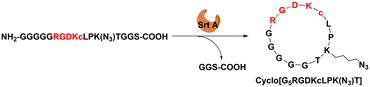Integrin-specific binding macrocyclic RGD peptides functionalized with dinitrophenol as multivalent antibody-recruiting molecules to enhance cytotoxicity in cancer immunotherapy
Xiaozhong
Cheng
 *a,
Chenrui
Hu
a,
Wanru
Gao
a,
Yajun
Chen
a,
Wei
Wang
a,
Guilan
Zhu
a and
Zhimeng
Wu
*a,
Chenrui
Hu
a,
Wanru
Gao
a,
Yajun
Chen
a,
Wei
Wang
a,
Guilan
Zhu
a and
Zhimeng
Wu
 *b
*b
aResearch Center for Animal Model and Functional of Bioactive Substances, Hefei Normal University, Hefei, 230601, China. E-mail: chengxiaozhong@hfnu.edu.cn; zwu@jiangnan.edu.cn
bKey Laboratory of Carbohydrate Chemistry & Biotechnology, Ministry of Education, School of Biotechnology, Jiangnan University, 214122, Wuxi, China
First published on 6th December 2025
Abstract
The diverse expression of antigenic subtypes on tumor cells can substantially influence the specific binding and tumor cytotoxicity of antibody-recruiting molecules (ARMs). Therefore, the development of multivalent ARMs with high selectivity and affinity for binding to different subtypes on tumor cells can be expected to improve clinical performance. In this study, multivalent ARMs incorporated with multivalent dinitrophenyl (DNP) haptens and an integrin-specific arginine–glycine–aspartic acid (RGD) macrocyclic peptide were synthesized using a chemoenzymatic approach. The molecules specifically recognized integrin αvβ3-positive tumor cells and exhibited robust antibody recruitment capacity and tumor-killing effects depending on the multivalent effects. Notably, the D3 molecule showed excellent anti-DNP antibody recruitment capacity in the αvβ3-positive tumor cells and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) and complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC)-mediated tumor cytotoxicity. Given the variable expression of integrin receptor subtypes among individuals, the multivalent ARMs developed in this study that specifically target αvβ3-positive tumor cells to enhance cancer cytotoxicity represent a promising strategy for tumor immunotherapy.
Introduction
Antibody-recruiting molecules (ARMs), a promising immunotherapy strategy, consist of an antibody-binding domain (ABD) to recruit endogenous antibodies and a target-binding domain (TBD) to bind to the target cancer for the elimination of cancer cells by immune-mediated toxicity.1–3 The ABD is usually designed as small molecule haptens, such as L-rhamnose, galactosyl-(1,3)-galactose, and 2,4-dinitrophenol (DNP), which bind with anti-hapten antibodies naturally existing in human serum.4–7 The TBD is responsible for binding to target cells, resulting in the formation of ternary complexes. Furthermore, anti-hapten antibodies can trigger immune responses, such as antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC), and antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis (ADCP), through the Fc end, thereby inducing the target cells' death.3 The therapeutic efficacy of ARMs in tumor treatment is substantially influenced by the binding capabilities of the ABD and TBD to their respective target cell membrane receptors and endogenous antibodies.3 For instance, the concentrations and isotype distributions of endogenous antibodies present in human serum can affect the antibody recruitment, and the amount and type of receptors on tumor cell membranes are critical determinants of the binding efficiency of the TBD to target cells.4,8–11 Consequently, ARMs that effectively facilitate the recruitment of endogenous