Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleMultiTaskDeltaNet: change detection-based image segmentation for operando ETEM with application to carbon gasification kinetics
Yushuo
Niu
 a,
Tianyu
Li
a,
Tianyu
Li
 b,
Yuanyuan
Zhu
b,
Yuanyuan
Zhu
 b and
Qian
Yang
b and
Qian
Yang
 *a
*a
aSchool of Computing, University of Connecticut, Storrs, CT, USA. E-mail: qyang@uconn.edu
bDepartment of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Connecticut, Storrs, CT, USA
First published on 11th November 2025
Abstract
Transforming in situ transmission electron microscopy (TEM) imaging into a tool for spatially-resolved operando characterization of solid-state reactions requires automated, high-precision semantic segmentation of dynamically evolving features. However, traditional deep learning methods for semantic segmentation often face limitations due to the scarcity of labeled data, visually ambiguous features of interest, and scenarios involving small objects. To tackle these challenges, we introduce MultiTaskDeltaNet (MTDN), a novel deep learning architecture that creatively reconceptualizes the segmentation task as a change detection problem. By implementing a unique Siamese network with a U-Net backbone and using paired images to capture feature changes, MTDN effectively leverages minimal data to produce high-quality segmentations. Furthermore, MTDN utilizes a multi-task learning strategy to exploit correlations between physical features of interest. In an evaluation using data from in situ environmental TEM (ETEM) videos of filamentous carbon gasification, MTDN demonstrated a significant advantage over conventional segmentation models, particularly in accurately delineating fine structural features. Notably, MTDN achieved a 10.22% performance improvement over conventional segmentation models in predicting small and visually ambiguous physical features. This work bridges key gaps between deep learning and practical TEM image analysis, advancing automated characterization of nanomaterials in complex experimental settings.
1 Introduction
Operando transmission electron microscopy (TEM) has recently emerged as a transformative technique in materials characterization by enabling in-depth investigations into the kinetics and mechanisms of structural, morphological, and phase transformations.1–3 Building on in situ TEM, operando TEM simultaneously measures material functionality (e.g., phase transformation reactivity) alongside in situ imaging, thereby facilitating quantitative correlations between microstructural evolution and reaction kinetics. Specifically, for gas–solid reactions studied using operando environmental TEM (ETEM),4in situ reactivity measurements are often performed by monitoring reactant and product gases or solid phases using auxiliary mass spectrometry (MS),5,6 electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS),7,8 or selected area electron diffraction (SAED).9,10 One of the grand challenges in operando ETEM studies is the difficulty in precisely correlating spatiotemporal structural changes with their corresponding reaction kinetics.1 While the current spatial and temporal resolutions of in situ imaging employed in conventional TEM are sufficient to capture microstructural evolution at the nanoscale for a broad range of solid-state reactions such as nanomaterials nucleation, growth, oxidation and reduction, operando ETEM employing conventional spectroscopic or diffraction techniques provides only an averaged in situ reactivity measurement. Consequently, these techniques lack the spatial resolution required to reliably connect reaction kinetics with the microstructural evolution of individual nanostructures, which often exhibit size or structural heterogeneities.Semantic segmentation—a pixel-level classification task in computer vision11—is well-suited for quantifying temporal changes in feature size from in situ ETEM videos. In our previous studies of nanostructure phase transformations, manual segmentation allowed us to obtain spatially-resolved reaction kinetics, providing unprecedented insights into size-dependent oxidation of Ni nanoparticles,10 quantitative comparison of competing reaction pathways during filamentous carbon gasification,12,13 and unexpected irradiation-decelerated tungsten nanofuzz oxidation that challenges conventional understanding.14 However, manual segmentation is labor-intensive and limits scalability, thereby calling for automated approaches to enhance statistical power and standardization.
Recent advances in deep learning, particularly convolutional neural networks (CNNs) including U-Net and transformer-based architectures such as Vision Transformer (ViT), have revolutionized segmentation tasks in many fields.11,15–31 However, segmentation of microscopy videos remains challenging due to limited annotated datasets, complex image features that differ significantly from natural images in texture and scale, and the presence of small and/or ambiguous objects.32 Foundation models such as the Segment Anything Model (SAM)33 offer zero-shot segmentation but struggle to generalize to scientific domains without extensive domain-specific data for fine-tuning or high-quality prompts.34–37 Self-supervised learning methods such as SimCLR and Barlow Twins can help address labeled data scarcity38–40 but also require large amounts of unlabeled data to be effective, especially for segmenting complex images.41–43
To develop automated and reliable segmentation models for microscopy videos, we adopt operando ETEM gasification of filamentous carbon as a model system to identify the specific challenges and current domain needs. Understanding filamentous carbon gasification is critical for gaining fundamental insights into catalyst regeneration mechanisms, enabling the development of more effective strategies to restore catalyst activity from coking, which is the leading cause of deactivation in thermal heterogeneous catalysis.44 As shown in Fig. 1a, microelectromechanical system (MEMS)-based ETEM experiments were conducted to emulate high-temperature carbon gasification under industrially relevant air-like conditions. An in situ ETEM video captured the dynamic behavior and gradual removal of over 100 filamentous carbon, revealing complex gasification phenomena involving three competing reaction pathways.13 For example, the classic catalytic gasification pathway is presented in Fig. 1a. Although combining built-in mass spectrometry (MS) with in situ ETEM observations provides viable operando characterization, MS measures the total gas products at the ETEM cell outlet, yielding only an averaged gasification kinetic measurement across mixed filamentous carbon sizes and reaction pathways. Therefore, a spatially-resolved method is needed to measure individual filament-level (i.e. filament-specific) gasification kinetics and thus deconvolute the mixed contributions, enabling quantitative comparison among the three gasification pathways.
