Heterogeneous water dynamics in hyaluronan–DPPC interfaces
Anirban
Paul
 *a and
Jaydeb
Chakrabarti
*a and
Jaydeb
Chakrabarti
 *ab
*ab
aDepartment of Physics of Complex Systems, S. N. Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences, Block-JD, Sector-III, Salt Lake, Kolkata 700106, India. E-mail: anirbanpaulhdb@gmail.com
bDepartment of Chemical and Biological Sciences and the Technical Research Centre, S. N. Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences, Block-JD, Sector-III, Salt Lake, Kolkata 700106, India. E-mail: jaydeb@bose.res.in
First published on 25th November 2025
Abstract
The synergistic interactions between hyaluronic acid (HA) and other cellular components, particularly lipids and water, play a vital role in maintaining cellular structure and function. Variations in HA concentration and chain length lead to changes in the mechanical and viscoelastic properties of diseased cells, such as those in colon cancer and osteoarthritis. Despite its biological significance, the microscopic dynamics at the HA–water and lipid bilayer interface remain poorly understood. In this study, we investigate the dynamic properties of water molecules at the interface between HA and a dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC) lipid bilayer using molecular dynamics simulations. The interfacial and hydration water exhibit non-Gaussian self van Hove functions, indicating dynamic heterogeneity. The diffusivity distributions reveal contrasts in the underlying translational and rotational dynamics between the two regions. In the diffusive interface, while the diffusion coefficients decrease with increasing HA concentration, they show only a weak dependence on HA chain length. However, the water dynamics in the subdiffusive hydration layer are largely unaffected by the presence of HA chains.
1 Introduction
A multi-component complex system often consists of coexisting regions with different relaxation time scales.1–4 Such systems show a distribution of transport coefficients corresponding to the local relaxation rates. The particles in the system get stuck in the local dynamic environment for some time and explore the entire phase space only if observed for a long enough time, exceeding the slowest relaxation in the system. Dynamic heterogeneity is a property of supercooled systems that has been well established in the literature.5 The particles in the shorter time scale show a distribution of diffusion coefficients. After a long enough time, however, the particles regain normal diffusive behaviour.4 Recent studies report heterogeneous water dynamics in various other systems other than supercooled liquids: water near organic and inorganic surfaces,1 nano-confinement6,7 and in a host of bio-molecular systems at physiological temperature, near protein molecules,8 in protein–DNA complexes,9 lipid bilayer,10–12 intrinsically disordered proteins13 and so on.Dynamic heterogeneity in a system is signaled via the self van Hove correlation function (self-vHf), G(ξ, Δt), that describes the probability distribution of displacements ξ (translation or rotation) of the particles in time interval Δt,6,14,15 the mean squared displacement (MSD) being the second moment of the self-vHf. For normal fluids with diffusive particles, the self-vHf assumes a Gaussian form.4,16 The diffusion coefficient of the particles is given by the slope of the MSD if the MSD is linear in time in the long-time limit.5 In the long-time limit, however, any information on the heterogeneous dynamics is lost. Hence, MSD is not a good marker for dynamic heterogeneity, the entire probability distribution G(ξ, Δt) is required. The self van Hove function has the advantage that it is experimentally measurable through scattering techniques.5 In the case of dynamic heterogeneity, G(ξ, Δt) is marked by deviation from Gaussian nature.4,17 The non-Gaussian self-vHf is typically interpreted as the result of a superposition of independent Gaussian diffusive processes, where the system exhibits a distribution P(Dξ) of diffusion coefficients (Dξ).4,18 This situation is also known as ‘Fickian yet non-Gaussian’ dynamics.19P(Dξ) can be computed from G(ξ, Δt) using Lucy's deconvolution formula.4,18,20
An aqueous suspension of hyaluronic acid (HA), a long-chain polyanionic glycan molecule, is present in extracellular matrices (ECM) of cells, synovial fluid, and other biological environments.21 The interaction between the aqueous HA suspension and lipids is shown to be crucial for various biological functions such as bio-lubrication,22,23 water permeation through proteins,24 and so on. The size and concentration of HA chains differ between normal and cancer cells. The HA chains are shorter near cancer cells, which may be used as a colon cancer biomarker.25,26 The variations in HA chain length lead to changes in the mechanical and viscoelastic response of the diseased cells.27–29 While the properties of bulk aqueous solutions with long HA chains have been well characterized,30–32 the studies with short HA chains near lipids, relevant for cancer cells, remain limited. In our recent studies, we have considered short HA chains near a model dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC) lipid bilayer. We have shown increased flexibility of the bilayer in the presence of HA chains.29 We have further shown that the water molecules within 5 angstrom distance from the lipid head group, namely, the hydration water molecules, are sub-diffusive both in rotation and translation.33 The water molecules beyond the hydration layer exhibit diffusive rotation and translation, which we designate as the diffusive interface.33 While earlier works11,12 on dynamical heterogeneity of water near bilayers focus on chemical confinement and translational diffusion, the full dynamical nature of the interfacial water molecules, including both translation and rotation, has not been illustrated. Since our earlier study33 shows that the diffusivities of both translational and rotational motions of water molecules are affected by the presence of a lipid bilayer and HA molecules,33 it is worth exploring the dynamical features of both translation and rotation of water molecules at the interface in the water–HA–DPPC ternary system, where both the HA and DPPC head groups are hydrophilic.
In this paper, we investigate the dynamics of water molecules near the DPPC bilayer in the presence of short HA chains using molecular dynamics simulation. Our simulation model represents an extracellular environment near a cancer cell membrane, which is typically rich in phosphatidylcholine lipids34–36 and shorter HA chains.25,26 We calculate the self van Hove functions (self-vHf) for translation GT(r, Δt) and rotation GR(ϕ, Δt). We observe non-Gaussian self-vHfs for water molecules in both the diffusive interface and the hydration layers, indicating heterogeneous dynamics. To further probe this behavior, we compute the probability distribution of diffusion coefficients from the self-vHfs.18 The diffusivity distributions reveal distinct behaviors for translational and rotational motions in the diffusive interface. The translational diffusivity is broadly distributed, while rotational diffusivity shows a sharp primary peak along with smaller secondary peaks. On the contrary, in the hydration layer, translational diffusivity displays a sharp peak at low values, suggesting localized motion, whereas rotational diffusivity exhibits multiple peaks, implying dynamic exchange among angular modes.
