Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleChemical conversion of recovered carbon black (rCB) from end-of-life tires (ELTs) pyrolysis to reduced graphene oxide (rGO): from waste to advanced materials
Bartosz
Dziejarski
 *abc,
Jarosław
Serafin
*d,
Diego Felipe
Hernández-Barreto
e,
Juan Carlos
Moreno-Piraján
e,
Liliana
Giraldo
f,
Narcis
Homs
dg,
Renata
Krzyżyńska
c,
Klas
Andersson
bh and
Pavleta
Knutsson
a
*abc,
Jarosław
Serafin
*d,
Diego Felipe
Hernández-Barreto
e,
Juan Carlos
Moreno-Piraján
e,
Liliana
Giraldo
f,
Narcis
Homs
dg,
Renata
Krzyżyńska
c,
Klas
Andersson
bh and
Pavleta
Knutsson
a
aDepartment of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Division of Energy and Materials, Chalmers University of Technology, SE-412 96 Gothenburg, Sweden. E-mail: bartoszd@chalmers.se
bDepartment of Space, Earth and Environment, Division of Energy Technology, Chalmers University of Technology, SE-412 96 Gothenburg, Sweden
cFaculty of Environmental Engineering, Wroclaw University of Science and Technology, 50-370 Wroclaw, Poland
dDepartment of Inorganic and Organic Chemistry, University of Barcelona, Martí i Franquès, 1-11, 08028, Barcelona, Spain
eDepartamento de Química, Facultad de Ciencias, Grupo de Investigación en Sólidos Porosos y Calorimetría, Universidad de los Andes, Cra. 1a No. 18A-10, Bogotá D.C. 11711, Colombia
fDepartamento de Química, Grupo de Calorimetría, Universidad Nacional de Colombia, Sede Bogotá, Cra. 45, Bogotá D.C. 11711, Colombia
gCatalonia Institute for Energy Research (IREC), Jardins de les Dones de Negre 1, Barcelona, 08930, Spain
hDepartment of Chemical Engineering, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, UT, USA
First published on 10th December 2024
Abstract
This study introduces a circular and economic strategy to produce reduced graphene oxide (rGO) from recovered carbon black (rCB). Using a modified Hummers' method followed by chemical reduction of graphene oxide (GO), this approach addresses environmental concerns while offering a cost-effective alternative to conventional rGO precursors. Furthermore, the effects of stirring duration (24 and 48 hours) on the rCB-to-rGO conversion process were examined to optimize production. The rCB-based rGO materials were characterized by N2 adsorption/desorption, SEM, FT-IR, Raman spectroscopy, TGA, XRD, and XPS. Results showed a notable increase in BET surface area (149 m2 g−1) and pore volume (0.350 cm3 g−1) with enhanced thermal stability. SEM analysis confirmed the successful reduction of GO, revealing folded graphene sheets and morphological changes in rCB during the conversion process. FT-IR spectra provided supporting evidence, showing that O–H and C–O vibration modes either disappeared or diminished in intensity after reduction of GO, which was further validated by XPS. Raman spectroscopy results, reflected by increased ID/IG ratios (0.982 and 1.017) in rGO samples, indicated the restoration of sp2 carbon structures and a reduction in the average sp2 domain sizes. XRD analysis clarified the formation mechanisms of various phases during oxidation (MnPO4·H2O, MnPO4·1.5H2O, Mn, and MnO) and reduction (Mn3(PO4)2·2H2O, K3H3(PO4)2, K2HPO4, and Mn2O3). This research introduces novel insights into the transformative potential of converting rCB into rGO through chemical processes, offering innovative pathways for advancing sustainable material production.
1. Introduction
The exponential progress in the scientific and technological fields has resulted in an increased need for advanced materials. Graphene, an allotrope of carbon with a two-dimensional structure, has gained significant attention in the scientific community owing to its wide range of properties.1,2 These properties include notable electron mobility, outstanding thermal conductivity, and remarkable mechanical strength.3 Here are different forms of graphene that have been tested through the years: few-layer graphene (FLG), graphene nanoribbons (GNRs), graphene quantum dots (GQDs), 3D graphene, and graphene oxide (GO). Among the different forms, GO laced with oxygen-containing groups (OCGs) has recently gained significant interest. The incorporation of OCGs not only enhances the solubility and processability of graphene but also paves the way for the synthesis of reduced graphene oxide (rGO). Even though graphene demonstrates substantial properties, limited processability and tunability hinder its wider implementation in materials science and technology.4 To unlock the full potential of graphene materials, and in particular graphene oxide, many researchers have focused on the development of an alternative material referred to as reduced graphene oxide (rGO).5–7Graphene oxide (GO) is produced by oxidizing graphene with strong oxidizing agents, such as sulfuric acid (H2SO4), nitric acid (HNO3), potassium permanganate (KMnO4), or hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Reduced graphene oxide (rGO) is subsequently obtained through the partial reduction of OCGs introduced during this oxidation process. This reduction can be accomplished through various methods, including thermal, chemical, and electrochemical techniques. The restoration of sp2 carbon–carbon bonds and the subsequent re-establishment of the conjugated π-electron system contribute to enhancing specific features that closely resemble those of pristine graphene.8 These include robust mechanical strength and inherent flexibility, enabling its incorporation into composite materials.9 Such qualities make rGO an exceptionally adaptable and attractive candidate in material science. Additionally, the superior electrical conductivity, substantial surface area, and excellent thermal stability of rGO offer significant benefits across various applications in diverse range of industry sectors, including energy, environmental technology, and electronics.10–14 For instance, the structure supports enhanced reaction rates in catalysis, the high surface area enables efficient adsorption for water purification and pollutant removal, conductivity and stability make it ideal for advancements in batteries and supercapacitors, and thermal properties improve durability in high-performance coatings.
The current limitation of producing large quantities of high-quality graphene, which serves as a precursor for obtaining rGO, has become a significant barrier for further development. These limitations are mainly due to concerns regarding scalability, cost-effectiveness, and the need for careful control of the preparation process.15 The conventional approaches used in the production of graphene include the exfoliation of graphite or the chemical vapor deposition (CVD) technique utilizing carbon precursors. These methodologies frequently require costly chemicals, energy-intensive operations, and intricate apparatus16 Consequently, there is an increasing tendency towards the development of alternative methodologies and precursors that exhibit low cost, sustainability, and environmental friendliness. Recent research has shown that biomass waste resources have the potential to be converted into graphitized carbon materials, including GO and rGO.17,18
In view of this, the utilization of recovered carbon black (rCB) offers a compelling solution to challenges of economic viability and scalability. As a commonly produced by-product of the pyrolysis of end-of-life tires (ELTs), rCB provides a plentiful and cost-effective source of carbon for synthesizing graphene-based materials.19 Moreover, approximately 1 billion waste tires are still generated annually, with this number projected to rise to 1.2 billion by the year 2030.20 On a global scale, the management and elimination of ELTs give rise to urgent and significant challenges connected to environmental, health, and safety issues. Using ELTs to produce rGO can both decrease the number of tires that are disposed of in landfills and aid in the resource management of carbon, thereby contributing to circularity in existing material flows.21 Some works have previously demonstrated the use of ELTs in the production of graphene-based materials. Wang et al.22 employed a one-step high-temperature pyrolysis with routine alkaline catalysis to convert waste tires directly into monolithic 3D graphene for use as a supercapacitor electrode. This study highlights a simple and abundant resource-based approach for large-scale graphene production, introducing a novel method for repurposing waste tires. Anuar et al.23 synthesized graphene oxide from one weight percent (1 wt%) of carbon black from waste tires using a straightforward modified Hummers' method. Despite previous very promising results in transforming rCB into graphene-based materials, the novelty of using rCB as a precursor for rGO synthesis remains unexplored, with the conversion mechanism and material characteristics still not thoroughly investigated.22–24
The presented methodology involves the preparation of GO from industrial obtained rCB via the conventional Hummers' method and the subsequent reduction of GO to rGO via chemical reduction. This study also highlights the significance of stirring duration (24 and 48 hours) in the synthesis of GO and rGO, as it substantially impacts the quality of the resulting graphene-based materials.25,26 Finally, the rCB, along with the synthesized GO and rGO, was characterized using various state-of-the-art techniques, including elemental analysis, N2 adsorption/desorption, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), Raman spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Through this study, we aim to contribute to and promote the utilization of globally available waste streams, such as ELTs, in the potential production of high-quality graphene-based materials. Furthermore, this work seeks to deepen understanding of the mechanisms involved in transforming rCB into rGO, supporting the circular economy and advancing ELT valorization.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Raw material – recovered carbon black (rCB)
The rGO precursor used in this study exhibited an average ash content ranging from 0.5% to 2%. The primary constituent of rCB was carbon (C), which varied in content from 92% to 99.5%. In addition, rCB contained volatile substances with a concentration exceeding 0.2%, as well as mineral matter that fluctuated between approximately 0.5% and 2%. The mineral matter included elements such as Si, Al, Zn, S, and Ca. In small amounts, these metals are unlikely to substantially impact on the oxidation and reduction processes or the quality of the resulting GO and rGO. Table 1 displays the main CHNS/O elemental analysis of the rCB sample.2.2. Preparation of rCB/rGO via chemical reduction
The synthesis of GO was carried out using a modified version of Hummers' method,27,28 starting with rCB powder (Fig. 1). A solution was prepared by mixing H2SO4 (98 wt%) and H3PO4 (75 wt%) in a ratio of 4![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 1 to a total volume of 200 mL and stirring at 500 rpm for 30 minutes. Subsequently, 5 g of rCB and 9 g of KMnO4 were gradually introduced into the mixture over 1 hour by continuous blending. Following Low et al.,29 who showed that high stirring speed (>1000 rpm) and duration (>24 h) with hydrazine as a reducing agent can synthesize ultrathin monolayer rGO, two mixtures were stirred at 1100 rpm for 24 and 48 hours to facilitate oxidation process. The influence of stirring time is evident in factors such as GO sheet tearing and the effectiveness of the chemical exfoliation process, underscoring that optimizing stirring duration is essential to mitigate these challenges.