Three main challenges hinder automated segmentation in this domain. First, there is currently no open-source benchmark database of professionally annotated in situ (E)TEM videos. Often, only a limited set of ground-truth labeling data specific to particular nanostructures and reactions is available for machine learning model training. This creates a “small data” problem for training deep learning-based models, which typically need large, pixel-level annotated datasets that are labor-intensive and require domain expertise to obtain.45
Second, to facilitate spatially-resolved reaction kinetics extraction from in situ ETEM videos, segmentation focuses on ‘reactivity descriptors’ of nanostructures rather than apparent image features. In this case (Fig. 1b), following the convention in dedicated ex situ gasification kinetic tests,46 filamentous carbon volume should be quantified as a function of gasification reaction time. This requires segmentation of two ‘reactivity descriptors’: A1 (the entire carbon projection area) and A2 (the hollow core area) of the multiwall carbon nanotube (MWCNT)-like filamentous carbon observed in this spent Ni catalyst,12 which are then used to quantify volume changes using an area-to-volume conversion (Fig. 1b). The visual similarity of A2 to the background is challenging for general-purpose segmentation models.
Third, segmentation tasks in this domain unavoidably involve “small objects”47—whether emerging reaction products that start small at early reaction stages (e.g., MWCNT growth) or solid reactants such as filamentous carbon, which become increasingly small towards the end of the reaction. This is particularly challenging for our ‘reactivity descriptor’ A2, as it begins as a small object.
Finally, additional complications, including overlapping nanostructures and feature blur due to rapid motion, further complicate segmentation. While physics-based machine learning models have been proposed as an attractive approach, they hinge on validated, known kinetic models that are frequently unavailable or untested at the nanoscale.10
To address these challenges in quantifying object evolution in microscopy video data, especially object size, we introduce MultiTaskDeltaNet (MTDN), a deep learning model tailored for filamentous carbon segmentation in ETEM videos. The key innovation of MTDN is to reframe the segmentation problem as a change detection task, by leveraging a Siamese architecture with pairwise data inputs to augment limited training data and improve generalization. A lightweight backbone, combined with pre-training and fine-tuning strategies, ensures efficiency while maintaining high performance. The model also employs a multi-task learning framework to simultaneously segment both reactivity descriptors A1 and A2, using their spatial and structural correlation to boost accuracy, especially for the more challenging A2 region. This approach is the first, to our knowledge, to robustly segment both filament areas in 1-bar ETEM videos, enabling operando analysis of carbon gasification kinetics.
2 Method
In the following sections, we will describe how the dataset is processed to enable reframing of segmentation as a change detection task, as well as the corresponding MultiTaskDeltaNet model architecture.2.1 Dataset
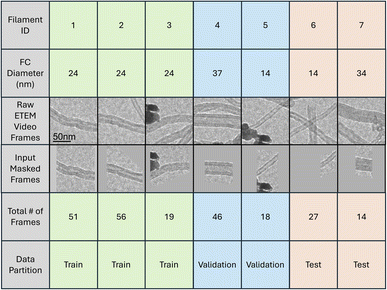
While the annotation was performed jointly by two experienced researchers to ensure consistency, we acknowledge that this may introduce some annotation bias. The relatively small number of annotated frames and filaments could limit statistical robustness. To mitigate these concerns, we performed leave-one-filament-diameter-out cross-validation, confirming consistent model performance across varying filament sizes (see SI Table S2).
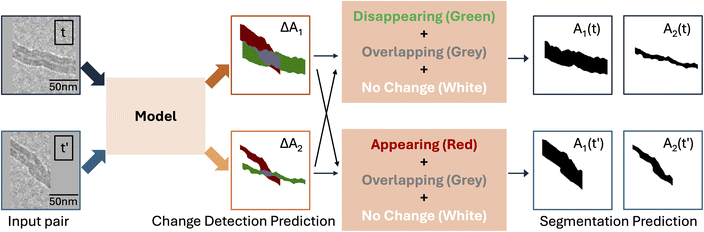
Here, we use labeled ETEM video frames from our dataset to create a change detection dataset, consisting of pairs of frames and the corresponding pixel-wise segmentation label. We consider all pairs of frames of the same filament at different reaction time steps, t and t′. For each pair (Fig. 3), the segmentation label categorizes pixels into one of four categories for each of i ∈ {1, 2} corresponding to the reactivity descriptors A1 and A2:
Category “appearing”, if a pixel is present in Ai(t′) but not in Ai(t).
Category “disappearing”, if a pixel is present in Ai(t) but not in Ai(t′).
Category “overlapping”, if a pixel is present in Ai(t) in both frames.
Category “no change”, if none of the above conditions apply. These correspond to background pixels that remain in the background.
As each frame contains two segmentation labels for two different areas, there are two change detection labels for each frame pair, which we refer to as ΔA1 and ΔA2. These change detection labels ΔAi can be computed directly from the original frame labels Ai(t) and Ai(t′) without any further manual labeling.
Converting our original labeled frame dataset to a pairwise change detection dataset naturally expands the effective size of the dataset, as shown in Table 1. This is particularly valuable in low-data environments where manual labeling is costly. Additionally, our pairwise method introduces an implicit regularization effect. The same piece of carbon filament captured at different time steps may exhibit slight variations in size, shape, and position. This variability helps prevent the model from overfitting to specific time step conditions and improves its generalization across various sequences of carbon filament frames. Pairing frames from different time steps within the same region instead of across regions is important, however, to ensure that the model is focused on capturing subtle changes to the object of interest rather than variations in filament diameter and other environmental differences.