2 Methods
2.1 System preparation & force field details
The all-atom model of a lipid bilayer of a total of 512 dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC) molecules (256 in each leaflet) is constructed in a simulation box of size 12.45 nm × 12.45 nm × 13.0 nm using the CHARMM-GUI membrane builder module.37 The bilayer is spanned in the xy plane and the normal is along the z axis. The initial structure of hyaluronic acid is taken from RCSB PDB id 2BVK38 and it is modified in the CHARMM GUI glycan modeler39 to obtain hyaluronan monomer (HA1), pentamer (HA5) and decamer (HA10) structures. To study the effect of HA concentration on the water dynamics, we consider 10, 30, and 50 HA5 above the bilayer. To investigate the HA chain size, we consider 150 HA1, 30 HA5, and 15 HA10, where the chain sizes are different but the monomer number is the same (150). The descriptions of the systems considered in the study are given in Table 1.| System tag | HA | HA monomers | Lipids | Water | Hydration (H2O/lipid) | HA concentration (mg mL−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a HA1: HA monomer, HA5: HA pentamer, HA10: HA decamer. b Systems nHA5 = 30 and N = 5 are same. | ||||||
| n HA5 = 10 | 10 HA5a | 50 | 512 | 57![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 348 348 |
112 | 18.4 |
| n HA5 = 30 | 30 HA5 | 150 | 512 | 64![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 669 669 |
126 | 49.0 |
| n HA5 = 50b | 50 HA5 | 250 | 512 | 52![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 551 551 |
102 | 100.3 |
| N = 1 | 150 HA1a | 150 | 512 | 67![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 687 687 |
132 | 36.9 |
| N = 5b | 30 HA5a | 150 | 512 | 64![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 669 669 |
126 | 49.0 |
| N = 10 | 15 HA10a | 150 | 512 | 62![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 778 778 |
122 | 50.4 |
HA molecules are randomly placed above the bilayer using Packmol.40 Sodium ions are added for electroneutrality, and additional sodium-chloride salt is added to maintain the 150 millimolar physiological salt concentration. The interaction potential is modeled using the CHARMM36 force field,41 where the TIP3P water model is used to hydrate the system. The CHARMM36 force field parameters used in the simulation have been validated for HA–lipid systems in earlier studies.24,29,33,42
2.2 Simulation details
Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations of all the systems shown in Table 1 are performed using the GROMACS package43 with the same protocol as reported in our previous works.29,33 The water-solvated HA–DPPC systems, after energy minimization, are equilibrated through short canonical (NVT) and isothermal–isobaric (NPT) simulations using position restraints on heavy atoms. The LINCS algorithm is used to constrain all covalent bonds involving hydrogen atoms during the production runs. The final production runs are executed for 600 nanoseconds (ns) in the NPT ensemble with 1 femtosecond (fs) integration time step using the leap-frog integrator, removing all restraints. The temperature is fixed at 323 K using the Nose–Hoover thermostat with coupling constant 1 picosecond (ps).44 The choice of the temperature is made to simulate the DPPC bilayer above its phase transition temperature of 315 K.45,46 The pressure is fixed at 1 bar along the x–y plane and the z direction separately using semi-isotropic pressure coupling with the Parrinello–Rahman barostat with coupling constant 5 ps.47 The periodic boundary condition is used in all three directions. The cut-off lengths for Lennard-Jones interactions and short-range electrostatic interactions are set to 12 Å.We confirm the equilibration from the saturation of area per lipid as described in ref. 29. The static results (the density profile) are obtained from the equilibrated trajectory of the last 400 ns. To analyze the interfacial dynamics, we perform three MD production runs of 3 ns length for each case, starting from three different equilibrium configurations. The trajectories are recorded at 0.5 picosecond intervals. The results reported are averaged over the three different trajectories.33
2.3 Analysis
 | (1) |
The rotational self van Hove function is defined15,48 as
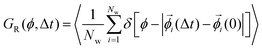 | (2) |
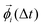 is the displacement of the i'th molecule in rotational space where
is the displacement of the i'th molecule in rotational space where 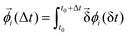 . The magnitude of
. The magnitude of 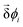 is given by cos−1[
is given by cos−1[![[small mu, Greek, circumflex]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0b3.gif) i(t)·
i(t)·![[small mu, Greek, circumflex]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0b3.gif) i(t + δt)] and its direction is given by [
i(t + δt)] and its direction is given by [![[small mu, Greek, circumflex]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0b3.gif) i(t) ×
i(t) × ![[small mu, Greek, circumflex]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0b3.gif) i(t + δt)], where
i(t + δt)], where ![[small mu, Greek, vector]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0e9.gif) i is the dipole moment of the i'th water moleucle.6,48
i is the dipole moment of the i'th water moleucle.6,48![[small mu, Greek, vector]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/i_char_e0e9.gif) i is defined as the straight line joining the oxygen atom and the center of mass of the two hydrogen atoms of the i'th water molecule. We take δt = 0.5 ps. Both GT(r, Δt) and GR(ϕ, Δt) are calculated using unfolded trajectory.