1 to a total volume of 200 mL and stirring at 500 rpm for 30 minutes. Subsequently, 5 g of rCB and 9 g of KMnO4 were gradually introduced into the mixture over 1 hour by continuous blending. Following Low et al.,29 who showed that high stirring speed (>1000 rpm) and duration (>24 h) with hydrazine as a reducing agent can synthesize ultrathin monolayer rGO, two mixtures were stirred at 1100 rpm for 24 and 48 hours to facilitate oxidation process. The influence of stirring time is evident in factors such as GO sheet tearing and the effectiveness of the chemical exfoliation process, underscoring that optimizing stirring duration is essential to mitigate these challenges.
The entire procedure was conducted in an ice-water bath at temperatures below 20 °C. The mixture was then cooled to room temperature over 5 hours. The obtained mixture was slowly poured into a container of ice, and 3 mL of H2O2 were added to terminate the oxidation process and eliminate any excess KMnO4. Centrifugation was performed five times to effectively separate the precipitate from the liquid, each cycle lasting 30 minutes at 4700 rpm. The remaining solid material was ultrasonicated and washed with hydrochloric acid (HCl) and deionized water (DI) until a neutral pH was achieved. The obtained GO samples were dried in an oven for 24 hours at 90 °C. Additionally, if manganese residues were still present in the GO structure, heat treatment in an inert gas (within the range of 500–800 °C) was applied to aid in the removal of residual impurities while preserving its integrity.
For the next step, GO powder obtained after 48 hours of stirring was introduced into purified water at a concentration of 3 mg mL−1 (Fig. 2). Following this, 1 mL of hydrazine was added to the mixture as a chemical reducing agent. The finely dispersed mixture was then immersed in a water bath at 90 °C to facilitate heat transfer and was vigorously stirred for either 24 or 48 hours. The mixture underwent ultrasonication to enhance rGO dispersion and aid in impurity removal, followed by multiple filtration processes with excess HCl and deionized water to eliminate undesired chemicals and impurities. As a final step, the rGO samples were dried in an oven at 90 °C for 48 hours. Similarly, if residues persisted, heat treatment in inert gas was applied to eliminate them, as in the GO synthesis procedure.
The recovered carbon black sample was labeled as rCB, while the graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide samples were systematically designated as GO-X and rGO-X, respectively. In these labels, ‘X’ represents the stirring time in hours applied during synthesis, reflecting the varying preparation conditions.
2.3. Characterization of rCB-based GO and rGO materials
The elemental analysis of the rCB precursor was conducted using a CHNS elemental analyzer FLASH 2000 from Thermo Fisher Scientific.The changes in textural characteristic of the produced rCB-based GO and rGO samples were assessed using N2 adsorption–desorption at a temperature of 77 K. Gas adsorption experiments were conducted using a QuadraSorb Station 4 gas sorption analyzer. Prior to the adsorption tests, the samples were degassed for 16 hours at 250 °C. The specific surface area (SBET) was estimated using the Brunauer, Emmett, and Teller (BET) method, applying the Rouquerol criteria to ensure accuracy.30 The total pore volume (VTOT) was calculated from N2 adsorption isotherms at a high relative pressure (P/P0 ≈ 0.98–0.99), capturing the full pore-filling capacity of the material. Finally, the non-local density functional theory (NLDFT) model was employed to determine the pore size distributions (PSD) of the samples based on experimental data.
Fourier-transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy in transmission mode was performed using a Thermo Nicolet 5700 FTIR instrument to identify the introduction and removal of functional groups present on the sample surfaces. The wavenumber region used for the acquisition of FTIR spectra was 4000–400 cm−1.
Raman spectroscopy was employed to examine the D, G, and 2D bands of the GO and rGO samples. This analysis provided detailed information on the defects (D band), graphitic ordering (G band), and layer structure (2D band) of the carbon skeleton, thereby clarifying the effects of oxidation and reduction processes. The measurements were performed using a Jobin-Yvon LabRaman HR 800 spectrometer. The spectra were obtained through three consecutive accumulations, each lasting 5 s, using a 50× objective lens. The samples were excited using a 532 nm solid-state laser, with the power restricted to 1.5 mW to mitigate any potential thermal impacts. The ratio between the intensities of the D and G peaks was determined using the formula:
 | (1) |
X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis was used to examine the crystalline phases of the samples and to explore potential mechanisms of conversion from rCB to rGO. The measurements were performed using a PANalytical X’Pert PRO MPD Alpha1 powder diffractometer equipped with Cu Kα radiation (λ = 1.5406 Å). The XRD patterns were recorded in the 2θ range of 10–80°.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was conducted using a JEOL JSM-7001F instrument equipped with secondary electron (SE) and backscattered electron (BSE) detectors to assess changes in the morphology of the samples.
Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) was carried out using a Mettler Toledo TGA-DSC 3+ thermal analyzer. The test involved heating the materials at a rate of 10 K min−1, starting at 25 °C and reaching 900 °C. The analysis was performed in an N2 environment to investigate the thermal stability and decomposition stages of the materials.
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was performed using was performed using Al Kα (hν = 1486.6 eV) radiation with a Prevac system equipped with a Scienta SES 2002 electron energy analyzer operating at a constant transmission energy (pass energy of 50 eV). This analysis provided insight into the surface chemistry and bonding environment of carbon in GO and rGO samples.
