Open Access Article
Open Access ArticleSystematic study of CVD-growth parameters in NaCl-assisted growth of MoSe2 nanostructures: nanoribbons, dendrites and spirals†
Mahima
Tyagi
 *a,
Srijata
Dey
a,
Pinky
Sahoo
b and
Deshdeep
Sahdev
b
*a,
Srijata
Dey
a,
Pinky
Sahoo
b and
Deshdeep
Sahdev
b
aDepartment of Physics, Birla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani, Pilani Campus, Vidya Vihar, Pilani, Rajasthan 333031, India. E-mail: mahima01tg@gmail.com
bResearch Division, Quazar Technologies, Sarvapriya Vihar, New Delhi 110016, India
First published on 3rd June 2025
Abstract
MoSe2, a two-dimensional (2D) transition metal dichalcogenide (TMDC), has garnered significant interest in recent years due to its semiconducting properties and tunable band gap with potential applications in optoelectronics, photocatalysis and atomically thin devices. In this study, we report the controlled synthesis of MoSe2 nanocrystals using a custom 12-zone atmospheric pressure chemical vapour deposition (APCVD) system. NaCl is used as a seed promoter to facilitate the growth of monolayer, bilayer, and multilayer films, often as large as 200 μm. Additionally, the morphological evolution of the MoSe2 nanostructures is controlled by tuning different growth parameters based on insights, which we discuss in detail. The growth of dominant nanostructures, which include nanoribbons, snowflakes, monolayers and multilayer domains, among others, are discussed. High-resolution optical microscopy, field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) and atomic force microscopy (AFM) are used to image the as-grown crystals. Raman spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) are used to verify the quality and elemental composition of our as-grown MoSe2 crystals. Our findings brighten the prospect of growing novel 1D and 2D TMDC nanostructures with sufficient control to make them suitable for advanced optoelectronic and catalytic devices.
1. Introduction
Over the last decade, two-dimensional layered transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDCs), in general, have attracted significant attention because of their exceptional electronic and optical characteristics.1–4 Of these, MoS2 and MoSe2 have been particularly popular because of the promise they hold for a range of applications. Within these, monolayer or few-layer MoSe2 nanostructures exhibit superior behaviour to MoS2 due to their unique band structures.5–8 Few-layer 2D TMDCs, including MoSe2, offer enhanced mechanical and chemical stability compared to their monolayer counterparts, making them more suitable for use in FETs. This stability is crucial, as it allows these materials to withstand the harsh conditions encountered during device fabrication. An increased number of layers also provides a larger number of transport channels and results in higher on-state current and carrier mobility.9Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) has been widely used to synthesize highly crystalline and large-area MoSe2 films. The successful growth of MoSe2 on SiO2/Si substrates using CVD was first reported by Shaw et al.10 Since then, there have been several reports of large-area MoSe2 nanocrystals grown by CVD on many other substrates.11–14 Chang et al.7 compared the optical and electronic properties of CVD-grown MoS2 and MoSe2 and found that the number of defects was lower in the latter. This was in part explained by Wang et al.,15 who initiated a discussion of the growth mechanisms involved in CVD-grown MoSe2.
Two of the important growth mechanisms are worth noting. With the metal oxide precursor and substrate conventionally placed in a high-temperature zone, and the chalcogen in a relatively low-temperature region12 crystals grow in the vapor–solid–solid (VSS) mode, wherein a solid crystal is deposited directly from the vapor phase onto a solid substrate. Vapor phase precursors directly adsorb and react on the substrate surface to form nuclei, which subsequently grow into solid, typically triangular or hexagonal, domains. These shapes are dictated primarily by the free energy of the crystal edges and the surface diffusion kinetics of the precursors. However, the morphologies produced by this route are limited.