| Dataset | Original | Pairwise |
|---|---|---|
| Training | 126 | 2968 |
| Validation | 64 | 1188 |
| Test | 41 | 442 |
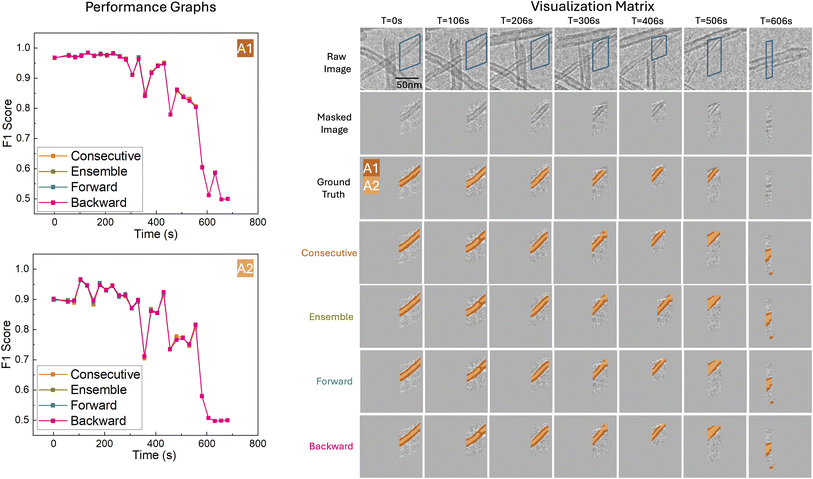
During testing, various methods are possible for transforming a change detection prediction to an image segmentation prediction for a particular time t. All methods require inputting two frames from the same filament to the change detection model. The first method is the forward transformation, where each frame is paired with the first frame in time for the same filament. The second method is the backward transformation, which pairs each frame with the last frame in time. The third method is consecutive transformation, where each frame is paired with the next consecutive frame in time. Lastly, the ensemble transformation involves pairing each frame with all other frames corresponding to the same filament, and averaging over the predictions: 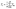 , where Tin is the transformation based on the pair of frames img(Ti) and img(Tn). Note that self-pairs are included in each of the methods above, allowing the model to be trained with examples of no change. We collectively call these methods prediction fusion methods.
, where Tin is the transformation based on the pair of frames img(Ti) and img(Tn). Note that self-pairs are included in each of the methods above, allowing the model to be trained with examples of no change. We collectively call these methods prediction fusion methods.
2.2 Siamese network architecture
As shown in Fig. 5, our MultiTaskDeltaNet model consists of two main components: a Siamese architecture based on U-Net branches (although this backbone can be varied), and a set of fully convolutional layers (FCN) for the final change mask generation for each task. The model takes as input a pair of carbon gasification frames from the same region at times t and t′. The Siamese architecture features two U-Net branches that share an identical architecture and weights, and first extracts feature maps (fm(t) and fm(t′)) from each frame. These feature maps are then concatenated, and each FCN then processes the merged features to generate the final change detection output ΔA1 and ΔA2, respectively.We employ pre-training to enhance model performance by training a U-Net model with the same architecture as the backbone of the MTDN branches. This U-Net takes one labeled image frame of filament gasification as its input, and its output is the corresponding segmentation label.
2.3 Training objective
Our model employs focal loss53 as the loss function to deal with the imbalance in change detection datasets between easy-to-classify background pixels and the smaller number of foreground pixels where changes may occur. The focal loss is a modification of the standard cross-entropy loss designed to address the class imbalance problem. It allows the model to concentrate more on the hard-to-classify and underrepresented classes while giving less attention to the majority of easily classified classes. The equation for the focal loss is as follows: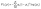 | (1) |
2.4 Implementation details
Model training was carried out on a Linux system, using Python 3.12, PyTorch 2.0, and CUDA 11.7. The hardware setup included an Nvidia GeForce A5000 GPU. During training, the input image size is set to 256 × 256. For data augmentation, we use vertical and horizontal flips, rotations, image cropping, blurring, and color jittering. The optimizer used is AdamW with β1 at 0.9, β2 at 0.999, and a weight decay of 0.01. The learning rate scheduler decreases the learning rate linearly throughout the training epochs. The default number of epochs is 500, with an early stopping mechanism in place. The learning rate and batch size are determined through hyperparameter tuning using Ray Tune,54 with the chosen values being 0.00095 for the learning rate and 16 for the batch size.3 Results
We compare our results across four models: U-Net,17 which is lightweight and the most commonly used segmentation model in scientific applications such as biomedical image analysis; our MTDN model trained from scratch, with U-Net as the backbone of its Siamese branches; and two variations of MTDN that initialize training with different pre-trained U-Net weights. All versions of MTDN are designed for change detection, and the simple transformation described in Section 2.1.4 is applied to convert the change detection results into corresponding segmentation results. For comparison, the U-Net baseline processes single frames to directly produce segmentation masks and does not use paired-frame or change-detection inputs. Consequently, all performance metrics are based on the final segmentation results.3.1 Evaluation metrics
We use several evaluation metrics to quantitatively assess our model performance on the segmentation problem. For similarity measures, we include the F1 (Dice) score and Intersection over Union (IoU). These metrics are denoted with an upward arrow (↑) to indicate that higher values represent better performance. The equations for the F1 Score and IoU are as follows: | (2) |
 | (3) |
The final F1 score we report is the macro-averaged F1 score, which computes the F1 score for each class individually and then takes a simple average across classes. Note that since we are only evaluating the final segmentation performance, there are only two classes for each reactivity descriptor, where the positive class corresponds to A1 (or A2), and the negative class corresponds to background. We report the macro-F1 score for A1 and A2 separately.