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Textural properties
In Fig. 3, the N2 adsorption isotherms at 77 K are presented. According to the IUPAC classification,31 the precursor material (rCB) exhibits a type III isotherm, characteristic of nonporous or macroporous materials. A similar shape is observed for GO samples; however, the isotherm for rCB shows a higher N2 uptake. Interestingly, the isotherms obtained for the rGO samples are classified as type IV, displaying a hysteresis loop of type H3, which is characteristic of mesoporous materials. Additionally, it is noteworthy that the amount of nitrogen adsorbed at low values of P/P0 (<0.1) is greater for the two rGO samples than for the rCB and GO materials. This behavior is likely due to the development of a certain degree of microporosity following the reduction of GO.The textural characteristics of GO and rGO samples obtained from the rCB are shown in Fig. 1. As shown, the rCB exhibited a SBET of 55 m2 g−1. After chemical treatment using the modified Hummers' method, this parameter decreased to 15 m2 g−1 and 25 m2 g−1 for GO-24 and GO-48, respectively. A similar trend was observed for VTOT values. This behavior can be attributed to the oxidation of the carbonaceous matrix, resulting in the formation of oxygenated groups on the surface and at the edges of the rCB pores, which hinder the entrance of N2 molecules into the pores. Additionally, it is evident that this type of chemical treatment on rCB modifies not only the surface chemistry but also the porous structure of the material, similar to other oxidation methodologies such as those using HNO3. Kamegawa and coworkers32 found that the porosity of carbon black varied depending on its nature and the oxidation time with HNO3. For time intervals shorter than 20 hours, an increase in SBET from 76 m2 g−1 to 268 m2 g−1 was observed. However, longer treatment times resulted in a rapid decrease in this textural property. In our study, regarding the effect of stirring, GO-48 demonstrated higher SBET and VTOT values compared to GO-24 (Table 2). Prolonged processing led to a more pronounced restructuring of the pore architecture, influencing both surface area and pore volume. Specifically for GO-48, the extended oxidation treatment may have enhanced the adhesion of graphene sheets, resulting in the formation of gaps or channels between layers and thereby expanding the surface area by creating larger pores.
| Sample | BET surface areaa [m2 g−1] | Total pore volumeb [cm3 g−1] |
|---|---|---|
| a Calculated by BET method using the Rouquerol criteria. b Calculated by N2 adsorption isotherm at a high relative pressure (P/P0 ≈ 0.98–0.99). | ||
| rCB | 57 ± 0.212 | 0.173 ± 0.007 |
| GO-24 | 15 ± 0.043 | 0.049 ± 0.003 |
| GO-48 | 25 ± 0.072 | 0.074 ± 0.004 |
| rGO-24 | 133 ± 0.074 | 0.350 ± 0.009 |
| rGO-48 | 149 ± 0.079 | 0.255 ± 0.008 |
The chemical reduction of GO with hydrazine led to an increase in the textural properties of the resulting rGO materials. As shown in Table 1, the BET surface area increased by 9 and 6 times for rGO-24 and rGO-48, respectively, compared to the GO samples. Additionally, the total pore volume also rose after reduction, indicating the development of the porous network, as confirmed by the pore size distribution presented in Fig. 4. The rGO samples exhibited pore widths predominantly mesoporous (2 to 10 nm), with some microporosity also present. Furthermore, extended stirring during the reduction process (48 hours) may have caused partial restacking, folding, or aggregation of the graphene sheets, leading to a more complex arrangement.33,34 These interactions promote closer sheet alignment and curling or overlapping at the edges, leading to a denser configuration with modified pore characteristics. This effect is evident in rGO-48, which showed a higher BET surface area but a lower total pore volume compared to rGO-24. The resulting structure generally consists of fewer but larger pores, as sheets bridge small gaps, reducing accessible spaces between layers.35 Larger pores can increase SBET by exposing more graphene surface; however, they also reduce the number of smaller pores, which contribute significantly to VTOT.
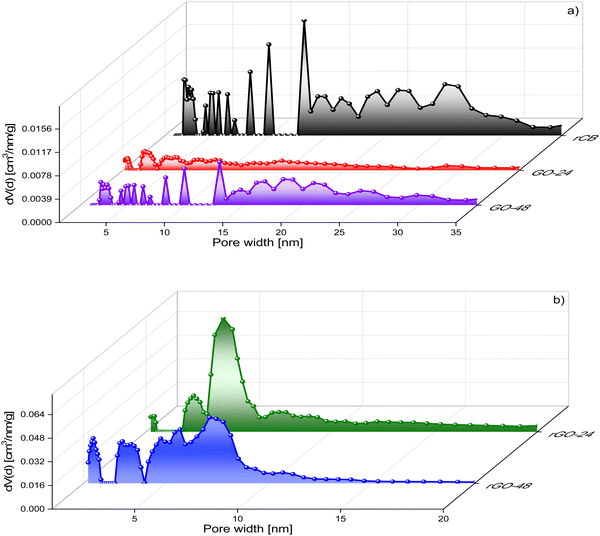 | ||
| Fig. 4 Pore size distribution of (a) rCB, GO-24, GO-48 and (b) rGO-24, rGO-48 based on N2 adsorption at 77 K. | ||
In principle, when comparing the textural properties of GO and rGO samples, it is expected that the oxygen surface groups of GO are eliminated after the reduction, depending on the process conditions, with minimal impact on the porous structure. However, some studies have shown that changes in surface chemical groups on GO can alter interactions between carbonaceous structures, potentially affecting porosity. For instance, the thermal reduction of GO conducted by Son et al.36 led to an increase in from 17 to 67 m2 g−1 at a reduction temperature of 2000 °C. More recently, Abakumov and co-workers37 achieved highly porous rGO structures with surface areas reaching up to 600 m2 g−1. They used GO derived from graphite flakes oxidized via a modified Hummers' method proposed by Marcano et al.38 Abakumov concluded that the suspension of GO during the reduction with hydrazine prevented the restacking of GO due to the formation of quasi-organized structures (nematic structures), which are highly stable. Additionally, the behavior of GO suspensions has been widely studied in the literature, where it is well-established that liquid crystal (LC) phases form from aqueous GO dispersions.39 This unique property depends on factors such as temperature, GO concentration, geometric shape, and particle size. In this study, the prepared suspension had a concentration of 3 mg mL−1, which aligns with the range used in Abakumov's work, suggesting the formation of a nematic phase in this case as well.