antibodies need to be further developed. Recently, multivalent ARMs have been developed to improve the antibody-recruiting ability.12–15 For example, Berthet et al. synthesized multivalent L-rhamnose and cRGD-based antibody-recruiting macromolecules.16 They demonstrated that multivalent ABD and TBD structures can enhance the binding of the anti-rhamnose antibody and target cells. Furthermore, antibody-recruiting polymers (ARPs), a novel class of multivalent ARMs, are engineered with multivalent haptens integrated into the polymer backbone, demonstrating high-avidity antibody binding and effective recruitment of antibodies to cancer cells.17–20 Although the development of multivalent hapten structures has been demonstrated to improve antibody recruitment efficiency, it is crucial to emphasize that the fundamental prerequisite for effective multivalent ARMs is their specific binding to tumor cells. However, the differential presentation of the antigen subtype on tumor cells affects the specific binding and tumor cytotoxicity of multivalent ARMs.9,12 For example, multiple subtypes of integrin receptors on many tumor cell surfaces significantly influence the selective binding capacity of integrin inhibitors.21–23Integrin is a heterodimeric transmembrane receptor consisting of α and β subunits, and it facilitates the interaction between cells and the extracellular matrix.24 These receptors are pivotal in various biological processes, including cell migration, proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis, with particular importance in tumorigenesis and metastasis.25,26 Currently, 18 α and 8 β subunits have been identified, which can combine to form at least 24 distinct integrin types. Among them, the overexpression of αvβ3 and αvβ5 integrins has been recognized as a distinctive marker of tumor-associated neoangiogenesis.26–28 Conversely, integrin expression patterns demonstrate variability across different tumor tissues. For example, integrin αvβ3 is highly expressed in malignant melanoma and malignant ovarian tumor cells, whereas it is either absent or expressed at low levels in colon, pancreatic, breast, or benign ovarian tumors, where αvβ5 or other integrin subtypes are more prevalent.29–33 Therefore, the development of high-affinity and selective multivalent ARMs that target specific integrin subtypes presents a promising avenue for tumor-targeted therapy. Importantly, the therapeutic efficacies of integrin-specific binding multivalent ARMs are largely unexplored.
The arginine–glycine–aspartic acid (RGD) tripeptide sequence has been identified as the core sequence for the interaction with integrins.26 In our previous research, a macrocyclic RGD peptide library was synthesized by a chemoenzymatic strategy to screen cell-based bioactivity and obtain cyclic RGD peptide c(G5RGDKcLPET) with high selectivity for integrins ανβ3 to ανβ5.34,35 This compound with high integrin selectivity can serve as a TBD structure to improve the tumor-specific binding ability of ARMs. In this study, the multivalent ARMs were synthesized using c(G5RGDKcLPET) to enhance the specific binding affinity for integrin-positive tumor cells. Meanwhile, the multivalent DNP structure was introduced to increase the efficiency of antibody recruitment, augmenting its tumoricidal effects.
Results and discussion
Synthesis of cyclic RGD peptide cyclo[G5RGDKcLPK(N3)T]