i is defined as the straight line joining the oxygen atom and the center of mass of the two hydrogen atoms of the i'th water molecule. We take δt = 0.5 ps. Both GT(r, Δt) and GR(ϕ, Δt) are calculated using unfolded trajectory.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) GT(r, Δt) as a double-Gaussian: for r < rc, −ln
GT(r, Δt) as a double-Gaussian: for r < rc, −ln![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) GT(r, Δt) = a1r2/σ12 + b1 (σ12 is the width of the central Gaussian), and for r > rc, −ln
GT(r, Δt) = a1r2/σ12 + b1 (σ12 is the width of the central Gaussian), and for r > rc, −ln![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) GT(r, Δt) = a2r2/σ22 + b2 (σ22 is the width of the Gaussian tail). We minimize the mean squared error between the simulation data and the fitted curve, χGG2, by varying the rc and the fitting parameters.49 Similarly we fit a Gaussian-exponential function: for r < rc, −ln
GT(r, Δt) = a2r2/σ22 + b2 (σ22 is the width of the Gaussian tail). We minimize the mean squared error between the simulation data and the fitted curve, χGG2, by varying the rc and the fitting parameters.49 Similarly we fit a Gaussian-exponential function: for r < rc, −ln![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) GT(r, Δt) = a1r2/σ2 + b1, and for r > rc, −ln
GT(r, Δt) = a1r2/σ2 + b1, and for r > rc, −ln![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) GT(r, Δt) = a2r/λ + b2, where λ is the decay constant of the exponential tail. Again, we minimize the mean squared error between the simulation data and the fitted curve, χGE2, by varying the rc and the fitting parameters. The fit with the lower value between χGG2 and χGE2 is chosen as the best functional fit. The same procedure is also applied to GR(ϕ, Δt) to extract the tail behavior and crossover angle ϕc. The exponent of the time dependence of rc, ϕc, σ2, and λ is obtained by averaging and estimating the error bars over three equilibrium trajectories. The error bars are computed by dividing the standard deviation of the quantity by the square root of the number of samples.
GT(r, Δt) = a2r/λ + b2, where λ is the decay constant of the exponential tail. Again, we minimize the mean squared error between the simulation data and the fitted curve, χGE2, by varying the rc and the fitting parameters. The fit with the lower value between χGG2 and χGE2 is chosen as the best functional fit. The same procedure is also applied to GR(ϕ, Δt) to extract the tail behavior and crossover angle ϕc. The exponent of the time dependence of rc, ϕc, σ2, and λ is obtained by averaging and estimating the error bars over three equilibrium trajectories. The error bars are computed by dividing the standard deviation of the quantity by the square root of the number of samples.
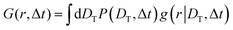 | (3) |
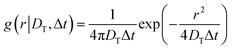 .
.
We calculate P(DT) iteratively from G(r, Δt) using Lucy's deconvolution method:18,50
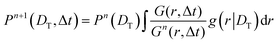 | (4) |
Here, Pn(DT) is the distribution of diffusivity obtained at the n'th iteration. The initial distribution is taken as 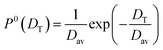 . We follow the same method to compute the probability distribution of rotational diffusivity P(DR) as well. For rotation, we consider
. We follow the same method to compute the probability distribution of rotational diffusivity P(DR) as well. For rotation, we consider  .48,51
.48,51
3 Results
The studies were carried out without HA chains, 10, 30, and 50 HA pentamers (HA5) (nHA5 = 0, 10, 30, and 50, respectively), and HA molecules of different chain lengths but the same monomer concentration: 150 HA monomer (HA1), 30 HA pentamer (HA5), and 15 HA decamer (HA10) (N = 1, 5, and 10, respectively).Fig. 1(a)–(c) show the density profiles of water, phosphorus atoms of the bilayer, and HA center of mass (com), along the bilayer normal (z-axis) and with respect to the origin at the center of the bilayer, for the HA free case (nHA5 = 0), nHA5 = 50 and N = 10, respectively. For the HA-free case in Fig. 1(a), the two peaks of the phosphorus density profile correspond to the phosphorus atoms from the upper and lower leaflets of the bilayer. The water density profile is zero inside the bilayer because of its hydrophobic core and increases to the bulk density far away from the bilayer, forming an interfacial region. The water layer within 5 Å distance from the bilayer peaks in the interface is the hydration water interacting directly with the lipid head groups. Our earlier study shows that water molecules in this layer have residence time τs = 10 ns and perform sub-diffusive translational and rotational motion until the residence time.33Fig. 1(b) and (c) show that the peak of the density profile of HA is 15 Å away from the peak of the phosphorus atoms, approximately where the density of bulk water sets in. The formation of water–bilayer and water–HA interfaces is in agreement with our previous reports.29 The water molecules beyond the hydration layer are reported to be diffusive both in translation and rotation, which we designate as the diffusive interface.33
We investigate the dynamics of the water molecules both in the subdiffusive hydration layer and the diffusive interfacial region by computing the self van Hove function (self-vHf) for translational dynamics GT(r, Δt) and rotational dynamics GR(ϕ, Δt). Here, r is the distance in two dimensions traveled by the water molecules in the lateral plane of the bilayer, and ϕ is the rotational displacement of the water dipole vectors in the time interval Δt.48 The self-vHfs are calculated while the water molecules reside in the interfacial or hydration layer. Hence Δt is restricted within the residence time of water in a particular region. We also calculate the probability distribution of diffusion coefficients from the self-vHf data.18,50
3.1 Dynamics of the diffusive interfacial water layer
First, we consider the water molecules in the diffusive interface in the HA free case. We define the time interval scaled by the residence time of the hydration water molecules, Δt* = Δt/τs. We consider GT(r, Δt*) and GR(ϕ, Δt*) for the diffusive interfacial water molecules for Δt* = 1.0 and 2.0 for the HA free case. Fig. 2(a) shows ln![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) GT(r, Δt*) vs. r data for Δt* = 1.0 and 2.0. We find that GT(r, Δt*) is double Gaussian in nature at both Δt. The crossover length rc between the two Gaussian curves, shown in Fig. 2(b), shows a sublinear dependence, indicating that the two distinct Gaussians persist up to the residence time of the interfacial water. We also find that the width of the fitted Gaussians varies linearly with Δt (inset of Fig. 2(b)), consistent with the diffusive translation. Fig. 2(c) shows the underlying distribution P(DT) derived from GT(r, Δt*) at both observation times using Lucy's deconvolution method.18,50P(DT) shows a broad distribution of DT. This is a signature of the coexistence of dynamically heterogeneous regions. P(DT) gets slightly sharper at larger Δt. The average diffusion constant 〈DT〉 (= 6.40 ± 0.07 × 10−3 nm2 ps−1), computed from P(DT) is comparable to the translational diffusion coefficient obtained from MSD data in ref. 33. This further demonstrates that MSD data in the long-time limit is averaged over dynamically heterogeneous regions.