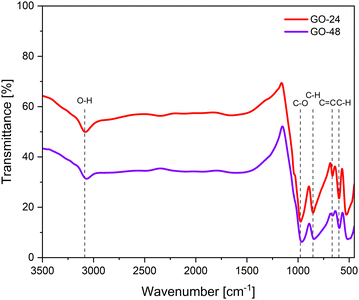
3.2. FT-IR spectroscopy
The FT-IR spectra of GO samples prepared at different synthesis times are shown in Fig. 5. The FT-IR analysis indicated that both GO samples exhibited similar spectral patterns, with characteristic vibrations observed around 3133–3016, 972, 849, 659, and 598 cm−1, which may correspond to oxygen-containing functional groups (OCFGs) such as hydroxyl (–OH), carbonyl (–C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O), carboxylic (–COOH), and epoxy (–O–) groups.40,41 These OCFGs are the most common surface functional groups found in GO. The band observed between 3016 and 3133 cm−1, associated with the stretching vibration of O–H bonds, signifies the presence of hydroxyl groups and highlights the role of hydrogen bonding interactions within the GO structure.42 Such interactions critically influence the physical properties of GO, including interlayer spacing and overall morphology, affecting its porosity, surface area, and mechanical properties. The band at 972 cm−1 is linked to the stretching vibrations of alkoxy (RO–) or epoxy (–O–) groups in the GO structure, while the signal at 659 cm−1 is attributed to the C
O), carboxylic (–COOH), and epoxy (–O–) groups.40,41 These OCFGs are the most common surface functional groups found in GO. The band observed between 3016 and 3133 cm−1, associated with the stretching vibration of O–H bonds, signifies the presence of hydroxyl groups and highlights the role of hydrogen bonding interactions within the GO structure.42 Such interactions critically influence the physical properties of GO, including interlayer spacing and overall morphology, affecting its porosity, surface area, and mechanical properties. The band at 972 cm−1 is linked to the stretching vibrations of alkoxy (RO–) or epoxy (–O–) groups in the GO structure, while the signal at 659 cm−1 is attributed to the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C skeletal stretching of the alkene group.43,44 Finally, the peaks at 849 and 578 cm−1 are related to the presence of aromatic C–H bonds.45,46
C skeletal stretching of the alkene group.43,44 Finally, the peaks at 849 and 578 cm−1 are related to the presence of aromatic C–H bonds.45,46
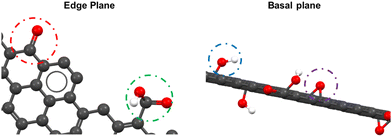
Multiple models of the GO structure have been proposed by authors such as Hofmann et al.,47 Ruess,48 Nakajima and Matsuo,49 Scholz and Boehm,50 Lerf–Klinowski,51 Dékány52 and Ajayan.53 These models demonstrate that different surface functional groups are present depending on the plane of the graphene layer. Fig. 6 depicts the two planes of a single GO layer, showing the distribution of surface functional groups. As illustrated, carbonyl (red circle) and carboxyl (green circle) groups are predominant on the edge plane, while hydroxyl (blue circle) and epoxide (purple circle) groups are primarily found on the basal plane.54
For the rGO samples (Fig. 7), FT-IR analysis revealed that the most characteristic vibrations in the spectral patterns are observed around 1600, 985, 938, and 552 cm−1. The band at 1600 cm−1 corresponds to structural vibrations within the graphitic domains, attributed to the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C stretching of aromatic rings. The presence of residual OFG and structural flaws in rGO may impact the C
C stretching of aromatic rings. The presence of residual OFG and structural flaws in rGO may impact the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C stretching vibration, resulting in slightly deformed spectra. Additionally, the peak at 985 cm−1 corresponds to the C–O stretching of epoxide or alkoxide group.55,56 Finally, the signals at 938 and 552 cm−1 are linked to the out-of-plane bending of aromatic C–H bond.57,58
C stretching vibration, resulting in slightly deformed spectra. Additionally, the peak at 985 cm−1 corresponds to the C–O stretching of epoxide or alkoxide group.55,56 Finally, the signals at 938 and 552 cm−1 are linked to the out-of-plane bending of aromatic C–H bond.57,58
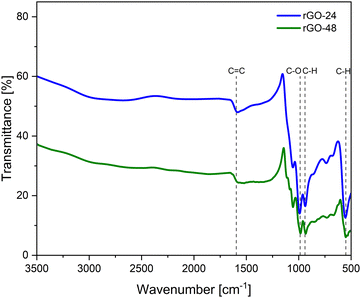 | ||
| Fig. 7 FT-IR spectrum of rGO samples, indicating bond types, prepared with stirring durations of 24 and 48 hours. | ||
These results indicate that effective reduction of graphene oxide was achieved at varying synthesis times. The FT-IR spectra of rGO clearly show that bands related to O–H and C–O vibration modes either disappear or become less intense. These signals are characteristic of GO, and the reduction in their intensity suggests that the reduction process successfully facilitates the removal of hydroxyl and carboxyl groups from the graphitic structure.29,31 Furthermore, it was observed that a longer synthesis time results in a more extensive reduction of rGO, as the signals for oxygen-containing functional groups are significantly diminished after 48 hours compared to 24 hours.
3.3. Raman spectroscopy
The Raman spectra of the prepared graphene-based materials are presented in Fig. 8. All GO and rGO samples exhibited two distinct bands within the Raman shift range of 1300–1600 cm−1. The first peak, observed at approximately 1353 cm−1, is commonly referred to as the D-band and represents the disordered phase. The D-band is associated with a breathing mode of j-point photons of A1g symmetry in the aromatic carbon ring.59 It arises due to sp3-like structural defects and imperfections in the carbon lattice of graphite. In contrast, the peak observed at 1578 cm−1 is associated with the G-band, which indicates the presence of the graphitic phase. This peak originates from the in-plane stretching vibrations of C–C bonds within graphite layers and includes sp2-bonded carbon atoms found in both aromatic rings and linear chains.60 Additionally, a noticeable secondary D peak appeared as a broad and upward-shifted 2D band (G′ band) at 1753 cm−1. The G′ band is connected with a second-order two-phonon process involving in-plane vibrational modes of carbon atoms within the graphene sheet.61The intensity of the G-band peak serves as an indicator of the carbon atom arrangement within the material. By examining the correlation between the D-to-G band intensity ratio (ID/IG), it is possible to identify key structural characteristics in the materials studied.62 A lower intensity ratio suggests a higher degree of carbon graphitization, while higher values indicate a more disordered phase. The ID/IG ratios of GO-24 and GO-48 were found to be 0.982 and 1.017, respectively (Table 3). After the reduction process, the ID/IG values for rGO samples increased, reflecting both the restoration of sp2 carbon and a reduction in the average sizes of sp2 domains, reaching 0.998 and 1.049. Furthermore, the I2D/IG ratio, which varied between 0.087 and 0.96, provided insights into the number of graphene layers and confirmed the presence of multilayer graphene.
| Sample | I D/IG | I 2D/IG |
|---|---|---|
| GO-24 | 0.982 | 0.096 |
| GO-48 | 1.017 | 0.104 |
| rGO-24 | 0.998 | 0.101 |
| rGO-48 | 1.049 | 0.087 |
3.4. X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis
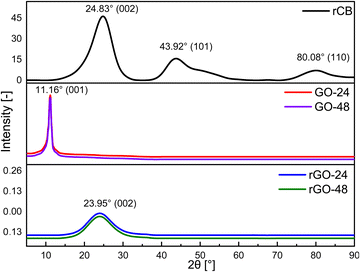
The XRD patterns of rCB, GO, and rGO with varying synthesis times are shown in Fig. 9. In the XRD pattern of recovered carbon black, the peak at 2θ = 24.83° is typically linked to the (002) plane of graphite, indicating the stacking of graphene layers. The peak near 2θ = 43.92° generally aligns with the (101) plane, reflecting in-plane crystalline order, while a peak around 2θ = 80.08° is often associated with the (110) plane, suggesting a higher degree of graphitization or structural ordering.In the XRD spectra of the synthesized samples, peaks at 2θ angles of 11.16° and 23.95° can be linked to GO and rGO, respectively, corresponding to the interlayer distances between the graphitic sheets.63 The peak observed in the XRD pattern of GO is attributed to the (001) plane of GO. These results indicate that during oxidation, there is an increase in the interlayer spacing due to the introduction of oxygen-containing functional groups (C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O, –OH, COOH) in both the basal plane and the sheet edges.64,65 For rGO samples, the diffraction peak at 23.95° is attributed to the (002) plane of rGO, and the variation in peak intensity may arise during the oxidation process or a substantial proportion of carbon in amorphous form. Upon reduction of GO to rGO, the interlayer distance decreases as oxygen-containing functional groups are removed, leading to the restacking of rGO sheets. The removal of these groups reduces the d-spacing and reestablishes the sp2 network during the reduction process.50,66
O, –OH, COOH) in both the basal plane and the sheet edges.64,65 For rGO samples, the diffraction peak at 23.95° is attributed to the (002) plane of rGO, and the variation in peak intensity may arise during the oxidation process or a substantial proportion of carbon in amorphous form. Upon reduction of GO to rGO, the interlayer distance decreases as oxygen-containing functional groups are removed, leading to the restacking of rGO sheets. The removal of these groups reduces the d-spacing and reestablishes the sp2 network during the reduction process.50,66
Furthermore, based on the XRD peaks observed in the synthesized samples of rCB-based GO/rGO prior to washing, a hypothesis regarding a mechanism that includes side reactions can be proposed. As shown in Fig. 10(a), the formation of MnPO4·H2O, MnPO4·1.5H2O, Mn, and MnO during the oxidation process is identified. In the presence of phosphoric acid, KMnO4 can lead to the production of manganese(II) phosphate monohydrate (MnPO4·H2O) and sesquihydrate (MnPO4·1.5H2O) as by-products or intermediate compounds. These compounds may form through reactions between manganese ions (from KMnO4) and phosphate ions (from H3PO4) in an aqueous environment, as presented in eqn (2) and (3), respectively.
| Mn2+ + HPO42− + H2O → MnPO4·H2O | (2) |
| Mn2+ + HPO42− + 1.5H2O → MnPO4·1.5H2O | (3) |
| 4KMnO4 + 2H2SO4 → 2K2SO4 + 4MnO2 + 2H2O + 3O2 | (4) |
| MnO2 + H2O2 → MnO + O2 + H2O | (5) |
| MnO2 + H2O2 + 2H+ → Mn2+ + O2 + 2H2O | (6) |
 | ||
| Fig. 10 (a) XRD patterns of GO-24 and GO-48 prior to the purification treatment. (b) XRD patterns of rGO-24 and rGO-48 prior to the purification treatment. | ||
In the case of unwashed rGO, XRD analysis revealed the presence of several phases (Fig. 10(b)). To provide a comprehensive understanding of all potential chemical reactions in rGO production as one step process, the unwashed GO samples were used, retaining Mn and phosphate impurities. The identified phases and interactions include:
• Mn3(PO4)2·2H2O: likely formed due to interactions between manganese and phosphate ions under the reducing conditions introduced by hydrazine.
