S. I. Ihsan and A. F. Ismail, A review of chemical absorption of carbon dioxide for biogas upgrading, Chin. J. Chem. Eng., 2016, 24, 693–702 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. H. Lee, K. T. Lee, S. Bhatia and A. R. Mohamed, Post-combustion carbon dioxide capture: Evolution towards utilization of nanomaterials, Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev., 2012, 16, 2599–2609 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Yang, R. J. Rees, W. Conway, G. Puxty, Q. Yang and D. A. Winkler, Computational Modeling and Simulation of CO2 Capture by Aqueous Amines, Chem. Rev., 2014, 117, 9524–9593 CrossRef PubMed.
- L. Cuccia, J. Dugay, D. Bontemps, M. Louis-Louisy and J. Vial, Analytical methods for the monitoring of post-combustion CO2 capture process using amine solvents: A review, Int. J. Greenhouse Gas Control, 2018, 72, 138–151 CrossRef CAS.
- T. Gelles, S. Lawson, A. A. Rownaghi and F. Rezaei, Recent advances in development of amine functionalized adsorbents for CO2 capture, Adsorption, 2020, 26, 5–50 CrossRef CAS.
- A. M. Varghese and G. N. Karanikolos, CO2 capture adsorbents functionalized by amine – bearing polymers: A review, Int. J. Greenhouse Gas Control, 2020, 96, 103005 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Che, Nobel Prize in chemistry 1912 to Sabatier: Organic chemistry or catalysis?, Catal. Today, 2013, 218–219, 162–171 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Du, S. Lim, Y. Yang, C. Wang, L. Pfefferle and G. L. Haller, Methanation of carbon dioxide on Ni-incorporated MCM-41 catalysts: The influence of catalyst pretreatment and study of steady-state reaction, J. Catal., 2007, 249(2), 370–379 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Wang, S. Wang, X. Ma and J. Gong, Recent advances in catalytic hydrogenation of carbon dioxide, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2011, 40, 3703–3727 RSC.
- K. Liu, X. Xu, J. Xu, X. Fang, L. Liu and X. Wang, The distributions of alkaline earth metal oxides and their promotional effects on Ni/CeO2 for CO2 methanation, J. CO2 Util., 2020, 38, 113–124 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Quindimil, U. De-La-Torre, B. Pereda-Ayo, A. Davó-Quiñonero, E. Bailón-García, D. Lozano-Castelló, J. A. González-Marcos, A. Bueno-López and J. R. González-Velasco, Effect of metal loading on the CO2 methanation: A comparison between alumina supported Ni and Ru catalysts, Catal. Today, 2020, 356, 419–432 CrossRef.
- R. Y. Chein and C. C. Wang, Experimental Study on CO2 Methanation over Ni/Al2O3, Ru/Al2O3, and Ru-Ni/Al2O3 Catalysts, Catalysts, 2020, 10, 1112 CrossRef.
- J. C. Navarro, M. A. Centeno, O. H. Laguna and J. A. Odriozola, Ru–Ni/MgAl2O4 structured catalyst for CO2 methanation, Renewable Energy, 2020, 161, 120–132 CrossRef.
- S. Sharma, Z. Hu, P. Zhang, E. W. McFarland and H. Metiu, CO2 methanation on Ru-doped ceria, J. Catal., 2011, 278, 297–309 CrossRef.
- M. A. Paviotti, B. M. Faroldi and L. M. Cornaglia, Ni-based catalyst over rice husk-derived silica for the CO2 methanation reaction: Effect of Ru addition, J. Environ. Chem. Eng., 2021, 9, 105173 CrossRef.
- T. Sakpal and L. Lefferts, Structure-dependent activity of CeO2 supported Ru catalysts for CO2 methanation, J. Catal., 2018, 367, 171–180 CrossRef.
- A. Porta, L. Falbo, C. G. Visconti, L. Lietti, C. Bassano and P. Deiana, Synthesis of Ru-based catalysts for CO2 methanation and experimental assessment of intraporous transport limitations, Catal. Today, 2020, 343, 38–47 CrossRef.
- Y. Li, et. al., Experimental and theoretical insights into an enhanced CO2 methanation mechanism over a Ru-based catalyst, Appl. Catal., B, 2022, 319, 121903 CrossRef.
- A. I. Tsiotsias, N. D. Charisiou, I. V. Yentekakis and M. A. Goula, Bimetallic Ni-Based Catalysts for CO2 Methanation: A Review, Nanomaterials, 2021, 11, 28 CrossRef PubMed.