In contrast, the vapor–liquid–solid (VLS) mode, facilitated by the introduction of alkali halide salts, e.g. NaCl or KCl, alters the free energy of the crystal edges16,17 and opens out several new possibilities. This mechanism involves vapor-phase precursors adsorbing onto a catalytic liquid metal droplet, dissolving therein, and later precipitating at the liquid–solid interface to produce a range of nanostructures such as nanowires and nanoribbons. Several van der Waals layered compounds, including BN,18 NiCl2,19 SnS220 and Bi2Se2,21 have been synthesized by this method. However, control of the morphology and quality of the resulting MoSe2 nanostructures continues to be an outstanding challenge.
In this context, it is worth mentioning that the addition of alkali halides to the metal oxide enhances the growth rates and sizes of the resulting crystals (or continuous films) and reduces the growth temperature. Li et al.22 reported that large WSe2 and WS2 monolayer crystals could be grown at moderate temperatures (700–850 °C) using alkali metal halides as growth promoters. Li et al.23 demonstrated a dramatic enhancement in the growth of 2D TMDC selenides and tellurides, namely MoSe2 and WTe2, using mixed transition metal salts and chalcogen salts. The addition of salts induced the wafer-scale growth of these TMDCs, forming a continuous monolayer film and a large gain size of 100–50 μm. Kim et al.24 made the same observation with regard to MoS2. Zhou et al.25 subsequently demonstrated that molten-salt-assisted CVD can be broadly applied to produce atomically thin TMDC films. They also showed that salt assistance increases the overall reaction rate by decreasing the melting point of the reactants, which in turn facilitates the formation of intermediate products. For example, metaloxyhalides, formed in reactions between halides and metal oxides, evaporate at relatively low temperatures, enhancing 2D growth in the process. Chen et al.5 reported the controlled CVD growth of large-scale monolayer and multi-layer MoSe2 films and nanoribbons. Li et al.26 synthesised single-crystal, monolayer MoSe2, with domain sizes reaching up to 250 μm, by employing NaCl-assisted CVD. Feng et al.27 reported that increasing the growth temperature in the presence of NaCl leads to drastic changes in the morphology of the as-grown WSe2 samples. Singh et al.28 similarly grew MoS2 on different substrates and demonstrated that NaCl facilitates the formation of seeding promoters, such as a water-soluble layer of Na2S and/or Na2SO4 on the substrate, which aids in the 2D planar nucleation of MoS2. Bay et al.29 further systematised this approach by growing MoSe2 nanocrystals, using five different water-soluble catalysts, namely sodium chloride (NaCl), zinc chloride (ZnCl2), potassium hydroxide (KOH), potassium chloride (KCl), and potassium oxalate (K2C2O4). These were applied as thin layers onto the SiO2/Si substrates. Among these five salts, the use of NaCl resulted in the most uniform growth of the as-synthesised flakes.
Each TMDC morphology, including nanoribbons, dendrites, fractals, and spiral formations, offers distinct advantages for various applications. For example, 1D nanoribbons have shown significant promise in electronic, magnetic, and catalytic applications;30–33 however, the controllable fabrication of MoSe2 nanoribbons is found to be scant in the literature. Similarly, dendritic and fractal structures are particularly advantageous for catalytic applications owing to the high density of the active edge sites and defects they possess. Studies have shown that the rate of the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) increases linearly with the density of these features.34–37 The CVD growth of MoS2 dendrites, as reported earlier by our group,38 can be further enhanced by adding NaCl to the precursor. The formation of dendrites or fractals in MoSe2 under optimised CVD-growth conditions, as reported here, would be suitable for HER catalytic activity. Additionally, spiral structures, which interlink the layers of MoSe2, provide unique pathways for electrical current, enhancing the vertical conductivity of the devices. This unique morphology was found to notably increase the vertical conductivity in MoS2,39 enhancing the overall electrical conductivity and making these structures ideal for use in nanoelectronic devices.40 Moreover, the non-inversion symmetry present in these nanostructures gives rise to interesting non-linear optical (NLO) effects, polarization and piezoelectricity, all of which promise to find applications in electronics and optoelectronics.41–43
In this study, we systematically investigate the morphological evolution of MoSe2 nanocrystals by varying a set of specific CVD-growth parameters. NaCl is employed as a seed promoter to enhance both the growth rate and size of the crystals. By meticulously tuning these parameters, a wide variety of nanocrystal morphologies were successfully synthesized. There are several studies on NaCl-assisted CVD growth of TMDCs available in the literature, as mentioned earlier; but in addition, there are substantial research gaps. Our studies are an attempt to address this gap by correlating the CVD growth of each of these different MoSe2 nanostructures, including nanoribbons, dendrites, and spiral structures, with specific regions of parameter space. This is essential for the controlled growth of large-area crystals with desired morphologies. Initially, an optimal NaCl concentration was identified to facilitate the formation of large flakes. Under these conditions, nanoribbons emerged as the predominant nanostructure. Subsequently, by varying the growth temperature and the concentration of the chalcogen precursor, a diverse array of nanostructures was obtained. This comprehensive analysis defines the range of achievable morphologies and offers valuable insights into the underlying growth mechanisms driving their formation.