GT(r, Δt*) vs. r data for Δt* = 1.0 and 2.0. We find that GT(r, Δt*) is double Gaussian in nature at both Δt. The crossover length rc between the two Gaussian curves, shown in Fig. 2(b), shows a sublinear dependence, indicating that the two distinct Gaussians persist up to the residence time of the interfacial water. We also find that the width of the fitted Gaussians varies linearly with Δt (inset of Fig. 2(b)), consistent with the diffusive translation. Fig. 2(c) shows the underlying distribution P(DT) derived from GT(r, Δt*) at both observation times using Lucy's deconvolution method.18,50P(DT) shows a broad distribution of DT. This is a signature of the coexistence of dynamically heterogeneous regions. P(DT) gets slightly sharper at larger Δt. The average diffusion constant 〈DT〉 (= 6.40 ± 0.07 × 10−3 nm2 ps−1), computed from P(DT) is comparable to the translational diffusion coefficient obtained from MSD data in ref. 33. This further demonstrates that MSD data in the long-time limit is averaged over dynamically heterogeneous regions.
The rotational self-vHF GR(ϕ, Δt*) in Fig. 2(d) shows the exponential tail at Δt* = 1.0 and double Gaussian form at Δt* = 2.0. The non-Gaussian GR(ϕ, Δt*) indicates dynamic heterogeneity in rotation for the interfacial waters in the diffusive layer. The crossover angle ϕc from the central Gaussian to the Gaussian tail varies sublinearly with observation time Δt, as shown in Fig. 2(e). The width of the fitted Gaussians increases linearly with Δt (inset of Fig. 2(e)). Fig. 2(f) show P(DR) at Δt* = 1.0 and 2.0. We observe a sharp peak at 〈DR〉 = 0.27 rad2 ps−1 with a very small peak at very small DR. We find that the principal peak of P(DR) gets sharper at larger observation time. The position of the sharper peak agrees well with the previous estimate from MSD data.33
Now we describe how the translational and rotational dynamics of the diffusive water layer respond to the presence of HA chains. First, we consider the nHA5 dependence. We find double Gaussian GT(r, Δt*) at Δt* = 2.0 (SI Fig. S1(a)–(c)) similar to the HA-free case. The variation of rc with time follows a sublinear dependence (SI Fig. S2(a)), while the widths of the two Gaussians σ12 and σ22 vary linearly with time (SI Fig. S2(b)) as observed in the HA-free case. The underlying distribution of diffusion coefficients P(DT) for different nHA5 is shown in Fig. 3(a). We observe that with increasing HA concentration, small peaks emerge at lower DT values, indicating that higher HA concentration reduces the translational diffusion of interfacial water molecules. SI Fig. S3 shows the average translational diffusion coefficient, 〈DT〉, for different values of nHA5. We observe that 〈DT〉 decreases linearly as nHA5 increases.
The GR(ϕ, Δt*) for the diffusive interfacial water at Δt* = 2.0 for varying nHA5 are shown in SI Fig. S4(a)–(c). We find that GR(ϕ, Δt*) is double Gaussian in nature as in the HA-free case. For all nHA5, the P(DR) distributions exhibit a prominent peak around 〈DR〉, along with smaller peaks at lower DR values. We note that the smaller peaks appear only in the presence of HA chains, suggesting the existence of water molecules with multiple rotational modes. SI Fig. S5 shows that 〈DR〉 decreases with nHA5. Hence, both translational and dynamical heterogeneity enhance with increasing HA concentration. Hence, both the translation and rotation of the water molecules become increasingly sluggish with increasing HA concentration, which is in agreement with our previous reports.33
G T(r, Δt) (SI Fig. S6(a)–(c)) and GR(ϕ, Δt) (SI Fig. S7(a)–(c)) for interfacial water molecules for different chain size N behave similarly as in the case of different HA concentration. However, P(DT) and P(DR), unlike the dependence on nHA5, show insensitivity to N as shown in Fig. 3(e) and (g) respectively. 〈DT〉 and 〈DR〉 from the respective distributions also show weak dependence on N, as described in the SI Fig. S8(a) and (b), respectively, which is in agreement with our earlier findings.33
3.2 Dynamics of hydration water
Next, we examine the dynamic property of the hydration water molecules where the translational and rotational dynamics are reported to be subdiffusive.33 Let us first consider the HA-free case. We compute the translational self-vHf GT(r, Δt*) for two observation times, namely Δt* = 0.5 and 1.0, shown in semi-log scale in Fig. 4(a). GT(r, Δt*) shows a central Gaussian followed by an exponential tail in both cases. Such exponential tails in self-vHf have been reported earlier in different soft-matter systems such as liposomal solution,4 colloids,16,52 glasses,53 and so on. This indicates the dynamic heterogeneity of the hydration water, namely, coexisting regions with different diffusion coefficients. We find in Fig. 4(b) that the cross-over distance between the central Gaussian and exponential tail, rc shows sublinear dependence. The sublinear dependence of rc means that the dynamic heterogeneity persists till the water molecules reside in the hydration layer. We also show the time variations of the width of the central Gaussian σ2 and decay length of the exponential tail λ in the inset of Fig. 4(b) both of which are sublinear. The time dependence of σ2 is consistent with the sub-diffusive behaviour observed earlier from the MSD data.33 This is in contrast with the linear dependence of the Gaussian width parameters observed in the case of diffusive interfacial water molecules. Now, we compute the normalized probability distribution of diffusivity P(DT) from GT(r, Δt*).18,50 We show data for Δt* = 0.5 and 1.0 in Fig. 4(b). A sharp peak is observed in P(DT) at a very small DT value with a long tail for both time intervals. The sharp peak at a very small DT value corresponds to dynamically arrested water molecules near the bilayer. The long tail indicates highly heterogeneous dynamics at the hydration layer.The rotational self-vHf GR(ϕ, Δt*) data in Fig. 4(d) show long exponential tails for both time intervals of Δt* = 0.5 and 1.0. The crossover angle ϕc remains unchanged with time, as shown in Fig. 4(e). The inset of Fig. 4(e) shows the time variation of σ2 of the central Gaussian and λ of the exponential tail. We find that both σ2 and λ vary sub-linearly, qualitatively similar to the translation case, and consistent with the sub-diffusive rotational motion of hydration water.33Fig. 4(f) shows the probability distributions of rotational diffusion constants P(DR). P(DR) exhibits multiple peaks of similar amplitude, unlike the diffusive water layer. The peaks at extremely small DR correspond to the water molecules that are stuck to the bilayer with little rotational freedom. However, multiple peaks imply the coexistence of slow and fast species of water molecules in this region.