The linear peptide G5RGDKcLPK(N3)TGGS was synthesized using Wang resin based on a solid-phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) approach. Within this sequence, RGDKc served as the integrin core-acting motif, with c representing a D-type amino acid. The sequences G5 and LPKTGGS were used as recognition motifs for sortase A (Srt A), where the lysine side-chain amino group was modified with an azide to facilitate conjugation with multivalent ARMs (Scheme 1). The linear peptide G5RGDKcLPK(N3) TGGS was cleaved from Wang resin and purified. The pure linear peptide was characterized by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and mass spectrometry (Fig. S1 and S2). The linear peptide was then cyclized by Srt A to form the final cyclic peptide cyclo[G5RGDKcLPK(N3)T] (Scheme 1). Reaction progress was monitored via HPLC (Fig. S3). The final product was purified and characterized via HPLC (Fig. S4) and mass spectrometry (Fig. S5) with 68% yield.Design and synthesis of multivalent ARMs based on macrocyclic RGD peptides
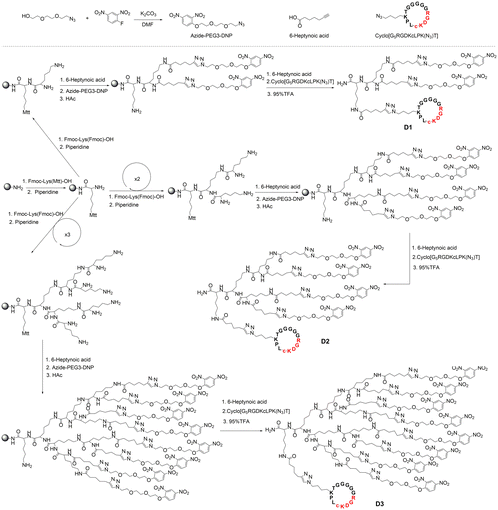
In the synthesis of multivalent ARMs based on integrin ligands, rink amide resin was used as a carrier, and the multivalent ARMs were constructed with a polylysine dendrimer as the core backbone, with DNP antigens appended on the polylysine dendrimer to provide multivalency (Scheme 2). In particular, the synthesis started with the coupling of Fmoc-Lys(Mtt)-OH involved attaching protected lysine via its free carboxylic acid terminal to the amine-bearing rink amide resin. After Fmoc was removed by the piperidine base, the free amino group was condensed with Fmoc-Lys(Fmoc)-OH, which continued to remove Fmoc to form two free amino groups (D1). Four amino ARMs can be formed by accessing Fmoc-Lys(Fmoc)-OH twice (D2), and the same process applies to form octavalent amino ARMs (D3). The introduction of 6-heptynoic acid facilitated the incorporation of an alkyne group, which was subsequently coupled with the DNP structure (azide-PEG3-DNP, Fig. S6–S8) via an azide reaction. Azide-PEG3-DNP was synthesized through a nucleophilic substitution reaction involving 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene and azido-PEG3-OH in the presence of potassium carbonate. The Mtt protecting group was removed under acidic conditions, and the free amino group was accessed to 6-heptynoic acid to introduce the alkynyl group, followed by coupling of the RGD macrocyclic peptide cyclo[G5RGDKcLPK(N3)T] via an azide reaction. However, the higher generation dendrimer (D3) tended to reduce the yield of the product and make Mtt removal difficult. This effect may be related to incomplete reactions and steric hindrance stemming from the dendrimer structure.36,37 The crude peptides were purified by semi-preparative HPLC, lyophilized, and characterized using analytical HPLC (Fig. S9–S11) and MALDI combined with time-of-flight mass spectrometry (Fig. S12–S14). The characterization data of the peptide compounds are summarised in Table S1.Evaluation of tumor-specific binding and antibody recruitment
With the multivalent ARMs D1–D3, we utilized surface plasmon resonance (SPR) technology in vitro to demonstrate that D1–D3 exhibits a strong binding affinity for anti-DNP antibodies (Table S2). Next, we explored whether D1–D3 could specifically bind to tumor cells and recruit DNP antibodies via the specific integrin–RGD ligand interaction. M21 cell lines with high expression levels of αvβ3 and MCF7 cell lines with high expression levels of αvβ5 were used to evaluate tumor-specific binding and antibody recruitment abilities.38,39 Given the unavailability of human-derived anti-DNP antibodies, rabbit anti-DNP antibodies are often employed for in vitro experiments. In this study, cancer cells were incubated with either cyclic RGD peptides (cyclo[G5RGDKcLPK(N3)T]) or multivalent ARMs D1–D3 and treated with Alexa Fluor 488-tagged anti-DNP IgG antibody. The treated cells were analysed using confocal fluorescence microscopy, and the findings are presented in Fig. 1.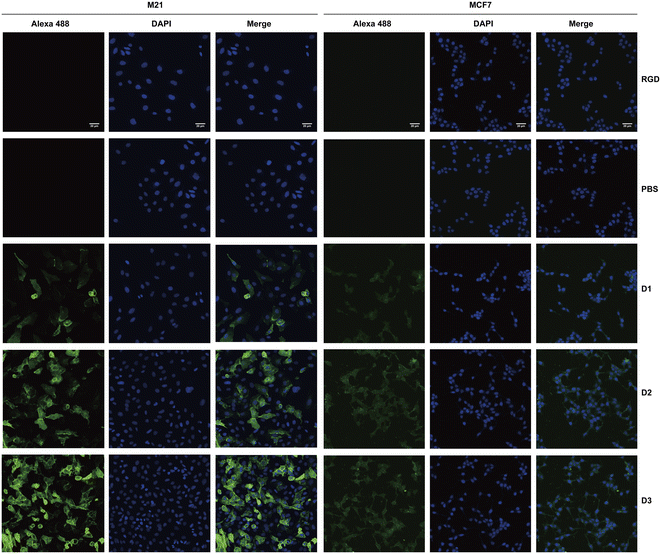 | ||