3.2 Quantitative results
Tables 2 and 3 compare the performance of our MTDN model and U-Net in predicting the reactivity descriptors A1 and A2 for the test set filaments 6 and 7 (recall Fig. 2). The best performance in each metric is indicated in bold.| Model | A 1 prediction | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 score (dice score) ↑ | IoU (intersection over union) ↑ | |||||
| Filament ID 6 | Filament ID 7 | Test total | Filament ID 6 | Filament ID 7 | Test total | |
| U-Net | 0.90293 | 0.97206 | 0.94102 | 0.83593 | 0.94673 | 0.89361 |
| MTDN | 0.91675 | 0.96746 | 0.94470 | 0.85614 | 0.93844 | 0.89964 |
| Model | A 2 prediction | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F1 score (dice score) ↑ | IoU (intersection over union) ↑ | |||||
| Filament ID 6 | Filament ID 7 | Test total | Filament ID 6 | Filament ID 7 | Test total | |
| U-Net | 0.76477 | 0.7597 | 0.76276 | 0.67606 | 0.66955 | 0.67357 |
| MTDN | 0.85717 | 0.8211 | 0.84080 | 0.77654 | 0.73349 | 0.75665 |
The reactivity descriptor A2 is significantly more challenging than A1 to segment due to its small size and visual similarity to the background. Therefore, improving the prediction performance of A2 is a key focus of our work. MTDN consistently and significantly outperforms U-Net across both metrics (F1 score and IoU), achieving a 10.22% improvement in F1 score and a 12.34% improvement in IoU for total A2 prediction. The most notable improvements are seen in IoU, which indicate that MTDN captures object boundaries with greater precision and achieves better overlap with ground truth labels. By contrast, traditional methods such as U-Net perform similarly to our MTDN model on the more straightforward A1 prediction, although MTDN still achieves a slightly higher total test performance. Despite the complexity of reactivity descriptor A2, we show in SI Table S1 that it is possible to reduce the training dataset by 40% (from 126 to approximately 76 images) while still achieving a Dice score of around 0.8, and the training dataset can be reduced by 50% while achieving the same performance as a U-Net model trained on the full dataset. These results suggest that our method might also potentially be applied effectively in other imaging modalities, such as atomic force microscopy or scanning tunneling microscopy, where acquiring large labeled datasets is more difficult.
To place these quantitative results in context, we consider the range of IoU values reported by other works attempting similar segmentation tasks on related types of TEM data. Recently, Yao et al.55 demonstrated that U-Net models trained on simulated liquid-phase TEM data could effectively extract dynamic nanoparticle features from noisy video sequences. They report an optimal IoU of approximately 0.92 for high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) images (dose rate = 10 e−·Å−2 s−1) and 0.90 for low SNR images (dose rate = 1 e− Å−2 s−1). However, their datasets consist of high-contrast and relatively simple morphologies, even under low SNR conditions. Similarly, Lu et al.45 proposed a semi-supervised segmentation framework for high-resolution TEM images of protein and peptide nanowires. With only eight labeled images per class, they achieved median Dice scores above 0.70 and IoU values ranging from 0.55 to 0.65 across various nanowire morphologies (e.g., dispersed, percolated). Thus, the quantitative performance of our MTDN is well within the higher range of performance on similar problems.
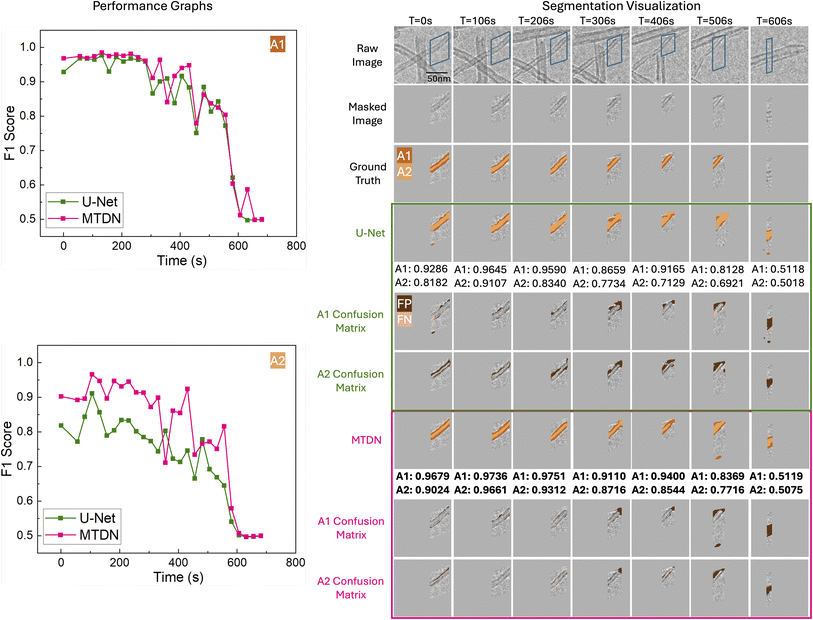
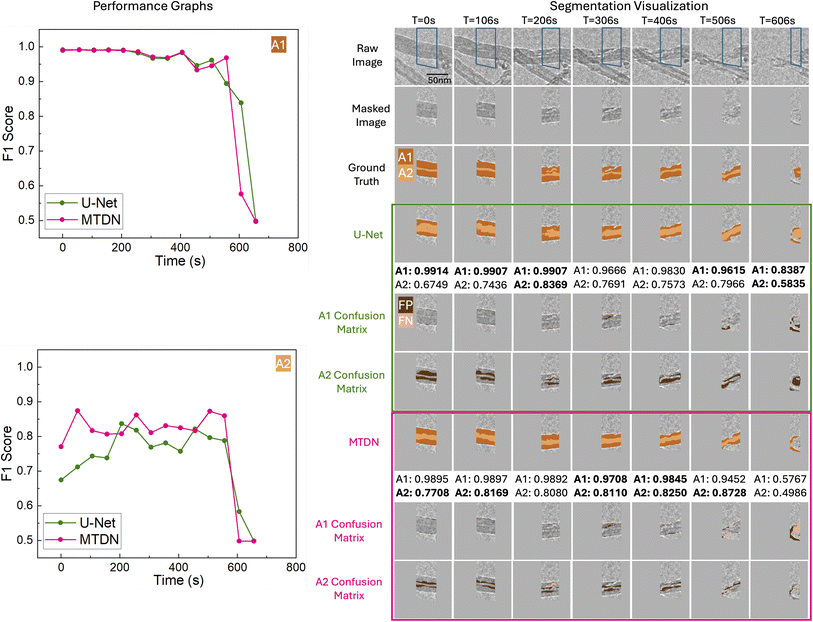
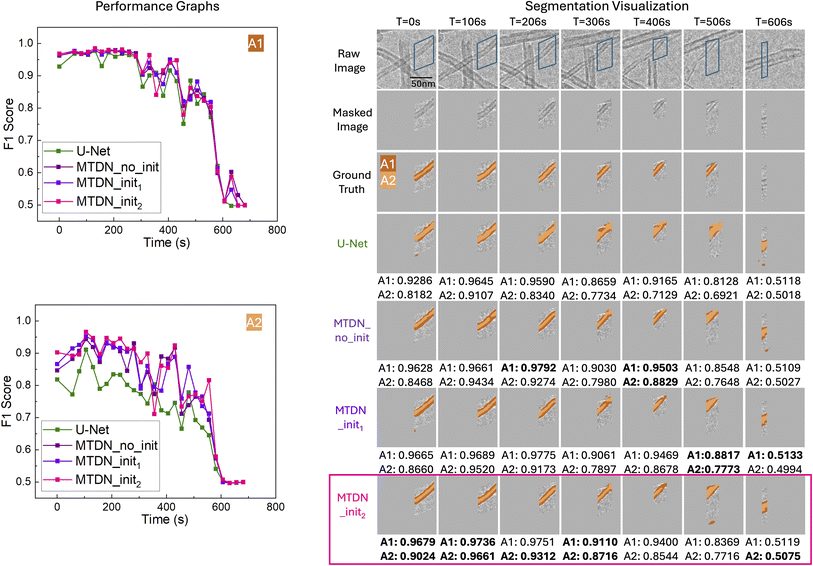
Our quantitative results highlight MTDN's advantage in segmenting smaller, more complex reactivity descriptors such as A2. To further validate the comparative performance of MTDN and U-Net on the test set, we assessed their performance on a frame-by-frame basis over time, confirming that MTDN consistently slightly outperforms U-Net on A1, and significantly outperforms U-Net on A2. These results are illustrated in Fig. 6 and 7 for Filament IDs 6 and 7, respectively. We note that both models initially achieve high F1 scores but experience a sharp decline after approximately 550 seconds. This decline occurs because A1 and A2 after 550 seconds are significantly smaller (indicating the filamentous carbon has been almost fully gasified) or almost gone, as illustrated in the Segmentation Visualization (right side of Fig. 6 and 7). Following convention, for the fully gasified A1 or A2, the F1 score of the positive class is set to 0, resulting in a much lower macro-averaged F1 score at the end of the gasification reaction.