Next, we show ln![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) GT(r, Δt*) vs. r data for nHA5 = 10, 30 and 50 in the SI Fig. S9(a)–(c). In the hydration layer, GT(r, Δt*) exhibits a central Gaussian with exponential tails similar to the HA free case. Moreover, the variations of rc (SI Fig. S10(a)), σ2, and λ (SI Fig. S10(b)) with time show power law dependencies as in the HA-free case. P(DT) for the two different time intervals are shown in Fig. 5(a) and (b). We observe a sharp peak at a small DT value, and a wide range of diffusivity contributes to the distribution. While HA concentration has a negligible effect on the tail of the distribution at Δt* = 0.5, the peak of P(DT) enhances at small DT value for nHA5 = 50 at Δt* = 1.0. This shows that the water molecules of the lipid hydration layer slow down at high HA concentration.
GT(r, Δt*) vs. r data for nHA5 = 10, 30 and 50 in the SI Fig. S9(a)–(c). In the hydration layer, GT(r, Δt*) exhibits a central Gaussian with exponential tails similar to the HA free case. Moreover, the variations of rc (SI Fig. S10(a)), σ2, and λ (SI Fig. S10(b)) with time show power law dependencies as in the HA-free case. P(DT) for the two different time intervals are shown in Fig. 5(a) and (b). We observe a sharp peak at a small DT value, and a wide range of diffusivity contributes to the distribution. While HA concentration has a negligible effect on the tail of the distribution at Δt* = 0.5, the peak of P(DT) enhances at small DT value for nHA5 = 50 at Δt* = 1.0. This shows that the water molecules of the lipid hydration layer slow down at high HA concentration.
The rotational self-vHf GR(ϕ, Δt*) for nHA5 = 10, 30, and 50 (shown in SI Fig. S11(a)–(c)) in the hydration layer behaves similarly to the HA-free cases. In all three cases, we observe an exponential tail following the central Gaussian. The crossover angle ϕc does not change with time (SI Fig. S12(a)). σ2, and λ (SI Fig. S12(b)) show power law dependencies as in the HA-free case. P(DR) curves, shown in Fig. 5(c) and (d), exhibit multiple peaks, implying multiple modes of rotational diffusion.
Next, we show ln![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) GT(r, Δt*) vs. Δt* data for different HA chain sizes, N = 1, 5 and 10 in SI Fig. S13(a)–(c) for hydration water. For all cases, GT(r, Δt*) shows a central Gaussian with an exponential tail. rc shows sublinear dependence on time (SI Fig. S14(a)). Hence, the heterogeneity persists until the residence time of water in the hydration layer. σ2 and λ show sublinear dependence with time (SI Fig. S14(b)). P(DT) data in Fig. 6(a) and (b) show peaks at a very small value of DT, and contribution from a wide range of DT values is noted, suggesting dynamic heterogeneity. We find that P(DT) remains similar for all values of N.
GT(r, Δt*) vs. Δt* data for different HA chain sizes, N = 1, 5 and 10 in SI Fig. S13(a)–(c) for hydration water. For all cases, GT(r, Δt*) shows a central Gaussian with an exponential tail. rc shows sublinear dependence on time (SI Fig. S14(a)). Hence, the heterogeneity persists until the residence time of water in the hydration layer. σ2 and λ show sublinear dependence with time (SI Fig. S14(b)). P(DT) data in Fig. 6(a) and (b) show peaks at a very small value of DT, and contribution from a wide range of DT values is noted, suggesting dynamic heterogeneity. We find that P(DT) remains similar for all values of N.
The rotational self-vHf GR(ϕ, Δt*) (SI Fig. S15(a)–(c)) for the hydration water molecules has a central Gaussian followed by an exponential tail for all N. We find that the crossover angle ϕc remains unchanged with time (SI Fig. S16(a)). The width σ2 of the central Gaussian and the decay constant λ of the exponential tail show sublinear power-law time dependence (SI Fig. S16(b)). P(DR), shown in Fig. 6(c) and (d), has multiple peaks, implying water molecules with different rotational diffusivity. The P(DR) is almost the same for all N values, the same as P(DT).