| Fig. 1 Immunofluorescence analysis of multivalent ARM-mediated tumor-specific binding and antibody recruitment. RGD:cyclo[G5RGDKcLPK(N3)T]. | ||
In this study, cyclic RGD peptide treatment served as the control group, where no green fluorescence signal was detected, suggesting that only the DNP-modified RGD cyclic peptide specifically attracted anti-DNP antibodies to the target cells. Conversely, in the experimental group treated with the cyclic RGD peptide conjugated with multivalent DNP antibody-recruiting molecules (D1, D2, and D3), remarkable green fluorescence signals were observed in the M21 cells, whereas the MCF7 cells exhibited weak fluorescence intensity. This observation indicates that the multivalent DNP antibody-recruiting molecules specifically bound to the αvβ3-positive tumor cells, but their binding affinity was reduced in the αvβ5-expressing tumor cells. Furthermore, an increase in DNP valence was positively correlated with the fluorescence intensity in M21 cells, suggesting that the binding efficiency of the anti-DNP antibody can be effectively enhanced by augmenting the DNP structure.
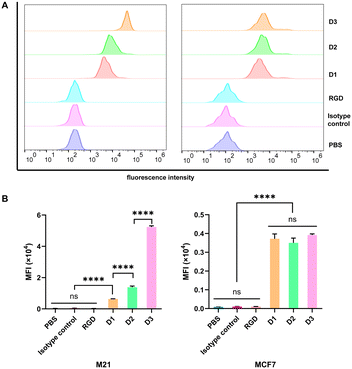
The aforementioned conclusion was further validated through flow cytometry experiments (Fig. 2 and S15). The flow histograms, obtained after treating various tumor cells with polyvalent DNP antibody-recruiting molecules (D1, D2, and D3), demonstrated a marked enhancement in fluorescence signals for the M21 cells. Specifically, the average fluorescence intensities for the M21 cells were 0.63 × 104, 1.38 × 104, and 5.23 × 104, which correspond to 27.3-fold, 60-fold, and 227.7-fold increments, respectively, compared with the control group (P < 0.0001). This fluorescence enhancement was highly correlated with the increasing valency of the DNP antibody-recruiting molecules, indicating a substantial improvement in their antibody-recruiting capability. By contrast, the MCF7 tumor cells exhibited only moderate fluorescence enhancement under identical treatment conditions, with average fluorescence intensities of 0.37 × 104, 0.34 × 104, and 0.39 × 104, which were 37.2, 34.9, and 39.1 times that of the control, respectively. However, in the MCF7 cells, no statistically significant differences were observed among the three treatments. To further demonstrate that the fluorescence intensity observed in MCF7 cells was not due to lower expression of αvβ5, flow cytometry assay was used for a quantitative assessment of αvβ3 and αvβ5 expression levels in M21 and MCF7 cells, respectively. The analysis indicated no significant difference in expression between the two cell lines (Fig. S16). Furthermore, in vitro cell adhesion assays demonstrated that D1–D3 exhibited a markedly higher binding affinity for αvβ3-positive cells compared to αvβ5-positive cells (Table S3). Therefore, these results reveal that multivalent DNP antibody-recruiting molecules D1, D2, and D3 exhibit specific binding affinity to αvβ3-expressing tumor cells and effectively recruit anti-DNP antibodies.