3.3 Qualitative Results
Fig. 6 and 7 also visualize the differences between U-Net and MTDN predictions of A1 and A2 over time for Filament IDs 6 and 7. The raw frames, masked frames, ground truth, segmentation predictions, and confusion matrices are shown for timesteps spanning early, middle and late times in the ETEM carbon gasification videos. Note that in the visualized predictions, the reactivity descriptor A2 is highlighted in the lighter color, while the reactivity descriptor A1 corresponds to both the dark and light colors combined. As the filamentous carbon gasifies, segmentation becomes more challenging for all models, but MTDN continues to perform consistently better. In particular, MTDN tends to produce narrower, better predictions for A2 compared to U-Net. This suggests that MTDN reduces false positive predictions, resulting in segmentation results that are more accurate and sharper, which is critically important for the area-to-volume conversion to quantify carbon volume changes for spatially-resolved operando ETEM characterization (Fig. 1).For Filament ID 6 (Fig. 6), we observe from time step 306 s to 406 s that, compared to MTDN, U-Net is too sensitive to the differences in pixel intensity. In particular, U-Net tends to overpredict low-intensity areas as A1, whereas MTDN identifies A1 more accurately. Additionally, from time step 306 s to 506 s, we encountered an overlap problem when an overlying carbon filament moved into proximity with the target filament, preventing us from fully excluding it by masking. U-Net incorrectly identifies all the carbon filaments as part of A1. In contrast, our model accurately distinguishes between the two separate carbon filaments and to a good extent correctly predicts A1 and A2 belonging to the target filament. Finally, at time step 606 s, an additional lower carbon filament appears in the masked region, while the target filament has been completely gasified so that the ground truth label is empty. In this situation, both U-Net and MTDN fail to track the correct filaments (although visually we can see that MTDN better captures the new filament). This failure reflects not a flaw of the model, but a necessary compromise to enable filament-specific gasification kinetic measurements that deconvolute the effects of size variation and distinct reaction pathways.
In Fig. 7, we again see that MTDN consistently outperforms U-Net across the entire gasification process for Filament ID 7, both quantitatively and visually. Similarly to before, towards the end of gasification at time step 606 s, a new lower carbon filament appears while only a tiny portion of the target filament remains. U-Net tends to over-segment high-contrast areas, mistakenly identifying both carbon filaments. Meanwhile, MTDN predicts the emerging filament but omits the target one, resulting in MTDN having more false negatives than U-Net. In this instance, U-Net inadvertently achieves better quantitative results.
Overall, the analysis of filaments 6 and 7 confirms that MTDN maintains strong and stable performance in complex segmentation scenarios, especially for the challenging A2 class. Its ability to produce precise segmentations with fewer false positives and better temporal consistency highlights its robustness compared to U-Net.
While our model demonstrates robust generalization across different filament morphologies and diameters, all training and test data were acquired under consistent imaging conditions on a single ETEM instrument. Future work will investigate model robustness across varying camera settings, electron dose rates, and TEM platforms, as well as pre-training strategies to improve cross-instrument generalization.