• K3H3(PO4)2: suggests interactions between potassium and phosphate ions during the reduction process.
• K2HPO4: a potassium phosphate compound, distinct from K3H3(PO4)2 in stoichiometry, implying diverse chemical interactions during the reduction due to factors such as ionic strength, acid–base characteristics, redox behavior, complexation, or crystal structure.
• Mn2O3: formed from the partial reduction of manganese compounds (e.g., MnO2, KMnO4) by hydrazine, indicating redox reactions during the reduction step.
Overall, a peak typical of GO was observed at approximately 11°, while a peak characteristic of rGO appeared at 44°, indicating complete oxidation and reduction. For example, Anuar et al.23 and Sujiono et al.18 attempted to synthesize GO using carbonaceous waste and observed two distinct peaks at 23.97–25.39° and 23.97–43.04°, respectively. They attributed these peaks to incomplete oxidation or variations in the degree of oxidation. Furthermore, these differences may also stem from the type of precursors used and their inherent properties. In this work, manganese and phosphate impurities were effectively removed from the material structure through washing combined with ultrasonication or additional thermal treatment. Potentially, any residual trace amounts of these contaminants are unlikely to significantly influence or alter the structural integrity of the samples. Minor amounts of manganese and phosphates, which may still appear in the XRD patterns, could intercalate between the GO and rGO layers or adsorb onto the surface of the carbon planes. However, these small quantities are generally insufficient to cause notable changes in interlayer spacing or crystallographic order, and thus do not substantially affect the structural properties of GO and rGO. The distinct phases identified at each step of the synthesis process reflect the complex reaction pathways involved in producing rCB/rGO, underscoring the need for careful control and a thorough understanding of each stage in the preparation procedure to achieve the desired material properties.
3.5. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis
Fig. 11 presents SEM micrographs of GO-48 and rGO-48 samples. Generally, the primary structure of pristine rCB consists of agglomerated spherical-shaped particles, as previously reported by Dziejarski et al.67 Following the formation of the primary structure, the rCB aggregates continue to merge, resulting in secondary structures with distinct shapes (expanding chain and prolate spheroid shape). The micrographs in Fig. 11(a and b) show GO-48 with a rough particle surface containing defects of varied sizes and a combined wrinkled layer structure. This material typically presents a thin, flexible morphology with folds, rolled-on, rippled, and/or crumpled structures, depending on the precursor and synthesis methodology.68 On the other hand, the micrographs in Fig. 11(c and d) illustrate rGO-48 with thinner structures composed of folded rGO sheets. These folds result from the reduction of oxygen functional groups at the edges of the GO layers, leading to more pronounced folding in this region.69 This localized reduction weakens interlayer repulsion, encouraging structural changes and causing the edges to fold or crumple more significantly than other areas, contributing to rGO's distinctive morphology. The overall morphological transformations in rCB during its conversion to rGO are illustrated in Fig. 12.3.6. Thermogravimetric analysis (TGA)
Fig. 13 shows the TGA curves of GO and rGO. In the GO samples, an initial weight loss (∼1.5 wt%) occurred below 110 °C, attributed to the removal of adsorbed water molecules from the graphene surface. As the temperature increased, a rapid weight loss (∼14 wt%) was observed between 110 and 450 °C, resulting from carbon oxidation and the decomposition of stable oxygen-containing functional groups, likely releasing CO, CO2, and water vapor.70 The third temperature range, from 450 to 900 °C, was linked to the oxidative pyrolysis of the carbon framework. This phase was due to the breakdown of graphitic carbon and the presence of unstable carbon within the GO structure, which led to additional weight loss (∼1.8 wt%).71 The TGA curve for GO-24 shows an earlier onset of weight loss compared to GO-48, indicating lower thermal stability. In contrast, the TGA curve for GO-48 exhibits a more gradual weight loss, suggesting enhanced thermal stability, potentially due to more effective oxidation over the extended treatment time. | ||
| Fig. 13 TGA curves of the rCB precursor, GO-24/48, and rGO-24/48 subjected to a heating rate of 10 K min−1 from 25 °C to 900 °C. | ||
Compared to GO, rGO samples demonstrated improved thermal stability, particularly within the temperature range of 200 to 450 °C (∼10 wt%). Furthermore, at temperatures below 800 °C, the overall weight loss of material was 14.5%. This indicates a substantial drop in the presence of labile oxygen-containing functional groups and a profound reduction of GO.72 The TGA curve for rGO-24 displays a steeper weight loss at lower temperatures, which could indicate incomplete reduction. In contrast, the rGO-48 curve suggests enhanced thermal stability, likely due to a more thorough reduction process as a result of the longer synthesis duration.
3.7. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS)
For the examination, GO-48 was chosen alongside rGO-48. The selection was made strategically for several reasons such as maintaining the uniformity of the GO material. Additionally, it aimed to compare the maximum studied reduction time for rGO, which represents the maximum removal of oxygen-containing groups from the GO. As shown in Fig. 14, the C 1s spectra partially validate the FT-IR findings, demonstrating the successful synthesis of graphene oxide and its reduction to reduced graphene oxide from rCB. Specifically, three distinct peaks were revealed, as also observed in many different works.73–75 These peaks may be assigned to the presence of sp2 hybridized C–C/C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C in aromatic rings (including C–H bonding), sp3 hybridized C–C in diamond-like structures or alkanes, C–O (hydroxyl or epoxide groups), and C
C in aromatic rings (including C–H bonding), sp3 hybridized C–C in diamond-like structures or alkanes, C–O (hydroxyl or epoxide groups), and C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O (carbonyl groups) chemical bonds. Furthermore, it was noted that the chemical reduction procedure resulted in a substantial decrease in the intensities of oxygen-related peaks in the rGO-48 sample as compared to those in GO-48. The notable decline in the value suggests the reestablishment of the delocalized π conjugation in the rGO sample.76
O (carbonyl groups) chemical bonds. Furthermore, it was noted that the chemical reduction procedure resulted in a substantial decrease in the intensities of oxygen-related peaks in the rGO-48 sample as compared to those in GO-48. The notable decline in the value suggests the reestablishment of the delocalized π conjugation in the rGO sample.76
4. Conclusions
The present work demonstrates a circular and cost-effective pathway for producing rGO from rCB obtained through the pyrolysis of end-of-life tires. Using a modified Hummers' method, followed by chemical reduction of GO with hydrazine under varying stirring times (as shown in Fig. 15), the synthesized rCB-based GO and rGO materials were characterized. Detailed analyses of structural, morphological, thermal, surface, and chemical properties occurring during the synthesis were performed using N2 adsorption/desorption, SEM, FT-IR, Raman spectroscopy, TGA, XRD, and XPS. | ||
| Fig. 15 Overview of rCB conversion via the Hummers' method and chemical reduction for rGO synthesis. | ||
The N2 adsorption/desorption analysis showed an enhanced BET surface area of 149 m2 g−1 and a pore volume of 0.350 cm3 g−1 for rGO compared to GO, indicating a significant increase in accessible surface area and porosity. SEM analysis revealed morphological changes, capturing the shift from carbon black particles to layered, folded graphene-like sheets characteristic of reduced GO, confirming the successful reduction of GO. FT-IR spectra showed decreased intensity of O–H and C–O vibration modes, indicating effective deoxygenation and structural reordering, further supported by XPS C 1s spectra. Raman spectroscopy, with increased ID/IG ratios (0.982 to 1.017 for rGO), demonstrated restored sp2 carbon domains and reduced domain size, suggesting a more graphitic structure. TGA results showed the thermal stability of synthesized rGO. XRD analysis revealed structural and phase changes during oxidation and reduction, clarifying crystallinity, distribution, and reduction mechanisms within the rGO matrix.