4 Discussions and outlook
We have extracted both the translational MSD, 〈r2〉 and the rotational MSD, 〈ϕ2〉 from the second moments of GT(r, Δt) and GR(ϕ, Δt), respectively. We consider different cases for the diffusive interfacial layer. SI Fig. S17(a) and (b) show the 〈r2〉 for different nHA5 and N, respectively. SI Fig. S17(c) and (d) depict the 〈ϕ2〉 for different nHA5 and N, respectively. In this region, 〈r2〉 and 〈ϕ2〉 increase linearly with time in agreement with our earlier MSD data.33 Next, we consider the hydration layer. SI Fig. S17(e) and (f) show 〈r2〉 and SI Fig. S17(g) and (h) show 〈ϕ2〉 for different nHA5 and N, respectively. We find that water molecules in the hydration layer exhibit subdiffusive behavior in both translational and rotational dynamics for different nHA5 and N. This is consistent with our earlier report, where we demonstrate the subdiffusive nature by directly computing the MSD.33 The main difference between the diffusive and subdiffusive self-vHf lies in the time dependence of the width of the central Gaussian. The width of the central Gaussian is linear in time for diffusive motion, but sublinear in time for subdiffusive motion.Unlike the diffusive region, exponential tails are observed in the self-vHFs in the hydration layer. Self-vHfs with exponential tails have also been reported for tracer beads in polymer networks,54 glassformers,55 mRNA molecules in the bacterial cytoplasm,56 and ionic liquids,20 all of which exhibit subdiffusive dynamics. Previous studies have shown that the diffusivity distribution underlying such exponential-tailed self-vHfs is typically skewed due to molecular caging.20 For translational motion at the hydration layer, we find that the diffusivity distribution shows a sharp peak at very low diffusivity, accompanied by a long tail. The peak reflects dynamically trapped water molecules, while the long tail is qualitatively consistent with the experimental observations,56 where an exponential diffusivity distribution is reported for RNA molecules in living E. coli and S. cerevisiae cells, leading to Laplace-distributed displacement and subdiffusive dynamics.56,57 We find that the rotational self-vHFs for subdiffusive hydration water also exhibit exponential tails.
The heterogeneity in the hydration water translational dynamics near the lipid bilayer is consistent with earlier reports.10,12,58 We show that the dynamic heterogeneity, both in translation and rotational motions of the water molecules, is extended from the hydration to the diffusive layer. We also note that both the average translational and rotational diffusivities at the diffusive interface are lower than those of bulk water (7.60 × 10−3 nm2 ps−1 and 0.30 rad2 ps−1, respectively).10 Hence, the lipid bilayer exhibits a long-range dynamical effect that slows down the surrounding water.
The dynamical features of the translational and rotational motions are different. The translational diffusivity distribution P(DT) exhibits a broad distribution of DT in the diffusive interface, while in the subdiffusive hydration layer it shows a sharp peak near vanishing diffusivity values, indicative of localized or trapped motion of water molecules. On the other hand, P(DR) shows a dominant primary peak along with minor secondary peaks in the diffusive layer. In contrast, for subdiffusive rotation, P(DR) displays multiple peaks, including vanishingly small values for the diffusion, which suggests possible dynamic exchange among discrete angular modes, including extremely sluggish dynamics. Nevertheless, unlike the translational case, there is no overall shift in the distribution from the diffusive to the hydration layer. This may be because rotational diffusion mainly depends on the hydrogen-bond network and its rearrangement.59 Hence, it remains less affected by spatial confinement than translation.
Upon introducing HA chains, additional hydrophilic interactions form between HA and interfacial water, making the water molecules more sluggish. However, since the HA molecules do not make any direct contact with the bilayer, their presence does not alter the dynamical features of the hydration layer. We find that, with increasing HA concentration, a finite probability of low diffusivity appears in both P(DT) and P(DR) in the diffusive interface. On the other hand, variations in HA chain length do not significantly alter the diffusivity distributions. This weak chain size dependence is likely to arise from the competition between HA chain flexibility and the strength of HA–water hydrophilic interaction, as discussed in the earlier paper.33 Such weak chain size-dependent water dynamics are reported for hydrophilic polyacrylamide solutions as well.60
The organization of the HA chains in the vicinity of cell membranes and the synergy between HA and lipid molecules plays a vital role in maintaining the viscoelasticity and lubrication of the synovial fluid23,27,61 as well as the elasticity of cells.29,62 These interactions are also crucial for the biomedical applications of HA in hydrogels,63 viscosupplements,28,64 and liposomes.65,66 Research shows that both HA concentration and molecular weight vary under different pathological conditions,21,67 thereby influencing the viscous and mechanical behavior of cells25,62,68 and consequently the fundamental cellular processes.69 Dynamic heterogeneity is related to the viscoelastic and mechanical relaxation.1,70,71 Hence, our study on the dynamic heterogeneity of water at the HA–DPPC interface can provide microscopic insights into the viscoelastic response of HA–lipid complexes, which may aid in distinguishing diseased cells from normal ones, tuning the properties of hydrogels, viscosupplements, ECM, and HA-coated liposomes.
It is also important to note a few limitations of this study. The concentration of HA chains in our simulations ranges from 20 to 100 mg mL−1 (see Table 1), which is consistent with experimental studies employing higher HA concentrations31,62 than physiological HA concentrations.67 Higher solute concentrations are often employed in molecular simulations to ensure statistically meaningful interactions within the finite system size and ensure relevance for in vivo processes. Furthermore, we take shorter atomistic HA chains than those typically present under physiological conditions67 to reduce computational cost.24,32,33,42 However, the low molecular-weight HA chains are characteristic of certain pathological conditions,26,29 making our model relevant to such environments. Hence, while the present model simplifies the complexity of the cellular environment and has certain caveats, it provides a reasonable approximation for systems such as cancerous tissues and synovial joints. Overall, this work advances the understanding of water dynamics at HA–lipid interfaces, which has received relatively limited attention to date. Employing coarse-grained models72,73 may help mitigate this limitation to some extent by enabling simulations of larger systems.