2. Experimental details
Fig. 1(a) depicts a schematic diagram of the (CVD) setup for MoSe2 growth. The CVD experiments were carried out in a commercial APCVD system, QRYSTAL-CVD-1100,44 manufactured by Quazar Technologies.45 The furnace comprises twelve independent, 75 mm-long thermal zones, each equipped with its own heater and temperature sensor. The temperature of each zone is individually adjustable through an intuitive graphical user interface, allowing for seamless control. Adjacent zones can be integrated by synchronizing their set temperatures, enabling the formation of composite heating regions of variable lengths. These zones maintain a temperature uniformity of ±5 °C. This sophisticated system facilitates exceptional control over growth parameters, ensuring the high precision necessary for the demands of this study.For the deposition of MoSe2, high-purity molybdenum trioxide (MoO3, ≥99.5%, Sigma Aldrich), selenium (Se, ≥99.5%, Sigma Aldrich), and sodium chloride (NaCl) powders (99.9%, CDH) were used as precursors, and 300 nm thermally oxidised SiO2/Si wafers were used as substrates. An alumina boat containing 1 mg of MoO3 and three substrates placed face down on top of it (labelled 1, 2 and 3 in Fig. 1(c)) were loaded into the quartz tube. A gap of 0.5 mm was kept between wafers 1 and 2, which acts as an outlet for the precursor vapor. This ensures that some of the vapors escape the alumina boat, and uniform deposition on wafers 4 and 5 occurs, which were placed face-up adjacent to the alumina boat (Fig. 1(c)). The boat containing Se powder (600 mg) was placed upstream at a distance of 31 cm away from the MoO3 boat (Fig. 1(a)). For the NaCl-assisted growth experiments, a mixture of the MoO3 and NaCl powder was used.
Prior to deposition, the substrates (10 mm × 10 mm) were cleaned ultrasonically in acetone and isopropyl alcohol (IPA), respectively, and then dried under Ar gas. The alumina boat containing the mixture of MoO3 and NaCl and the substrates was then loaded into a quartz tube. The CVD furnace was configured into two heating zones: a chalcogen zone heated up to 500 °C for Se vaporisation and the growth zone comprising MoO3, NaCl and the substrates, which was heated up to a higher temperature for MoSe2 synthesis. The temperature profile of these zones is shown in Fig. 1(b). The CVD system was initially evacuated and purged. This procedure was repeated five times over a total period of 30 minutes, during which the chalcogen zone and the growth zone were maintained at room temperature and 150 °C, respectively. Subsequently, the gas flow rate was set to 10 sccm, which comprised Ar (8 sccm) and H2 (2 sccm), with H2 acting as a reducing agent. The growth zone temperature was then ramped up at a rate of 15 °C min−1 until it reached 750 °C. Se was rapidly evaporated at 500 °C when the growth zone reached 725 °C. The system was maintained under this condition for 20 minutes. Finally, the system was cooled gradually with Ar flow at 200 sccm, stopping the H2 flow.