3.4 Ablation study
In this section, we study the relative importance of various components of our MTDN model: the performance gains from our multi-task formulation, the efficacy of pre-training the U-Net branches, and various fusion methods for transforming the change detection prediction to image segmentation results.| Model | F1 score (dice score) ↑ | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A 1 prediction | A 2 prediction | |||||
| Filament ID 6 | Filament ID 7 | Test total | Filament ID 6 | Filament ID 7 | Test total | |
| U-Net (single-task) | 0.90293 | 0.97206 | 0.94102 | 0.76477 | 0.75970 | 0.76276 |
| MTDN (single-task) | 0.88336 | 0.97039 | 0.93014 | 0.81126 | 0.81154 | 0.81152 |
| MTDN (multi-task) | 0.91678 | 0.96940 | 0.94588 | 0.83740 | 0.82362 | 0.83117 |
While multi-task learning is advantageous when segmentation targets share spatial and structural correlations (as with A1 and A2), the architecture may struggle with substantially different features due to potential negative transfer. We note from Table 4 that the single-task version still substantially outperforms U-Net on the more challenging A2, demonstrating that the core benefit of MTDN derives from reframing segmentation as change detection. For applications with morphologically distinct features, we recommend using the single-task version of MTDN, which retains the advantages of change-detection-based segmentation while avoiding potential negative transfer.
We present the numerical results in Table 5 and the corresponding visualizations in Fig. 8. Our results indicate that pre-training the UNet to initialize our Siamese branches slightly enhances overall performance. Considering the overall F1 score, MTDN_init2 is the best model. This is the final MTDN model that is reported in the Quantitative and Qualitative Results sections above. It is important to note that although we have employed a U-Net backbone for our Siamese branches, the MTDN model is compatible with any state-of-the-art encoder-decoder architecture. Given the limited amount of labeled data, a lightweight backbone such as U-Net is preferred. We acknowledge that alternative architectures such as DeepLabv3 may offer different trade-offs in accuracy and computational cost. Exploring these alternatives is planned for future work.
| Model | F1 score (dice score) ↑ | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A 1 prediction | A 2 prediction | Overall | |||||
| Filament ID 6 | Filament ID 7 | Test total | Filament ID 6 | Filament ID 7 | Test total | ||
| MTDN_no_init | 0.91678 | 0.96940 | 0.94588 | 0.83800 | 0.82295 | 0.83117 | 0.88853 |
| MTDN_init1 | 0.92036 | 0.96679 | 0.94601 | 0.84970 | 0.82484 | 0.83866 | 0.89234 |
| MTDN_init2 | 0.91675 | 0.96746 | 0.94470 | 0.85717 | 0.82110 | 0.84080 | 0.89275 |
| Model | Fusion method | F1 score (dice score) ↑ | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A 1 prediction | A 2 prediction | Overall | ||||||
| Filament ID 6 | Filament ID 7 | Test total | Filament ID 6 | Filament ID 7 | Test total | |||
| MTDN_no_init | Backward | 0.91678 | 0.96940 | 0.94588 | 0.83800 | 0.82295 | 0.83117 | 0.88853 |
| Consecutive | 0.91801 | 0.96910 | 0.94638 | 0.83083 | 0.82597 | 0.82873 | 0.88756 | |
| Ensemble | 0.91699 | 0.96894 | 0.94566 | 0.83812 | 0.82491 | 0.83216 | 0.88891 | |
| Forward | 0.91798 | 0.96865 | 0.94604 | 0.83591 | 0.82599 | 0.83146 | 0.88875 | |
| MTDN_init1 | Backward | 0.92036 | 0.96679 | 0.94601 | 0.84970 | 0.82484 | 0.83866 | 0.89234 |
| Consecutive | 0.92149 | 0.96622 | 0.94627 | 0.84588 | 0.82682 | 0.83744 | 0.89186 | |
| Ensemble | 0.92042 | 0.96598 | 0.94554 | 0.84982 | 0.82704 | 0.83976 | 0.89265 | |
| Forward | 0.92163 | 0.96562 | 0.94597 | 0.84781 | 0.82685 | 0.83852 | 0.89225 | |
| MTDN_init2 | Backward | 0.91675 | 0.96746 | 0.94470 | 0.85717 | 0.82110 | 0.84080 | 0.89275 |
| Consecutive | 0.91840 | 0.96661 | 0.94512 | 0.85479 | 0.82291 | 0.84034 | 0.89273 | |
| Ensemble | 0.91677 | 0.96734 | 0.94458 | 0.85722 | 0.82107 | 0.84085 | 0.89272 | |
| Forward | 0.91738 | 0.96708 | 0.94481 | 0.85569 | 0.82105 | 0.83996 | 0.89239 | |
4 Conclusions
In this work, we introduce MTDN, a novel deep learning framework that reframes semantic segmentation as a change detection task, enabling spatially-resolved operando ETEM characterization of filamentous carbon gasification, to accelerate the fundamental understanding of catalyst regeneration. By leveraging a Siamese U-Net architecture that takes pairwise data as input, MTDN efficiently utilizes limited training data, achieving high segmentation performance on complex reactivity descriptors. Critically, our prediction fusion methods convert change detection results into image segmentations quickly and efficiently, without suffering from error accumulation and without requiring additional manual labeling. Our model also benefits from a lightweight design, enabling flexible backbone replacement and efficient training. We further employ a multi-task learning strategy to enhance the model's ability to segment the two reactivity descriptors - the outer and inner regions of the carbon filament - simultaneously.Extensive quantitative and qualitative analyses confirm that MTDN consistently outperforms traditional segmentation models such as U-Net, particularly in generalization and robustness across temporal variations and structural complexities. Ablation studies validate the impact of multi-task training, weight initialization with fine-tuning, and segmentation prediction fusion strategies, underscoring the effectiveness of our architectural and methodological choices.
Overall, MTDN accelerates the transformation of conventional in situ (E)TEM imaging into spatially-resolved operando (E)TEM characterization, by offering an automated approach to track the spatiotemporal evolution of (nano)materials with unprecedented speed, precision, and statistical rigor. This advance opens tremendous opportunities for mechanistic studies of solid-state reactions, where feature-specific reaction kinetics resolved at the nanometer scale can be directly correlated with their microstructural evolution. Looking ahead, this framework establishes a strong foundation for future research in deep learning-driven microscopy, particularly in domains where labeled data are scarce and small objects are inherently present.