5 Conclusion
In summary, we present a systematic study of the dynamic heterogeneity of water molecules at the HA–water and DPPC interface, focusing on how the HA concentration and HA chain size influence the dynamics. The interfacial and hydration water at the HA–water and DPPC interface exhibit dynamic heterogeneity, characterized by non-Gaussian self van Hove functions. Furthermore, the diffusivity distributions provide a detailed understanding of the underlying dynamics. In the interfacial layer, translational diffusivity exhibits a broad distribution, whereas rotational diffusivity displays a dominant peak with minor secondary modes. Increased HA concentration decreases both translational and rotational diffusion at the interface, whereas HA chain length has minimal influence. In the hydration layer, translational diffusivity is sharply peaked at very low translational diffusivity, indicating highly restricted motion, while its rotational distributions are multimodal. Importantly, HA chains have minimal impact on hydration-layer dynamics. Our study provides insights into the interfacial dynamics of HA–lipid complexes, which could help in their spectroscopic characterization, with potential implications in many biomedical applications.Author contributions
Anirban Paul: conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, methodology, validation, visualization, software, investigation, writing – original draft, writing – review and editing. J. Chakrabarti: conceptualization, methodology, validation, project administration, resources, supervision, writing – review and editing.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Data availability
The data supporting this article have been included within the article and its supplementary information (SI). Supplementary information is available. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d5cp03169a.Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Technical Research Centre at S. N. Bose National Centre for Basic Sciences, Kolkata for its computational facilities. A. P. acknowledges financial support from Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), India [File No. 09/575(0134)/2020-EMR-I] and SNBNCBS for the ‘Bridge Fellowship’.Notes and references
- S. Pronk, E. Lindahl and P. M. Kasson, Nat. Commun., 2014, 5, 3034 CrossRef PubMed
.
- I. Tah, A. Mutneja and S. Karmakar, ACS Omega, 2021, 6, 7229–7239 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- J. P. Garrahan, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2011, 108, 4701–4702 CrossRef CAS
.
- B. Wang, J. Kuo, S. C. Bae and S. Granick, Nat. Mater., 2012, 11, 481–485 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
-
J.-P. Hansen and I. R. McDonald, Theory of simple liquids: with applications to soft matter, Academic Press, 2013 Search PubMed
.
- E. Tendong, T. S. Dasgupta and J. Chakrabarti, J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, 2020, 32, 325101 CrossRef CAS
.
- M. Karzar Jeddi and S. Romero-Vargas Castrillon, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2017, 121, 9666–9675 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- L. Damien,
et al.
, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2014, 118, 7715–7729 Search PubMed
.
- S.-H. Chong and S. Ham, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2016, 7, 3967–3972 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- A. Srivastava, S. Malik and A. Debnath, Chem. Phys., 2019, 525, 110396 CrossRef CAS
.
- A. Srivastava, S. Karmakar and A. Debnath, Soft Matter, 2019, 15, 9805–9815 RSC
.
- S. Malik, S. Karmakar and A. Debnath, J. Chem. Phys., 2023, 158, 091103 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- S. Mondal, K. P. Ghanta and S. Bandyopadhyay, J. Chem. Inf. Model., 2022, 62, 1942–1955 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- M. G. Mazza, N. Giovambattista, H. E. Stanley and F. W. Starr, Phys. Rev. E:Stat., Nonlinear, Soft Matter Phys., 2007, 76, 031203 CrossRef PubMed
.
- Q. Zhang, T. Wu, C. Chen, S. Mukamel and W. Zhuang, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2017, 114, 10023–10028 CrossRef CAS
.
- S. Dutta and J. Chakrabarti, Europhys. Lett., 2016, 116, 38001 CrossRef
.
- S. Dutta, M. Ghosh, R. Karmakar and J. Chakrabarti, Phys. Rev. E, 2019, 100, 062411 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- S. Sengupta and S. Karmakar, J. Chem. Phys., 2014, 140 DOI:10.1063/1.4882066
.
- A. Cuetos, N. Morillo and A. Patti, Phys. Rev. E, 2018, 98, 042129 CrossRef CAS
.
- M. Casalegno, G. Raos, G. B. Appetecchi, S. Passerini, F. Castiglione and A. Mele, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2017, 8, 5196–5202 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- G. Kogan, L. Šoltés, R. Stern, J. Schiller and R. Mendichi, Stud. Nat. Prod. Chem., 2008, 34, 789–882 CrossRef CAS
.
- M. Wang, C. Liu, E. Thormann and A. Dedinaite, Biomacromolecules, 2013, 14, 4198–4206 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- C. Liu, M. Wang, J. An, E. Thormann and A. Dėdinaitė, Soft Matter, 2012, 8, 10241–10244 RSC
.
- H. Zhang, W. Cai and X. Shao, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2021, 23, 25706–25711 RSC
.
- D. Paul, A. Roy, A. Nandy, B. Datta, P. Borar, S. K. Pal, D. Senapati and T. Rakshit, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2020, 11, 5569–5576 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- G. Zhang, R. Lu, M. Wu, Y. Liu, Y. He, J. Xu, C. Yang, Y. Du and F. Gao, FEBS J., 2019, 286, 3148–3163 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- Z. Liu, W. Lin, Y. Fan, N. Kampf, Y. Wang and J. Klein, Biomacromolecules, 2020, 21, 4345–4354 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- Z. Cai, H. Zhang, Y. Wei, M. Wu and A. Fu, Biomater. Sci., 2019, 7, 3143–3157 RSC
.
- D. Paul, A. Paul, D. Mukherjee, S. Saroj, M. Ghosal, S. Pal, D. Senapati, J. Chakrabarti, S. K. Pal and T. Rakshit, J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2022, 13, 8564–8572 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- J. Dedic, H. Okur and S. Roke, Sci. Adv., 2021, 7, eabf2558 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- J. Hunger, A. Bernecker, H. J. Bakker, M. Bonn and R. P. Richter, Biophys. J., 2012, 103, L10–L12 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- M. Susaki and M. Matsumoto, Polymers, 2022, 14, 4031 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- A. Paul and J. Chakrabarti, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2024, 26, 20440–20449 RSC
.
- W. Khuntawee, R. Amornloetwattana, W. Vongsangnak, K. Namdee, T. Yata, M. Karttunen and J. Wong-Ekkabut, RSC Adv., 2021, 11, 8475–8484 RSC
.
- A. Hendrich and K. Michalak, Curr. Drug Targets, 2003, 4, 23–30 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- T. E. Merchant, P. M. Diamantis, G. Lauwers, T. Haida, J. N. Kasimos, J. Guillem, T. Glonek and B. D. Minsky, Cancer, 1995, 76, 1715–1723 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- E. L. Wu, X. Cheng, S. Jo, H. Rui, K. C. Song, E. M. Dávila-Contreras, Y. Qi, J. Lee, V. Monje-Galvan, R. M. Venableet al., CHARMM-GUI membrane builder toward realistic biological membrane simulations, 2014 Search PubMed.