Overall, this sustainable approach from waste to advanced materials not only contributes to the circular economy by repurposing ELT wastes but also offers an environmentally friendly route for the bulk production of rGO. The multi-technique characterization employed in this study provides an in-depth understanding of the material's characteristics and suitability for potential applications. Additionally, the conclusion presents an outlook on examining the efficiency, yield, cost, and environmental footprint of our rCB-based rGO synthesis method compared to conventional approaches. Further investigation could focus on optimizing key influencing parameters beyond stirring duration, such as the rCB/KMnO4 ratio, blending time, amount of H2O2, GO/hydrazine ratio, and the stirring temperature of the GO/hydrazine mixture. Fine-tuning these factors may enhance the quality and yield of the produced GO and rGO, providing a more comprehensive understanding of how these parameters interrelate and affect the final material properties.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.Acknowledgements
Jarosław Serafin and Narcis Homs acknowledge financial support from MICINN (PID2020-116031RB I00/AEI/10.13039/501100011033/FEDER) and from the Generalitat de Catalunya through the AGAUR grant for Project No. 2023 CLIMA 00009.References
- Y. Luo, C. Ren, Y. Xu, J. Yu, S. Wang and M. Sun, A first principles investigation on the structural, mechanical, electronic, and catalytic properties of biphenylene, Sci. Rep., 2021, 11(1), 19008, DOI:10.1038/s41598-021-98261-9.
- G. Yang, Synthesis, properties, and applications of carbyne nanocrystals, Mater. Sci. Eng., R, 2022, 151, 100692, DOI:10.1016/j.mser.2022.100692.
- B. Mortazavi, B. Javvaji, F. Shojaei, T. Rabczuk, A. V. Shapeev and X. Zhuang, Exceptional piezoelectricity, high thermal conductivity and stiffness and promising photocatalysis in two-dimensional MoSi2N4 family confirmed by first-principles, Nano Energy, 2021, 82, 105716, DOI:10.1016/j.nanoen.2020.105716.
- Y. Li, F. Meng, Y. Mei, H. Wang, Y. Guo, Y. Wang and Z. Zhou, Electrospun generation of Ti3C2Tx MXene@ graphene oxide hybrid aerogel microspheres for tunable high-performance microwave absorption, Chem. Eng. J., 2020, 391, 123512, DOI:10.1016/j.cej.2019.123512.
- R. Kumar, S. Sahoo, W. K. Tan, G. Kawamura, A. Matsuda and K. K. Kar, Microwave-assisted thin reduced graphene oxide-cobalt oxide nanoparticles as hybrids for electrode materials in supercapacitor, J. Energy Storage, 2021, 40, 102724, DOI:10.1016/j.est.2021.102724.
- M. A. Ali, C. Hu, S. Jahan, B. Yuan, M. S. Saleh, E. Ju and R. Panat, Sensing of COVID-19 antibodies in seconds via aerosol jet nanoprinted reduced-graphene-oxide-coated 3D electrodes, Adv. Mater., 2021, 33(7), 2006647, DOI:10.1002/adma.202006647.
- M. Sharma, S. Rani, D. K. Pathak, R. Bhatia, R. Kumar and I. Sameera, Temperature dependent Raman modes of reduced graphene oxide: Effect of anharmonicity, crystallite size and defects, Carbon, 2021, 184, 437–444, DOI:10.1016/j.carbon.2021.08.014.
- M. Kashif, E. Jafaar, S. K. Sahari, F. W. Low, N. D. Hoa, A. Ahmad and A. Qurashi, Organic sensitization of graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide thin films for photovoltaic applications, Int. J. Energy Res., 2021, 45(6), 9657–9666, DOI:10.1002/er.6414.
- S. Yasami, S. Mazinani and M. Abdouss, Developed composites materials for flexible supercapacitors electrode:“Recent progress & future aspects”, J. Energy Storage, 2023, 72, 108807, DOI:10.1016/j.est.2023.108807.
- M. Lundie, Ž. Šljivančanin and S. Tomić, Electronic and optical properties of reduced graphene oxide, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2015, 3(29), 7632–7641, 10.1039/C5TC00437C.
- S. Gupta, C. Chang, A. K. Anbalagan, C. H. Lee and N. H. Tai, Reduced graphene oxide/zinc oxide coated wearable electrically conductive cotton textile for high microwave absorption, Compos. Sci. Technol., 2020, 188, 107994, DOI:10.1016/j.compscitech.2020.107994.
- W. Hooch Antink, Y. Choi, K. D. Seong, J. M. Kim and Y. Piao, Recent progress in porous graphene and reduced graphene oxide-based nanomaterials for electrochemical energy storage devices, Adv. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 5(5), 1701212, DOI:10.1002/admi.201701212.
- S. J. Rowley-Neale, E. P. Randviir, A. S. A. Dena and C. E. Banks, An overview of recent applications of reduced graphene oxide as a basis of electroanalytical sensing platforms, Appl. Mater. Today, 2018, 10, 218–226, DOI:10.1016/j.apmt.2017.11.010.
- F. Hu, S. Tong, K. Lu, C. M. Chen, F. Y. Su, J. Zhou and R. Zhang, Reduced graphene oxide supported Ni-Ce catalysts for CO2 methanation: The support and ceria promotion effects, J. CO2 Util., 2019, 34, 676–687, DOI:10.1016/j.jcou.2019.08.020.
- S. E. Lowe, G. Shi, Y. Zhang, J. Qin, S. Wang, A. Uijtendaal and H. Zhao, Scalable production of graphene oxide using a 3D-printed packed-bed electrochemical reactor with a boron-doped diamond electrode, ACS Appl. Nano Mater., 2019, 2(2), 867–878, DOI:10.1021/acsanm.8b02126.
- X. J. Lee, B. Y. Z. Hiew, K. C. Lai, L. Y. Lee, S. Gan, S. Thangalazhy-Gopakumar and S. Rigby, Review on graphene and its derivatives: Synthesis methods and potential industrial implementation, J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng., 2019, 98, 163–180, DOI:10.1016/j.jtice.2018.10.028.
- M. A. Faiz, C. C. Azurahanim, Y. Yazid, A. B. Suriani and M. S. N. Ain, Preparation and characterization of graphene oxide from tea waste and it's photocatalytic application of TiO2/graphene nanocomposite, Mater. Res. Express, 2020, 7(1), 015613, DOI:10.1088/2053-1591/ab689d.
- E. H. Sujiono, D. Zabrian, M. Y. Dahlan, B. D. Amin and J. Agus, Graphene oxide based coconut shell waste: synthesis by modified Hummers' method and characterization, Heliyon, 2020, 6(8) DOI:10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04568.
- N. Cardona-Uribe, M. Betancur and J. D. Martínez, Towards the chemical upgrading of the recovered carbon black derived from pyrolysis of end-of-life tires, Sustainable Mater. Technol., 2021, 28, e00287, DOI:10.1016/j.susmat.2021.e00287.
- M. Adamu, S. I. Haruna, Y. E. Ibrahim and H. Alanazi, Investigating the properties of roller-compacted rubberized concrete modified with nanosilica using response surface methodology, Innov. Infrastruct. Solut., 2022, 7(1), 119, DOI:10.1007/s41062-021-00717-4.
- J. D. Martínez, An overview of the end-of-life tires status in some Latin American countries: Proposing pyrolysis for a circular economy, Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev., 2021, 144, 111032, DOI:10.1016/j.rser.2021.111032.