Author contributions
Yushuo Niu: data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, software, validation, visualization, writing – original draft. Tianyu Li: data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, software, validation, visualization, writing – original draft. Yuanyuan Zhu: conceptualization, methodology, funding acquisition, project administration, resources, writing – review & editing. Qian Yang: conceptualization, methodology, funding acquisition, project administration, resources, supervision, writing – review & editing.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Data availability
Data and source code for this article, as well as scripts to reproduce experiments, are available in the MultiTaskDeltaNet GitHub repository archived on Zenodo at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.16415665.Supplementary information (SI) with additional experimental results is available. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d5dd00333d.
Acknowledgements
Y. N. and Q. Y. are supported by funding from the National Science Foundation under Grant No. DMR-2102406. This material is based upon work supported by the U.S. Department of Energy's Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy (EERE) under the Hydrogen and Fuel Cell Technologies Office (HFTO) Award Number DE-EE0011303. The views expressed herein do not necessarily represent the views of the U.S. Department of Energy or the United States Government. T. L. and Y. Z. are supported by the Catalysis Program, in the Division of Chemical, Bioengineering, Environmental, and Transport Systems of the United States National Science Foundation under award NSF CBET-2238213.References
- S. W. Chee, T. Lunkenbein, R. Schlögl and B. Roldán Cuenya, Chem. Rev., 2023, 123, 13374–13418 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Yang, J. Feijóo, V. Briega-Martos, Q. Li, M. Krumov, S. Merkens, G. De Salvo, A. Chuvilin, J. Jin, H. Huang, C. J. Pollock, M. B. Salmeron, C. Wang, D. A. Muller, H. D. Abruña and P. Yang, Curr. Opin. Electrochem., 2023, 42, 101403 CrossRef.
- H. Zheng, MRS Bull., 2021, 46, 443–450 CrossRef CAS.
- J. R. Jinschek, S. Helveg, L. F. Allard, J. A. Dionne, Y. Zhu and P. A. Crozier, MRS Bull., 2024, 49, 174–183 CrossRef.
- B. K. Miller and P. A. Crozier, Microsc. Microanal., 2014, 20, 815–824 CrossRef CAS.
- S. B. Vendelbo, C. F. Elkjaer, H. Falsig, I. Puspitasari, P. Dona, L. Mele, B. Morana, B. J. Nelissen, R. van Rijn, J. F. Creemer, P. J. Kooyman and S. Helveg, Nat. Mater., 2014, 13, 884–890 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Chenna and P. A. Crozier, ACS Catal., 2012, 2, 2395–2402 CrossRef CAS.
- Q. Jeangros, T. W. Hansen, J. B. Wagner, R. E. Dunin-Borkowski, C. Hébert, J. Van Herle and A. Hessler-Wyser, Acta Mater., 2014, 67, 362–372 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Yu, W. Yuan, H. Yang, Q. Xu, Y. Wang and Z. Zhang, Angew. Chem., Int. Ed., 2018, 57, 11344–11348 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. Sainju, W.-Y. Chen, S. Schaefer, Q. Yang, C. Ding, M. Li and Y. Zhu, Sci. Rep., 2022, 12, 15705 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. P. Horwath, D. N. Zakharov, R. Mégret and E. A. Stach, npj Comput. Mater., 2020, 6, 108 CrossRef.
- M. R. Nielsen, S. March, R. Sainju, C. Zhu, P.-X. Gao, S. L. Suib and Y. Zhu, Microsc. Microanal., 2023, 29, 1296–1297 CrossRef.
- M. R. Nielsen, T. Li, R. Sainju, S. March, C. Zhu, P. Gao, S. Suib and Y. Zhu, ACS Catal., 2025, 15(20), 17393–17406 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Sainju, M. Patino, M. J. Baldwin, O. E. Atwani, R. Kolasinski and Y. Zhu, Acta Mater., 2024, 278, 120282 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Long, E. Shelhamer and T. Darrell, Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2015, pp. 3431–3440 Search PubMed.
- F. Milletari, N. Navab and S.-A. Ahmadi, 2016 Fourth International Conference on 3D vision (3DV), 2016, 2016, pp. 565–571 Search PubMed.
- O. Ronneberger, P. Fischer and T. Brox, in Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2015, ed. N. Navab, J. Hornegger, W. Wells and A. Frangi, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Springer, Cham, 2015, vol. 9351 Search PubMed.
- A. Dosovitskiy, L. Beyer, A. Kolesnikov, D. Weissenborn, X. Zhai, T. Unterthiner, M. Dehghani, M. Minderer, G. Heigold, S. Gelly, J. Uszkoreit and N. Houlsby, International Conference on Learning Representations, 2021 Search PubMed.
- F. Yu and V. Koltun, 4th International Conference on Learning Representations, ICLR 2016, San Juan, Puerto Rico, May 2-4, 2016, Conference Track Proceedings, 2016 Search PubMed.
- L.-C. Chen, Y. Zhu, G. Papandreou, F. Schroff and H. Adam, Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision, ECCV, 2018, pp. 801–818 Search PubMed.
- K. He, X. Zhang, S. Ren and J. Sun, Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2016, pp. 770–778 Search PubMed.
- Z. Zhang, Q. Liu and Y. Wang, IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 15, 749–753 Search PubMed.
- G. Huang, Z. Liu, L. Van Der Maaten and K. Q. Weinberger, Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2017, pp. 4700–4708 Search PubMed.
- X. Li, H. Chen, X. Qi, Q. Dou, C.-W. Fu and P.-A. Heng, IEEE Trans. Med. Imag., 2018, 37, 2663–2674 Search PubMed.
- G. Roberts, S. Y. Haile, R. Sainju, D. J. Edwards, B. Hutchinson and Y. Zhu, Sci. Rep., 2019, 9, 12744 CrossRef.