- P. Frontera, A. Macario, M. Ferraro and P. L. Antonucci, Supported Catalysts for CO2 Methanation: A Review, J. Catal., 2017, 7, 59 Search PubMed.
- N. D. M. Ridzuan, M. S. Shaharun, M. A. Anawar and I. Ud-Din, Ni-Based Catalyst for Carbon Dioxide Methanation: A Review on Performance and Progress, J. Catal., 2022, 12, 469 Search PubMed.
- L. Li, W. Zeng, M. Song, X. Wu, G. Li and C. Hu, Research Progress and Reaction Mechanism of CO2 Methanation over Ni-Based Catalysts at Low Temperature: A Review, J. Catal., 2022, 12, 244 Search PubMed.
- X. Xu, C. Song, R. Wincek, J. M. Andresen, B. G. Miller and A. W. Scaroni, Separation of CO2 from Power Plant Flue Gas Using a Novel CO2 “Molecular Basket” Adsorbent, Fuel Chemistry Division Preprints, 2003, 48, 162–163 Search PubMed.
- K. Müller, M. Fleige, F. Rachow and D. Schmeißer, Sabatier based CO2-methanation of Flue Gas Emitted by Conventional Power Plants, Energy Procedia, 2013, 40, 240–248 CrossRef.
- C. Fukuhara, A. Kamiyama, M. Itoh, N. Hirata, S. Ratchachat, M. Sudoh and R. Watanabe, Auto-methanation for transition-metal catalysts loaded on various oxide supports: A novel route for CO2 transformation at room-temperature and atmospheric pressure, Chem. Eng. Sci., 2020, 219, 115589 CrossRef.
- C. Fukuhara, S. Ratchachat, A. Kamiyama, M. Sudoh and R. Watanabe, Auto-methanation Performance of Structured Ni-type Catalyst for CO2 Transformation, Chem. Lett., 2019, 48, 441–444 CrossRef.
- C. Fukuhara, S. Ratchachat, Y. Suzuki, M. Sudoh and R. Watanabe, Auto-methanation of Carbon Dioxide: A Novel Route for Transforming CO2 over Ni-based Catalyst, Chem. Lett., 2019, 48, 196–199 CrossRef CAS.
- N. Hirata, R. Watanabe and C. Fukuhara, Performance characteristics of auto-methanation using Ru/CeO2 catalyst, autonomously proceeding at room temperature, Fuel, 2020, 282, 118619 CrossRef CAS.
- M. S. Hossain, H. Akama, P. Verma, R. Watanabe and C. Fukuhara, Effect of twist angle in spiral-type Ru/CeO2 catalysts on CO2 auto-methanation performance, J. Chem. Eng. Jpn., 2023, 56, 2182628 CrossRef.
- M. Usman, W. M. A. Wan Daud and H. F. Abbas, Dry reforming of methane: Influence of process parameters—A review, Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev., 2015, 45, 701–744 CrossRef.
- Y. Wang, L. Yao, S. Wang, D. Mao and C. Hu, Low-temperature catalytic CO2 dry reforming of methane on Ni-based catalysts: A review, Fuel Process. Technol., 2018, 169, 199–206 CrossRef CAS.
- C. He, S. Wu, L. Wang and J. Zhang, Recent advances in photo-enhanced dry reforming of methane: A review, J. Photochem. Photobiol., C, 2022, 51, 100468 CrossRef CAS.
- J. W. Han, J. S. Park, M. S. Choi and H. Lee, Uncoupling the size and support effects of Ni catalysts for dry reforming of methane, Appl. Catal., B, 2017, 203, 625–632 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Abdullah, N. A. A. Ghani and D.-V. N. Vo, Recent advances in dry reforming of methane over Ni-based catalysts, J. Cleaner Prod., 2017, 162, 170–185 CrossRef CAS.
- Y. A. Zhu, D. Chen, X. G. Zhou and W. K. Yuan, DFT studies of dry reforming of methane on Ni catalyst, Catal. Today, 2009, 148, 260–267 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Djaidja, S. Libs, A. Kiennemann and A. Barama, Characterization and activity in dry reforming of methane on NiMg/Al and Ni/MgO catalysts, Catal. Today, 2006, 113, 194–200 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Fukuhara, R. Hyodo, K. Yamamoto, K. Masuda and R. Watanabe, A novel nickel-based catalyst for methane dry reforming: A metal honeycomb-type catalyst prepared by sol–gel method and electroless plating, Appl. Catal., A, 2013, 468, 18–25 CrossRef CAS.