Evaluation of ADCC and CDC induced by the multivalent ARMs (D1, D2, and D3)
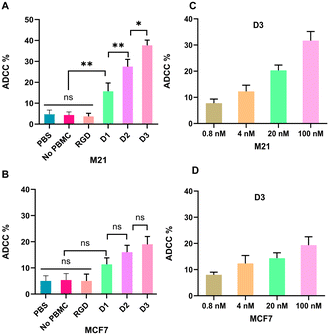
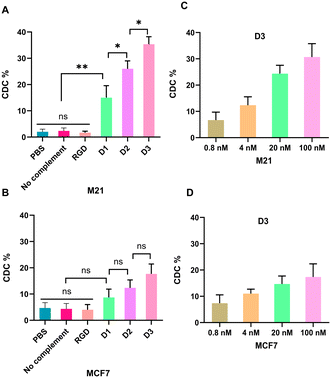
The Fc region of antibodies is critical in tumor immunotherapy because it facilitates binding to Fc receptors on the membranes of effector cells or complementary components within the immune system. This interaction subsequently activates ADCC or CDC, leading to the destruction of tumor cells. In this study, M21 or MCF7 cells were initially incubated with varying concentrations of these multivalent molecules and anti-DNP antibodies to determine if multivalent ARMs can induce tumor cell death via ADCC activation. Effector cells isolated from human blood were introduced, and cell death was quantified using a lactate dehydrogenase assay kit. As illustrated in Fig. 3, the three multivalent ARMs demonstrated remarkable cell lysis in the M21 cells, whereas the control RGD cyclic peptide did not exhibit such an effect (Fig. 3A). Although some cell lysis was observed in the MCF7 cells, the overall cytotoxic effect was less pronounced compared with that on the M21 cells, with the maximum lysis rate in the MCF7 cells reaching only 19% (Fig. 3B). These findings suggest that the multivalent ARMs effectively target tumor cells by binding specifically to αvβ3 integrins, thereby inducing ADCC. Furthermore, ADCC-mediated cytotoxicity was markedly enhanced by the increase in the number of DNP units within the multivalent ARMs in the M21 cells, whereas the cytotoxic effect was less potent in the MCF7 cells. This finding indicates that the multivalent DNP structure substantially augments tumor cell-killing efficacy via ADCC. Additionally, the multivalent ARM D3, containing eight DNP antigenic structures, exhibited a pronounced concentration-dependent cytotoxic effect on M21 cells within a concentration range of 0.8 nM to 100 nM, as compared to its effect on MCF7 cells (Fig. 3C and D).In the experiments conducted on CDC, M21 and MCF7 cells were incubated with varying concentrations of multivalent ARMs and anti-DNP antibodies, followed by exposure to rabbit complement. The cytotoxic effects were assessed via CCK8 assay. As depicted in Fig. 4, much higher cytotoxicity was observed in the M21 cells compared with the MCF7 cells. Specifically, the mortality rates for D1–D3 in the M21 cells were 15%, 26%, and 35.3%, respectively, whereas in the MCF7 cells, the rates were 8.6%, 12.3%, and 17.6%, respectively (Fig. 4A and B). Conversely, the control group treated with the RGD cyclic peptide did not exhibit remarkable cytotoxic effects. These findings suggest that the multivalent ARMs can mediate specific cytotoxic effects on M21 cells through CDC by recruiting anti-DNP antibodies to form complement complexes. Furthermore, in the M21 cells, the CDC-mediated cytotoxicity of D1, D2, and D3 exhibited an enhancement proportional to the increase in the number of DNP units. This observation suggests that augmenting DNP valence can effectively amplify the CDC effect, thereby exerting substantial tumor cytotoxicity. In addition, the CDC-mediated cytotoxicity of D3 was also determined under a concentration range of 0.8 nM to 100 nM in both cell lines and a marked concentration-dependent tumor killing was observed in M21 cells (Fig. 4C and D).