2.1. Characterization
High-resolution optical images of the as-grown MoSe2 flakes were captured using a Carl Zeiss Axio Lab. A1 microscope equipped with an AxioCam ERc5s camera. Raman spectra were recorded with a Horiba Jobin Yvon LabRAM HR spectrometer using a 532 nm excitation laser. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) measurements were conducted using a Thermo Fisher Scientific K-Alpha instrument. Field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) images were acquired with an FEI Apreo LoVac microscope. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) measurements were performed using an Agilent LS5600 system.3. Results and discussion
MoSe2 crystals deposited using the standard recipe (without any NaCl) are triangular, with a maximum domain size of ∼25 μm as shown in Fig. 2(a). The crystals grown are uniform monolayers, as confirmed by Raman spectra (Fig. 2(b)) obtained at different points on the same crystal. The standard A1g (out-of-plane vibrational mode) and E2g (in-plane vibrational mode) peaks for monolayer MoSe2 are observed at 239.7 cm−1 and 286.2 cm−1, respectively.46 The combination modes of the longitudinal (LA(M)) and the transverse (TA(M)), originating from the vicinity of the high-symmetry M point of the MoSe2 Brillouin zone, are observed at 247.4 cm−1.47,48Fig. 2(c) and (d) show high-resolution deconvoluted XPS spectra of Mo 3d and Se 3d core-level signals, respectively. The Mo 3d3/2 and 3d5/2 peaks are located at 232.5 eV and 229.3 eV, respectively, as depicted in Fig. 2(c). Those of Se are detected around 54 eV, as shown in Fig. 2(d). These data are in agreement with the respective values of MoSe2 found in the literature.14,49 These two Mo 3d peaks represent the oxidation charge state of MoSe2. The Mo peak positions are shifted significantly from their hexavalent positions of ∼235.9 eV and 232.5 eV (Mo 3d3/2 and 3d5/2 core levels of MoO3), indicating the reduction of Mo from Mo 6p to Mo 4p. The two comparatively weak peaks present in the Mo 3d plot are linked to Mo6+ 3d and Se2− 3s states, respectively.50 The presence of an Mo6+ peak indicates that a relatively minor amount of MoO3 is expected to be present in the MoSe2 flakes. The peak of Se around 54 eV relates to the doublet core level 3d5/2 and 3d3/2, with peak positions at 54.8 eV and 55.5 eV, respectively.3.1. Variation in growth parameters
NaCl plays a crucial role in influencing the morphology and distribution of the MoSe2 flakes. The intermediate species formed in the reaction of NaCl with MoO3 lowers the energy barrier and decreases the reaction temperature, thereby facilitating the synthesis. The following chain of chemical reactions occurs:| 2MoO3 + 2NaCl → MoO2Cl2↑ + Na2MoO4 |
| 3MoO3 + 2NaCl → MoO2Cl2↑ + Na2Mo2O7 |
The MoO3–NaCl mixture has a large weight loss at ∼550 °C,51 much lower than the melting points of MoO3 and NaCl (Tm(MoO3) = 795 °C, Tm(NaCl) = 801 °C). Volatile MoO2Cl2 is one product of the reaction,52 which sublimates at a relatively low temperature of 175 °C. The vapors of these metal oxychlorides can travel long distances to the substrates and initiate VSS (vapor–solid–solid) growth, resulting in early nucleation of TMDCs. Furthermore, some reports indicate that metal oxychlorides may undergo selenisation at a significantly faster rate than metal oxides, which enhances the reaction rate during the growth process.25,53 Thus, the reactions of intermediate metal oxychlorides (MoO2Cl2), Se, and H2 are faster and eventually facilitate the nucleation and layered growth by lowering the energetic barrier. In contrast, Na reacts with the transition metal oxides to form non-volatile molten salts (NaxMoOy) with high melting points (>600 °C) on the growth substrate without vapor phase transportation.54 After reaction with chalcogen vapor, MoSe2 crystals are grown from liquid melts in the VLS (vapor–liquid–solid) mode. The coexistence of the VSS and VLS induced by oxychlorides and sodium metal oxides results in an increased growth rate, large-area crystals and different morphological nanostructures. We investigated the morphological variation of the as-grown MoSe2 nanocrystals as the CVD-growth parameters were changed in a methodical manner.