- C. Fukuhara, Y. Matsui, M. Tanebayashi and R. Watanabe, A novel catalytic reaction system capturing solid carbon from greenhouse gas, combined with dry reforming of methane, Chem. Eng. J. Adv., 2021, 5, 100057 CrossRef CAS.
- W. Kawasaki, H. Kato, S. Ratchachat, R. Watanabe and C. Fukuhara, Development of a novel synthesis-gas production system combining with carbon capture, J. CO2 Util., 2017, 22, 91–96 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Witte, Social Acceptance of Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS) from Industrial Applications, Sustainability, 2021, 13, 12278 CrossRef CAS.
- I. Butnar, J. Cronin and S. Pye, Review of Carbon Capture Utilisation and Carbon Capture and Storage in Future EU Decarbonisation Scenarios, UCL Energy Institute, ( 2020) pp. 1–53 Search PubMed.
- N. Koukouzas, et. al., Current CO2 Capture and Storage Trends in Europe in a View of Social Knowledge and Acceptance. A Short Review, Energies, 2022, 15, 5716 CrossRef CAS.
- Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan, https://www.mofa.go.jp/mofaj/ic/ch/page1w_000121.html.
- A. K. Gupta, D. G. Lilley and N. Syred, Swirl flows, Tunbridge Wells, Abacus Press, Kent, 1984 Search PubMed.
- C. Fukuhara, CO2 resource conversion process using dry reforming of CH4 and solid carbon capture, Catal. Catal., 2022, 64(1), 9–14 CAS.
- S. J. Goldie and K. S. Coleman, Graphitization by metal particles, ACS Omega, 2023, 8, 3278–3285 CrossRef CAS.
- R. D. Hunter, J. Ramírez-Rico and Z. Schnepp, Iron-catalyzed graphitization: mechanistic insights into Fe–C interactions and cementite formation, J. Mater. Chem. A, 2022, 10, 4489–4516 RSC.
- X. Deng, L. Zhao, T. Gao, Q. Xue, J. Wang and H. Zuo, Advancements in the study of carbon deposition behavior during the metallurgical high-reductive potential gas reforming and heating processes, Fuel Process. Technol., 2024, 257, 108087 CrossRef CAS.
- I. R. Hamdani, A. Ahmad, H. M. Chulliyil, C. Srinivasakannan, A. A. Shoaibi and M. M. Hossain, Methane decomposition to H2 via Fe3C intermediate formation and breakdown, ACS Omega, 2023, 8, 28945–28967 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Guo, X. Zhang, B. Shao, S. Sang and X. Yang, In situ Fe3C-assisted transformation of amorphous carbon into graphitic fibers, RSC Adv, 2022, 12, 7935–7940 RSC.
- W. J. Sagues, J. Yang, N. Monroe, S. D. Han, T. Vinzant, M. Yung, H. Jameel, M. Nimlos and S. Park, Iron-catalyzed biomass graphitization via Fe3C intermediate under CO-reductive conditions, Green Chem., 2020, 22, 7093–7108 RSC.
- S. Takenaka, M. Serizawa and K. Otsuka, Generation and decomposition of Fe3C during CH4/CO dissociation over iron catalysts, J. Catal., 2004, 222, 520–531 CrossRef CAS.
- H. P. Boehm, CO disproportionation on iron and Fe3C crystal-containing carbon filaments, Carbon, 1973, 11, 583–590 CrossRef.
- Z. H. Ni, H. M. Fan, X. F. Fan, H. M. Wang, Z. Zheng, P. Feng, Y. H. Wu and Z. X. Shen, High temperature Raman spectroscopy studies of carbon nanowalls, J. Raman Spectrosc., 2007, 38, 1449–1453 CrossRef CAS.
- A. C. Ferrari and J. Robertson, Interpretation of Raman spectra of disordered and amorphous carbon, Phys. Rev. B, 2000, 61, 14095–14107 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Zhao, Y. Ando, L.-C. Qin, H. Kataura, Y. Maniwa and R. Saito, Radial breathing modes of multiwalled carbon nanotubes, Chem. Phys. Lett., 2002, 361, 169–174 CrossRef CAS.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2026 |