- C. Wang, D. Li, T. Zhai, H. Wang, Q. Sun and H. Li, Direct conversion of waste tires into three-dimensional graphene, Energy Storage Mater., 2019, 23, 499–507, DOI:10.1016/j.ensm.2019.04.014.
- A. U. Anuar, N. N. Bonnia, N. M. Jamil and N. D. N. Affandi, Graphene oxide based regenerated carbon waste tyre (rCB): Synthesis by modified Hummers' method and characterization, Mater. Today Proc., 2023 DOI:10.1016/j.matpr.2023.02.280.
- A. U. Anuar, N. N. Bonnia, N. D. N. Affandi, H. Al Garalleh, M. Khouj, F. N. A. M. Fauzi and N. M. Jamil, Graphene oxide nanoparticles synthesized from waste tires: A multi-faceted analysis of structure, morphology and antibacterial behavior, Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects, 2024, 38, 101176, DOI:10.1016/j.nanoso.2024.101176.
- M. Fathy, A. Gomaa, F. A. Taher, M. M. El-Fass and A. E. H. B. Kashyout, Optimizing the preparation parameters of GO and rGO for large-scale production, J. Mater. Sci., 2016, 51, 5664–5675, DOI:10.1007/s10853-016-9869-8.
- S. Abdolhosseinzadeh, H. Asgharzadeh and H. Seop Kim, Fast and fully-scalable synthesis of reduced graphene oxide, Sci. Rep., 2015, 5(1), 10160, DOI:10.1007/s10853-016-9869-8.
- H. Yu, B. Zhang, C. Bulin, R. Li and R. Xing, High-efficient synthesis of graphene oxide based on improved Hummers' method, Sci. Rep., 2016, 6(1), 36143, DOI:10.1038/srep36143.
- H. Omar, N. S. A. Malek, M. Z. Nurfazianawatie, N. F. Rosman, I. Bunyamin, S. Abdullah and N. A. Asli, A review of synthesis graphene oxide from natural carbon based coconut waste by Hummers' method, Mater. Today Proc., 2023, 75, 188–192, DOI:10.1016/j.matpr.2022.11.427.
- F. W. Low, C. W. Lai and S. B. Abd Hamid, Easy preparation of ultrathin reduced graphene oxide sheets at a high stirring speed, Ceram. Int., 2015, 41(4), 5798–5806, DOI:10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.01.008.
- J. W. Osterrieth, J. Rampersad, D. Madden, N. Rampal, L. Skoric, B. Connolly and D. Fairen-Jimenez, How reproducible are surface areas calculated from the BET equation?, Adv. Mater., 2022, 34(27), 2201502, DOI:10.1002/adma.202201502.
- M. Thommes, K. Kaneko, A. V. Neimark, J. P. Olivier, F. Rodriguez-Reinoso, J. Rouquerol and K. S. W. Sing, IUPAC Technical Report Physisorption of Gases, with Special Reference to the Evaluation of Surface Area and Pore Size Distribution (IUPAC Technical Report), Pure Appl. Chem., 2015, 87(9–10), 1051–1069, DOI:10.1515/pac-2014-1117.
- K. Kamegawa, K. Nishikubo and H. Yoshida, Oxidative Degradation of Carbon Blacks with Nitric Acid (I)—Changes in Pore and Crystallographic Structures, Carbon, 1998, 36(4), 433–441, DOI:10.1016/S0008-6223(97)00227-3.
- J. Li and M. Östling, Prevention of graphene restacking for performance boost of supercapacitors—a review, Crystals, 2013, 3(1), 163–190, DOI:10.3390/cryst3010163.
- F. Guo, M. Creighton, Y. Chen, R. Hurt and I. Külaots, Porous structures in stacked, crumpled and pillared graphene-based 3D materials, Carbon, 2014, 66, 476–484, DOI:10.1016/j.carbon.2013.09.024.
- Z. Fan, Q. Zhao, T. Li, J. Yan, Y. Ren, J. Feng and T. Wei, Easy synthesis of porous graphene nanosheets and their use in supercapacitors, Carbon, 2012, 50(4), 1699–1703, DOI:10.1016/j.carbon.2011.12.016.
- L. Song, F. Khoerunnisa, W. Gao, W. Dou, T. Hayashi, K. Kaneko, M. Endo and P. M. Ajayan, Effect of High-Temperature Thermal Treatment on the Structure and Adsorption Properties of Reduced Graphene Oxide, Carbon, 2013, 52, 608–612, DOI:10.1016/j.carbon.2012.09.060.
- A. A. Abakumov, I. B. Bychko, O. O. Voitsihovska, R. M. Rudenko and P. E. Strizhak, Tuning the Surface Area of Reduced Graphene Oxide by Modulating Graphene Oxide Concentration during Hydrazine Reduction, Mater. Lett., 2024, 354, 135417, DOI:10.1016/j.matlet.2023.135417.
- D. C. Marcano, D. V. Kosynkin, J. M. Berlin, A. Sinitskii, Z. Sun, A. Slesarev, L. B. Alemany, W. Lu and J. M. Tour, Improved Synthesis of Graphene Oxide, ACS Nano, 2010, 4(8), 4806–4814 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Narayan, J. E. Kim, J. Y. Kim, K. E. Lee and S. O. Kim, Graphene Oxide Liquid Crystals: Discovery, Evolution and Applications, Adv. Mater., 2016, 28(16), 3045–3068, DOI:10.1002/ADMA.201505122.
- S. Thakur and N. Karak, Green Reduction of Graphene Oxide by Aqueous Phytoextracts, Carbon, 2012, 50(14), 5331–5339, DOI:10.1016/j.carbon.2012.07.023.
- X. Jiao, Y. Qiu, L. Zhang and X. Zhang, Comparison of the Characteristic Properties of Reduced Graphene Oxides Synthesized from Natural Graphites with Different Graphitization Degrees, RSC Adv., 2017, 7(82), 52337–52344, 10.1039/C7RA10809E.
- Y. B. Wu, L. Ren and G. Y. Dong, Syntheses, crystal structures, luminescent sensing and photocatalytic properties of two 2D cadmium (II) coordination polymers constructed from mixed ligands, Inorg. Chim. Acta, 2022, 530, 120703 CrossRef CAS.
- F. M. Casallas Caicedo, E. Vera López, A. Agarwal, V. Drozd, A. Durygin, A. Franco Hernandez and C. Wang, Synthesis of Graphene Oxide from Graphite by Ball Milling, Diamond Relat. Mater., 2020, 109, 108064, DOI:10.1016/j.diamond.2020.108064.
- I. Sengupta, S. Chakraborty, M. Talukdar, S. K. Pal and S. Chakraborty, Thermal Reduction of Graphene Oxide: How Temperature Influences Purity, J. Mater. Res., 2018, 33(23), 4113–4122, DOI:10.1557/jmr.2018.338.
- M. Ebrahimi Naghani, M. Neghabi, M. Zadsar and H. Abbastabar Ahangar, Synthesis and Characterization of Linear/Nonlinear Optical Properties of Graphene Oxide and Reduced Graphene Oxide-Based Zinc Oxide Nanocomposite, Sci. Rep., 2023, 13(1), 1496, DOI:10.1038/s41598-023-28307-7.
- X. Yan, J. Chen, J. Yang, Q. Xue and P. Miele, Fabrication of Free-Standing, Electrochemically Active, and Biocompatible Graphene Oxide−Polyaniline and Graphene−Polyaniline Hybrid Papers, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2010, 2(9), 2521–2529, DOI:10.1021/am100293r.
- U. Hofmann and R. Holst, Über Die Säurenatur Und Die Methylierung von Graphitoxyd, Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges., 1939, 72(4), 754–771, DOI:10.1002/cber.19390720417.
- G. Ruess, Über Das Graphitoxyhydroxyd (Graphitoxyd)., Monatsh. Chem., 1947, 76(3–5), 381–417, DOI:10.1007/BF00898987.
- T. Nakajima and Y. Matsuo, Formation Process and Structure of Graphite Oxide, Carbon, 1994, 32(3), 469–475, DOI:10.1016/0008-6223(94)90168-6.