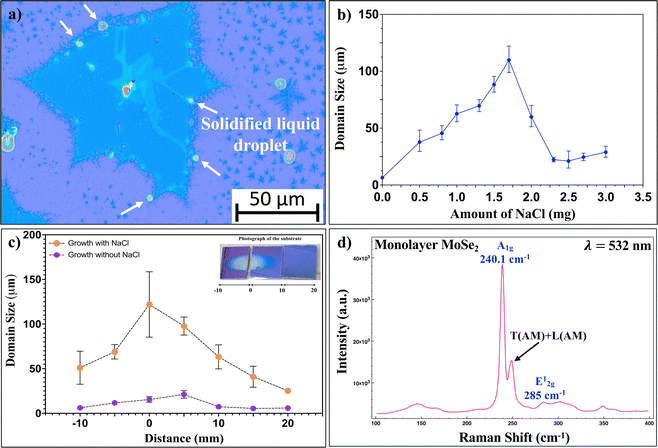
As the size of the crystals increased with the amount of NaCl, it was observed that the large area crystals were surrounded by solidified liquid droplets along the edges. This is depicted in the OM image of Fig. 4(a). These droplets attach themselves to the energy favourable sites along the edges of the as-grown crystals, serving as catalysts, enhancing the mass transport along the edges, thereby increasing the lateral size of the crystals.17,55 In Fig. 4(c), the domain size of the crystals was plotted as a function of the distance between the metal precursor (MoO3 + NaCl) and the position of the as-grown crystals on the substrate. Zero denotes the position of the metal oxide precursor. It is evident from the graphs that the addition of NaCl increases the size of the crystals considerably. The reduction in the size of the crystal as the distance from the source precursor increases is evident in Fig. 4(c). This is due to a concentration gradient of the Mo vapors across the substrate. The presence of such a concentration gradient is due to the fact that the local Mo![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Se ratio varies along the length of the growth substrate. The crystal quality of the NaCl-assisted MoSe2 crystal was determined by Raman spectroscopy (Fig. 4(d)). A1g and E2g peaks for monolayer MoSe2 are observed at 239.9 cm−1 and 28 cm−1, respectively. The separation, Δ, between the A1g and E12g peaks is 45.1 cm−1, further confirming the monolayer nature of the crystals.56
Se ratio varies along the length of the growth substrate. The crystal quality of the NaCl-assisted MoSe2 crystal was determined by Raman spectroscopy (Fig. 4(d)). A1g and E2g peaks for monolayer MoSe2 are observed at 239.9 cm−1 and 28 cm−1, respectively. The separation, Δ, between the A1g and E12g peaks is 45.1 cm−1, further confirming the monolayer nature of the crystals.56
XPS experiments were carried out to study the chemical composition of the MoSe2 grown using NaCl. Peaks of Mo, Se, and O elements can be clearly seen in the XPS survey spectrum (Fig. 5a). Fig. 5b shows the binding energy of Na 1s located at 1072.7 eV, indicating that Na from NaCl combines with the precursor, forming intermediates such as Na2MoO4.57Fig. 5c displays energy core-level peaks located at 229.4 eV and 232.6 eV, which are attributed to Mo 3d5/2 and Mo 3d3/2 of Mo4+, respectively. The Mo6+ 3d peak is not observed in the spectrum, indicating that the films are high-quality MoSe2 and the addition of NaCl does not compromise the quality of the crystal. The peaks located at 54.9 eV and 55.8 eV correspond to the binding energies for Se 3d5/2 and Se 3d3/2, representing the Se2− oxidation state (Fig. 5d).