- A. G. Howard, M. Zhu, B. Chen, D. Kalenichenko, W. Wang, T. Weyand, M. Andreetto and H. Adam, arXiv, 2017, preprint arXiv:1704.04861, DOI:10.48550/arXiv.1704.04861.
- H. Zunair and A. B. Hamza, Computers in biology and medicine, 2021, 136, 104699 CrossRef.
- S. Woo, J. Park, J.-Y. Lee and I. S. Kweon, Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision, ECCV, 2018, pp. 3–19 Search PubMed.
- O. Oktay, J. Schlemper, L. L. Folgoc, M. Lee, M. Heinrich, K. Misawa, K. Mori, S. McDonagh, N. Y. Hammerla, B. Kainz, B. Glocker and D. Rueckert, Medical Imaging with Deep Learning, 2018, https://openreview.net/forum?id=Skft7cijM Search PubMed.
- J. Chen, J. Mei, X. Li, Y. Lu, Q. Yu, Q. Wei, X. Luo, Y. Xie, E. Adeli, Y. Wang, M. P. Lungren, S. Zhang, L. Xing, L. Lu, A. Yuille and Y. Zhou, Med. Image Anal., 2024, 97, 103280 CrossRef PubMed.
- H. Cao, Y. Wang, J. Chen, D. Jiang, X. Zhang, Q. Tian and M. Wang, European Conference On Computer Vision, 2022, pp. 205–218 Search PubMed.
- M. Ziatdinov, O. Dyck, A. Maksov, X. Li, X. Sang, K. Xiao, R. R. Unocic, R. Vasudevan, S. Jesse and S. V. Kalinin, ACS Nano, 2017, 11, 12742–12752 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Kirillov, E. Mintun, N. Ravi, H. Mao, C. Rolland, L. Gustafson, T. Xiao, S. Whitehead, A. C. Berg, W.-Y. Loet al., Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference On Computer Vision, 2023, pp. 4015–4026 Search PubMed.
- M. A. Mazurowski, H. Dong, H. Gu, J. Yang, N. Konz and Y. Zhang, Med. Image Anal., 2023, 89, 102918 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. Ma, Y. He, F. Li, L. Han, C. You and B. Wang, Nat. Commun., 2024, 15, 654 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Li, M. Hu and X. Yang, Medical Imaging 2024: Computer-Aided Diagnosis, 2024, vol. 12927, pp. 749–754 Search PubMed.
- J. Wu, Z. Wang, M. Hong, W. Ji, H. Fu, Y. Xu, M. Xu and Y. Jin, Med. Image Anal., 2025, 103547 CrossRef.
- T. Chen, S. Kornblith, M. Norouzi and G. Hinton, International Conference On Machine Learning, 2020, pp. 1597–1607 Search PubMed.
- S. Lu, B. Montz, T. Emrick and A. Jayaraman, Digital Discovery, 2022, 1, 816–833 RSC.
- J. Zbontar, L. Jing, I. Misra, Y. LeCun and S. Deny, International Conference On Machine Learning, 2021, pp. 12310–12320 Search PubMed.
- S. Konstantakos, J. Cani, I. Mademlis, D. I. Chalkiadaki, Y. M. Asano, E. Gavves and G. T. Papadopoulos, Neurocomputing, 2025, 620, 129199 CrossRef.
- Z. Xie, Z. Zhang, Y. Cao, Y. Lin, Y. Wei, Q. Dai and H. Hu, 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR, 2023, 10365–10374 Search PubMed.
- A. El-Nouby, G. Izacard, H. Touvron, I. Laptev, H. Jégou and E. Grave, arXiv, 2021, preprint, arXiv:2112.10740, DOI:10.48550/arXiv:2112.10740.
- A. J. Martín, S. Mitchell, C. Mondelli, S. Jaydev and J. Pérez-Ramírez, Nat. Catal., 2022, 5, 854–866 CrossRef.
- R. Wang, S. Cao, K. Ma, Y. Zheng and D. Meng, Med. Image Anal., 2021, 67, 101876 CrossRef.
- F. Alenazey, C. G. Cooper, C. B. Dave, S. S. E. H. Elnashaie, A. A. Susu and A. A. Adesina, Catal. Commun., 2009, 10, 406–411 CrossRef CAS.
- K. Tong, Y. Wu and F. Zhou, Image Vis. Comput., 2020, 97, 103910 CrossRef.
- X. Lu, W. Wang, J. Shen, D. Crandall and J. Luo, IEEE Transactions On Pattern Analysis And Machine Intelligence, 2020, vol. 44, pp. 2228–2242 Search PubMed.
- Z. Zhang, L. Sun, L. Si and C. Zheng, 2021 IEEE 6th International Conference on Computer and Communication Systems (ICCCS), 2021, pp. 335–340 Search PubMed.
- C. Xie, H. Liu, S. Cao, D. Wei, K. Ma, L. Wang and Y. Zheng, 2021 IEEE 18th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), 2021, pp. 38–41 Search PubMed.
- Y. Niu, E. Chadwick, A. W. Ma and Q. Yang, International Conference on Computer Vision Systems, 2023, pp. 183–196 Search PubMed.
- H. Kim, B. K. Karaman, Q. Zhao, A. Q. Wang, M. R. Sabuncu and A. D. N. Initiative, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2025, 122, pp. e2411492122 Search PubMed.
- T.-Y. Lin, P. Goyal, R. Girshick, K. He and P. Dollár, Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2017, pp. 2980–2988 Search PubMed.
- R. Liaw, E. Liang, R. Nishihara, P. Moritz, J. E. Gonzalez and I. Stoica, arXiv, 2018, preprint arXiv:1807.05118, DOI:10.48550/arXiv.1807.05118.
- L. Yao, Z. Ou, B. Luo, C. Xu and Q. Chen, ACS Cent. Sci., 2020, 6, 1421–1430 CrossRef CAS.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2026 |