In this work, the maximum lysis rate caused by ADCC was 37.6%, while the maximum mortality rates caused by CDC reached 33.5%. Extending the incubation time did not further improve efficacy. These findings were consistent with previous reports.18 However, other ARMs containing 16 Rha units and 4 cRGD have exhibited greater ADCC and CDC efficacy.40 This discrepancy may be attributed to the intrinsic properties of the ARMs.
Conclusions
In this study, multivalent ARMs modified with integrin-specific binding macrocyclic RGD peptides and multiple units of DNP haptens were successfully synthesized using a combination of SPPS and a chemoenzymatic cyclisation approach. These molecules could selectively recognize and bind to integrin αvβ3-positive tumor cells through the RGD cyclic peptides. This binding facilitated the recruitment of anti-DNP antibodies, inducing tumor cytotoxicity via ADCC or CDC. Notably, the efficacy of antibody recruitment and the resultant tumor cytotoxicity depended on the number of DNP units present in the multivalent ARMs. The molecules with high valence of DNP units could substantially enhance the antibody recruitment ability and tumor toxicity effect, indicating a multivalent effect associated with integrin receptor-targeted DNP multivalent ARMs. However, further work could explore the effect of different linkers on the activity of multivalent ARMs and the production yield of dendrimers at high generation. Given the variability in integrin receptor expression among different individuals, the synthesized DNP-based multivalent ARMs with an integrin receptor-specific binding capability offer a flexible strategy for tumor immunotherapy.Author contributions
The manuscript was written through contributions of all authors. All authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript. Xiaozhong Cheng: writing, methodology, conceptualization, and funding acquisition. Chenrui Hu and Wanru Gao: synthesis. Yajun Chen: evaluation of activity. Wei Wang and Guilan Zhu: data analysis. Zhimeng Wu: writing – review & editing and supervision.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Data availability
Supplementary information (SI) related to this article can be found in the online version. Supplementary information: enzyme expression, synthetic details, experimental methods and supporting figures. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d5md00879d.Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation (2208085MH258) and partly funded by the Foundation of Anhui Educational Committee (2024AH051586) and Anhui Engineering Laboratory for Medicinal and Food Homologous Natural Resources Exploration (YSTY2022029).References
- C. G. Parker, R. A. Domaoal, K. S. Anderson and D. A. Spiegel, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 16392–16394 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. P. Murelli, A. X. Zhang, J. Michel, W. L. Jorgensen and D. A. Spiegel, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131, 17090–17092 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. J. McEnaney, C. G. Parker, A. X. Zhang and D. A. Spiegel, ACS Chem. Biol., 2012, 7, 1139–1151 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- W. Z. Charles, C. R. Faries, Y. h. T. Street, L. S. Flowers and B. R. McNaughton, ChemBioChem, 2022, 23, e202200092 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. E. Jakobsche, C. G. Parker, R. N. Tao, M. D. Kolesnikova, E. F. Douglass Jr and D. A. Spiegel, ACS Chem. Biol., 2013, 8, 2404–2411 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. K. Hossain, A. Vartak, P. Karmakar, S. J. Sucheck and K. A. Wall, ACS Chem. Biol., 2018, 13, 2130–2142 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- K.-S. Ju and R. E. Parales, Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev., 2010, 74, 250–272 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Lake, N. Serniuck, E. Kapcan, A. Wang and A. F. Rullo, ACS Chem. Biol., 2020, 15, 1089–1095 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Achilli, N. Berthet and O. Renaudet, RSC Chem. Biol., 2021, 2, 713–724 RSC.
- K. Karjalaninen and O. Mäkelä, Eur. J. Immunol., 1976, 6, 88–93 CrossRef PubMed.
- E. Ortega, M. Kostovetzky and C. Larralde, Mol. Immunol., 1984, 21, 883–888 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Uvyn and B. G. De Geest, ChemBioChem, 2020, 21, 3036–3043 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Li, H. Lin, H. Hong, D. Li, L. Gong, J. Zhao, Z. Wang and Z. Wu, Adv. Sci., 2024, 11, 2307613 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Hong, Y. Li, D. Li, H. Lin, J. Zhao, Z. Wang and Z. Wu, Chin. J. Chem., 2025, 43, 46–52 CrossRef CAS.