The morphological evolution in the MoSe2 domains on temperature can be explained by the diffusion rates of Mo, Se, and NaCl at elevated temperatures. The diffusion rate and the deposition of the MoO3, Se, and NaCl vapors on the substrate surface vary with the change in temperature. At lower temperatures, the MoO3 clusters deposited on the substrate's surface have a lower concentration and are small in size. At the onset of deposition, monolayers are formed on the substrate surface by reducing the MoO3 vapors. Further deposition results in an increase in the domain size, and the MoSe2 domains are thus formed with both monolayer and bilayer structures. In the case of growth at high temperatures, the high diffusion rate of the precursor results in the transport of a high concentration of nanoparticles on the surface of the substrate. This results in rapid selenisation and growth of the MoSe2 crystals with the deposition of multilayer nuclei of the MoO3−xSey nanoparticles. Thus causing higher vapor pressure of the metal precursors and enhanced reaction rate. The further growth of these nanoparticles induces the growth of larger crystals. As the temperature is increased beyond 750 °C, the flake size decreases along with predominant multilayer deposition. The domain sizes decrease due to enhanced desorption, favouring vertical growth. Thus, 750 °C was the optimal temperature for the growth of large-area MoSe2 crystals.
The Raman spectrum in Fig. 7(a) further confirms the dependence of growth temperature on the thickness of the MoSe2 films. At a growth temperature of 675 °C, the A1g vibrational mode appears at 239.2 cm−1, characteristic of monolayer MoSe2. At 700 °C, a further shift to 240 cm−1 is observed. Consequently, with increasing growth temperature, a blue shift in the A1g peak is observed (as plotted in Fig. 7(b)), indicating an increase in the film thickness.58,59 At 800 °C, a maximum shift of 3 cm−1 is measured. This is consistent with the formation of multilayer MoSe2. The low-intensity E1g peak at ∼283.4 cm−1 diminishes considerably with increasing thickness. The effects of the growth temperature on the morphology of the MoSe2 crystals are summarised in Table S2 (ESI†).
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Se ratio is the primary criterion affecting the growth of TMDCs. Here, we investigated the effect of Se concentration on the growth of MoSe2 films while keeping the NaCl amount and growth temperatures fixed at 1.7 mg and 750 °C, respectively. By controlling the Se vapor pressure, the as-grown atomic crystals undergo a three-stage shape transformation from fractals and dendrite deposition to 2D compact nanocrystals and eventually to nanoribbons, as illustrated by the flowchart in Fig. 8.
Se ratio is the primary criterion affecting the growth of TMDCs. Here, we investigated the effect of Se concentration on the growth of MoSe2 films while keeping the NaCl amount and growth temperatures fixed at 1.7 mg and 750 °C, respectively. By controlling the Se vapor pressure, the as-grown atomic crystals undergo a three-stage shape transformation from fractals and dendrite deposition to 2D compact nanocrystals and eventually to nanoribbons, as illustrated by the flowchart in Fig. 8.
 | ||
| Fig. 8 Flowchart illustrating the change in morphology of MoSe2 crystals with varied amounts of Se precursor. | ||
At lower Se concentration (150 mg), fractal and dendritic crystals with thick branches were observed. The size of these crystals varies, with a maximum length of ∼100 μm. At higher Se concentrations (300 mg), the gaseous atmosphere becomes enriched with Se and Mo. More Se atoms reach the substrate, resulting in compact triangular crystal structures. When the concentration of Se is further increased to 600 mg, nanoribbons with lengths ≥100 μm were observed. Preferential growth of the nanoribbons along the edges of the triangular MoSe2 domains was predominant. The variation in morphology with Se concentration is summarised in Table S3 (ESI†).