- W. Scholz and H. P. Boehm, Untersuchungen Am Graphitoxid. VI. Betrachtungen Zur Struktur Des Graphitoxids, Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem., 1969, 369(3–6), 327–340, DOI:10.1002/ZAAC.19693690322.
- H. He, T. Riedl, A. Lerf and J. Klinowski, Solid-State NMR Studies of the Structure of Graphite Oxide, J. Phys. Chem., 1996, 100(51), 19954–19958, DOI:10.1021/JP961563T.
- T. Szabó, O. Berkesi, P. Forgó, K. Josepovits, Y. Sanakis, D. Petridis and I. Dékány, Evolution of Surface Functional Groups in a Series of Progressively Oxidized Graphite Oxides, Chem. Mater., 2006, 18(11), 2740–2749, DOI:10.1021/cm060258+.
- W. Gao, L. B. Alemany, L. Ci and P. M. Ajayan, New Insights into the Structure and Reduction of Graphite Oxide, Nat. Chem., 2009, 1(5), 403–408, DOI:10.1038/nchem.281.
- M. U. Khan and M. A. Shaida, Reduction Mechanism of Graphene Oxide Including Various Parameters Affecting the C/O Ratio, Mater. Today Commun., 2023, 36, 106577, DOI:10.1016/j.mtcomm.2023.106577.
- H.-L. Guo, X.-F. Wang, Q.-Y. Qian, F.-B. Wang and X.-H. Xia, A Green Approach to the Synthesis of Graphene Nanosheets, ACS Nano, 2009, 3(9), 2653–2659, DOI:10.1021/nn900227d.
- B. D. Ossonon and D. Bélanger, Synthesis and Characterization of Sulfophenyl-Functionalized Reduced Graphene Oxide Sheets, RSC Adv., 2017, 7(44), 27224–27234, 10.1039/C6RA28311J.
- N. Sharma, V. Sharma, Y. Jain, M. Kumari, R. Gupta, S. K. Sharma and K. Sachdev, Synthesis and Characterization of Graphene Oxide (GO) and Reduced Graphene Oxide (rGO) for Gas Sensing Application, Macromol. Symp., 2017, 376(1), 1700006, DOI:10.1002/masy.201700006.
- N. Sharma, R. Vyas, V. Sharma, H. Rahman, S. K. Sharma and K. Sachdev, A Comparative Study on Gas-Sensing Behavior of Reduced Graphene Oxide (rGO) Synthesized by Chemical and Environment-Friendly Green Method, Appl. Nanosci., 2020, 10(2), 517–528, DOI:10.1007/s13204-019-01138-7.
- B. M. Gunasekaran, J. B. B. Rayappan, G. K. Rajendran, G. Gopalakrishnan, N. Nesakumar, S. Muthiah and J. R. Sivanesan, Electrochemical Sensing of Arsenic Ions Using a Covalently Functionalized Benzotriazole-Reduced Graphene Oxide-Modified Screen-Printed Carbon Electrode, ChemistrySelect, 2022, 7(25), e202201169 CrossRef CAS.
- Z. Zhai, N. Huang, B. Yang, L. Liu, H. Li, J. Chen and X. Jiang, In situ construction of hierarchical diamond supported on carbon nanowalls/diamond for enhanced electron field emission, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12(7), 8522–8532 CrossRef CAS.
- A. Armano and S. Agnello, Two-dimensional carbon: a review of synthesis methods, and electronic, optical, and vibrational properties of single-layer graphene, C, 2019, 5(4), 67 CAS.
- I. Ahmad, S. S. Roy, P. D. Maguire, P. Papakonstantinou and J. A. McLaughlin, Effect of substrate bias voltage and substrate on the structural properties of amorphous carbon films deposited by unbalanced magnetron sputtering, Thin Solid Films, 2005, 482(1–2), 45–49 CrossRef CAS.
- B. A. Aragaw, Reduced Graphene Oxide-Intercalated Graphene Oxide Nano-Hybrid for Enhanced Photoelectrochemical Water Reduction, J. Nanostruct. Chem., 2020, 10(1), 9–18, DOI:10.1007/s40097-019-00324-x.
- R. Al-Gaashani, A. Najjar, Y. Zakaria, S. Mansour and M. A. Atieh, XPS and Structural Studies of High Quality Graphene Oxide and Reduced Graphene Oxide Prepared by Different Chemical Oxidation Methods, Ceram. Int., 2019, 45(11), 14439–14448, DOI:10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.04.165.
- N. G. de Barros, A. C. Gonzaga Neto, K. B. Vaccioli, H. R. V. Angulo, L. G. de Andrade e Silva, S. M. Toffoli and T. S. Valera, Graphene oxide: A comparison of reduction methods, C, 2023, 9(3), 73, DOI:10.3390/c9030073.
- N. M. S. Hidayah, W. W. Liu, C. W. Lai, N. Z. Noriman, C. S. Khe, U. Hashim and H. C. Lee, Comparison on graphite, graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide: Synthesis and characterization, AIP Conf. Proc., 2017, 1892(1) DOI:10.1063/1.5005764.
- B. Dziejarski, D. F. Hernández-Barreto, J. C. Moreno-Piraján, L. Giraldo, J. Serafin, P. Knutsson and R. Krzyżyńska, Upgrading recovered carbon black (rCB) from industrial-scale end-of-life tires (ELTs) pyrolysis to activated carbons, Environ. Res., 2024, 247 DOI:10.1016/j.envres.2024.118169.
- J. Liu, S. Chen, Y. Liu and B. Zhao, Progress in preparation, characterization, surface functional modification of graphene oxide: A review, J. Saudi Chem. Soc., 2022, 26(6), 101560, DOI:10.1016/j.jscs.2022.101560.
- S. Tamang, S. Rai, R. Bhujel, N. K. Bhattacharyya, B. P. Swain and J. Biswas, A concise review on GO, rGO and metal oxide/rGO composites: Fabrication and their supercapacitor and catalytic applications, J. Alloys Compd., 2023, 947, 169588, DOI:10.1016/j.jallcom.2023.169588.
- C. Zhang, X. Fu, Q. Yan, J. Li, X. Fan and G. Zhang, Study on the thermal decomposition mechanism of graphene oxide functionalized with triaminoguanidine (GO-TAG) by molecular reactive dynamics and experiments, RSC Adv., 2019, 9(57), 33268–33281, 10.1039/C9RA04187G.
- P. L. Yap, S. Kabiri, D. N. Tran and D. Losic, Multifunctional binding chemistry on modified graphene composite for selective and highly efficient adsorption of mercury, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 11(6), 6350–6362, DOI:10.1021/acsami.8b17131.
- M. Ifat-Al-Karim, M. Al Mamun, F. Nahid, M. Ismail, S. M. Hoque and M. M. Haque, Comparison of structural and antimicrobial activity between graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide-reinforced hydroxyapatite-based nanocomposites for biomedical application, Bull. Mater. Sci., 2023, 46(4), 212 CrossRef CAS.
- R. Al-Gaashani, A. Najjar, Y. Zakaria, S. Mansour and M. A. Atieh, XPS and structural studies of high quality graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide prepared by different chemical oxidation methods, Ceram. Int., 2019, 45(11), 14439–14448 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Kim, J. Lee, T. Liu and C. P. Grey, Characterizing nitrogen sites in nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide: a combined solid-state 15N NMR, XPS, and DFT approach, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2021, 125(19), 10558–10564 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Chen, X. Wang and D. Fang, A review on C1s XPS-spectra for some kinds of carbon materials, Fullerenes, Nanotubes Carbon Nanostruct., 2020, 28(12), 1048–1058 CrossRef CAS.
- M. K. Rabchinskii, S. D. Saveliev, D. Y. Stolyarova, M. Brzhezinskaya, D. A. Kirilenko, M. V. Baidakova and P. N. Brunkov, Modulating nitrogen species via N-doping and post annealing of graphene derivatives: XPS and XAS examination, Carbon, 2021, 182, 593–604 CrossRef CAS.
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2025 |