- L. Zheng, Y. Li, H. Lin, H. Hong, J. Shi, Z. Zhou and Z. Wu, Synthesis, 2024, 56, 999–1006 CrossRef CAS.
- B. Liet, E. Laigre, D. Goyard, B. Todaro, C. Tiertant, D. Boturyn, N. Berthet and O. Renaudet, Chem. – Eur. J., 2019, 25, 15508–15515 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Uvyn, R. De Coen, M. Gruijs, C. W. Tuk, J. De Vrieze, M. van Egmond and B. G. De Geest, Angew. Chem., 2019, 131, 13122–13127 CrossRef.
- H. Lin, K. Zhou, D. Li, H. Hong, Y. Xie, L. Gong, Y. Shen, Z. Zhou, J. Shi and Z. Wu, ChemMedChem, 2021, 16, 2960–2968 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Hong, K. Zhou, H. Lin and Z. Wu, J. Carbohydr. Chem., 2025, 44, 31–42 CrossRef CAS.
- B. P. Lake, R. G. Wylie, C. Bařinka and A. F. Rullo, Angew. Chem., 2023, 62, e202214659 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. C. Tucker, Curr. Opin. Invest. Drugs, 2003, 4, 722–731 CAS.
- L. Zhao-He, Z. You, D. You-Xiang, G. Qing-Long and Z. Li, Chin. J. Nat. Med., 2019, 17, 241–251 Search PubMed.
- R. Slack, S. Macdonald, J. Roper, R. Jenkins and R. Hatley, Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery, 2022, 21, 60–78 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Van der Flier and A. Sonnenberg, Cell Tissue Res., 2001, 305, 285–298 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. O. J. C. Hynes, Cell, 1992, 69, 11–25 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Jin and J. Varner, Br. J. Cancer, 2004, 90, 561–565 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Liu, F. Wang and X. Chen, Drug Dev. Res., 2008, 69, 329–339 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Rathinam and S. K. Alahari, Cancer Metastasis Rev., 2010, 29, 223–237 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- H. Liapis, A. Flath and S. Kitazawa, Diagn. Mol. Pathol., 1996, 5, 127–135 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Wang, X. Wang, Y. Zhang, S. Yang, J. Wang, X. Zhang and Q. Zhang, J. Drug Targeting, 2009, 17, 459–467 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Felding-Habermann, E. Fransvea, T. E. O'Toole, L. Manzuk, B. Faha and M. Hensler, Clin. Exp. Metastasis, 2002, 19, 427–436 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- F. Danhier, A. Le Breton and V. Préat, Mol. Pharmaceutics, 2012, 9, 2961–2973 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. R. Cooper, C. H. Chay and K. J. Pienta, Neoplasia, 2002, 4, 191–194 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Z. Wu, X. Cheng, H. Hong, X. Zhao and Z. Zhou, Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2017, 27, 1911–1913 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- X. Cheng, C. Li, H. Hong, Z. Zhou and Z. Wu, RSC Med. Chem., 2025, 16, 3077–3083 RSC.
- S. Svenson, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2015, 44, 4131–4144 RSC.
- A. Y.-T. Huang, C.-L. Kao, A. Selvaraj and L. Peng, Mater. Today Chem., 2023, 27, 101285 CrossRef.
- R. M. Owen, C. B. Carlson, J. Xu, P. Mowery, E. Fasella and L. L. Kiessling, ChemBioChem, 2007, 8, 68–82 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- E. F. Plow, T. A. Haas, L. Zhang, J. Loftus and J. W. Smith, J. Biol. Chem., 2000, 275, 21785–21788 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- B. Todaro, S. Achilli, B. Liet, E. Laigre, C. Tiertant, D. Goyard, N. Berthet and O. Renaudet, Biomater. Sci., 2021, 9, 4076–4085 RSC.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2026 |