- A. Almond, P. L. DeAngelis and C. D. Blundell, J. Mol. Biol., 2006, 358, 1256–1269 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- S.-J. Park, J. Lee, Y. Qi, N. R. Kern, H. S. Lee, S. Jo, I. Joung, K. Joo, J. Lee and W. Im, Glycobiology, 2019, 29, 320–331 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- L. Martnez, R. Andrade, E. G. Birgin and J. M. Martnez, J. Comput. Chem., 2009, 30, 2157–2164 CrossRef PubMed
.
- O. Guvench, S. S. Mallajosyula, E. P. Raman, E. Hatcher, K. Vanommeslaeghe, T. J. Foster, F. W. Jamison and A. D. MacKerell Jr, J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2011, 7, 3162–3180 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- P. Smith, R. M. Ziolek, E. Gazzarrini, D. M. Owen and C. D. Lorenz, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2019, 21, 9845–9857 RSC
.
- D. Van Der Spoel, E. Lindahl, B. Hess, G. Groenhof, A. E. Mark and H. J. Berendsen, J. Comput. Chem., 2005, 26, 1701–1718 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- S. U. I. Nosé, Mol. Phys., 2002, 100, 191–198 CrossRef
.
- J. Nagle, Biophys. J., 1993, 64, 1476–1481 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- E. Lindahl and O. Edholm, J. Chem. Phys., 2001, 115, 4938–4950 CrossRef CAS
.
- M. Parrinello and A. Rahman, J. Appl. Phys., 1981, 52, 7182–7190 CrossRef CAS
.
- M. G. Mazza, N. Giovambattista, F. W. Starr and H. E. Stanley, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2006, 96, 057803 CrossRef PubMed
.
-
W. H. Press, Numerical recipes in Fortran 77: the art of scientific computing, Cambridge University Press, 1992, pp. 653–660 Search PubMed
.
- L. B. Lucy, Astron. J., 1974, 79, 745 CrossRef
.
- L. Agosta, M. Dzugutov and K. Hermansson, J. Chem. Phys., 2021, 154 DOI:10.1063/5.0039693
.
- S. Dutta and J. Chakrabarti, Soft Matter, 2018, 14, 4477–4482 RSC
.
- P. Chaudhuri, L. Berthier and W. Kob, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2007, 99, 060604 CrossRef PubMed
.
- R. Singh, J. Mahato, A. Chowdhury, A. Sain and A. Nandi, J. Chem. Phys., 2020, 152, 024903 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- H. Srinivasan, V. Sharma, V. Garca Sakai and S. Mitra, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2024, 132, 058202 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- T. J. Lampo, S. Stylianidou, M. P. Backlund, P. A. Wiggins and A. J. Spakowitz, Biophys. J., 2017, 112, 532–542 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- A. V. Chechkin, F. Seno, R. Metzler and I. M. Sokolov, Phys. Rev. X, 2017, 7, 021002 Search PubMed
.
- V. R. Hande and S. Chakrabarty, J. Phys. Chem. B, 2022, 126, 1125–1135 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- I. Ohmine and S. Saito, Acc. Chem. Res., 1999, 32, 741–749 CrossRef CAS
.
- S. A. Roget, Z. A. Piskulich, W. H. Thompson and M. D. Fayer, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2021, 143, 14855–14868 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- J. Seror, L. Zhu, R. Goldberg, A. J. Day and J. Klein, Nat. Commun., 2015, 6, 6497 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- N. Nagy, A. de la Zerda, G. Kaber, P. Y. Johnson, K. H. Hu, M. J. Kratochvil, K. Yadava, W. Zhao, Y. Cui and G. Navarro,
et al.
, J. Biol. Chem., 2018, 293, 567–578 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- X. Xu, A. K. Jha, D. A. Harrington, M. C. Farach-Carson and X. Jia, Soft Matter, 2012, 8, 3280–3294 RSC
.
- H. K. Vincent, S. S. Percival, B. P. Conrad, A. N. Seay, C. Montero and K. R. Vincent, Open Orthop. J., 2013, 7, 378 CrossRef PubMed
.
- F. Quemeneur, M. Rinaudo, G. Maret and B. Pépin-Donat, Soft Matter, 2010, 6, 4471–4481 RSC
.
- A. A. Gasperini, X. E. Puentes-Martinez, T. A. Balbino, T. de Paula Rigoletto, G. de Sa Cavalcanti Correa, A. Cassago, R. V. Portugal, L. G. de La Torre and L. P. Cavalcanti, Langmuir, 2015, 31, 3308–3317 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- M. K. Cowman, H.-G. Lee, K. L. Schwertfeger, J. B. McCarthy and E. A. Turley, Front. Immunol., 2015, 6, 261 Search PubMed
.
- M. K. Cowman, T. A. Schmidt, P. Raghavan and A. Stecco, F1000Research, 2015, 4 DOI:10.12688/f1000research.6885.1
.
- O. Chaudhuri, J. Cooper-White, P. A. Janmey, D. J. Mooney and V. B. Shenoy, Nature, 2020, 584, 535–546 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- A. Furukawa and H. Tanaka, Phys. Rev. Lett., 2009, 103, 135703 CrossRef PubMed
.
- R. J. Masurel, S. Cantournet, A. Dequidt, D. R. Long, H. Montes and F. Lequeux, Macromolecules, 2015, 48, 6690–6702 CrossRef CAS
.
- S. Shakibi, P. R. Onck and E. Van der Giessen, J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2023, 19, 5491–5502 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
- S. A. Samsonov, L. Bichmann and M. T. Pisabarro, J. Chem. Inf. Model., 2015, 55, 114–124 CrossRef CAS PubMed
.
| This journal is © the Owner Societies 2026 |