The analysis of XPS data to study the stoichiometry of these crystals is reported in the ESI† (Section S2). The high-resolution deconvoluted XPS spectra of Mo 3d and Se 3d peaks of crystals grown at 150 mg, 300 mg and 600 mg Se concentrations are shown in Fig. S1, S2 and S3 (ESI†), respectively. The Mo![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Se ratio for the dendritic crystals was determined to be ∼0.47, corresponding to a Se-deficient condition. This sub-stoichiometric composition can also be ascribed to Se vacancies.56 This ratio for the triangular crystals was found to be 0.5, which is congruent with the literature. Whereas, for the nanoribbons, the value of the Mo
Se ratio for the dendritic crystals was determined to be ∼0.47, corresponding to a Se-deficient condition. This sub-stoichiometric composition can also be ascribed to Se vacancies.56 This ratio for the triangular crystals was found to be 0.5, which is congruent with the literature. Whereas, for the nanoribbons, the value of the Mo![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Se ratio was ∼0.67, corresponding to a Se-rich environment. The details of these calculations are reported in Table S4 (ESI†).
Se ratio was ∼0.67, corresponding to a Se-rich environment. The details of these calculations are reported in Table S4 (ESI†).
3.2. Morphological evolution
On systematic variation of the growth parameters, diverse nanostructures were deposited. Among them, nanoribbons were dominant. The transition from fractals to snowflakes and dendrites was also prevalent. In addition, spiral growth on MoSe2 triangular domains was found. The growth mechanism of these nanostructures is discussed in the following sub-sections.In the synthesis process, the precursors evaporate and undergo a chemical reaction between the vapors of MoO3 and NaCl, forming intermediate species like Na2MoO4/Na2MoO7.33 A mixture of gas–liquid droplets is formed when these intermediate species diffuse and melt on the substrate. Vaporised Se dissolves into the droplet continuously and results in the formation of MoSe2 seeds. As the droplet crawls on the surface, Se continues to dissolve into the droplet, inducing further growth and yielding ribbon-like structures.60 In the XPS data (Fig. S4 and S5, ESI†), the Na 1s peak is observed at 1071.69 eV corresponding to Na2MoOx,61 which confirms the presence of intermediate Na–Mo compounds on the surface. This peak intensifies at higher growth temperatures, namely 750 °C. This was also the optimal temperature for the CVD growth of long MoSe2 nanoribbons in our studies. This further gives evidence of the role of intermediate species in the growth of nanoribbons.
The average length of the nanoribbons was measured to be ∼70 μm, with a maximum length of ∼120 μm. The lengths vary with the amount of NaCl mixed with the MoO3 precursor. It was found that the growth of nanoribbons was initiated with NaCl concentration greater than 1.3 mg. The length increases with increase in NaCl concentration, reaching a saturation point. Beyond this, there is no effect on the length of the nanoribbons with the addition of NaCl. This observation is congruent with the variation in the size of the crystals with NaCl concentration. The variation in the average nanoribbon length as a function of NaCl amount is shown in Fig. 9(e). The growth of nanoribbons observed in this study is predominantly along the edges of the underlying domain, as evident from Fig. 9(a) and (f).
The alignment of these ribbons is primarily determined by the orientation of the underlying crystal. Additionally, few-layered nanoribbons extending from the nucleation site on the MoSe2 domain are observed as shown in the high resolution OM images of Fig. 9(b) and (c). These ribbons are locally aligned but exhibit occasional regular kinks, suggesting that the growth is guided either by the substrate or the crystal facets of the underlying MoSe2 domain. It is observed that some of the nanoribbons are terminated with a nanoparticle. Fig. 9(g) shows a zoomed-in FESEM image of such nanoparticles. The size of these particles is measured to match with that of the width of the ribbons (∼0.14 μm). As mentioned earlier, these characteristic features of nanostructures result from the crawling mode of VLS growth. For a few nanoribbons, there were no nanoparticles at their ends. In some cases, the absence of the nanoparticle can be explained by the fact that the liquid droplet precursor might have been consumed during the growth of the ribbon. Fig. 9(d) shows the Raman measurement of the nanoribbons grown on triangular MoSe2 domains. The difference between A1g and E2g (Δ = 42 cm−1) in the data confirms that the multilayer nanoribbons are grown on few-layer MoSe2 domains. AFM measurements were acquired to study the surface morphology and the thickness of the MoSe2 nanoribbons. Fig. 9(h) depicts the AFM image and the height profile of a nanoribbon scanned in the non-contact mode, respectively. The contrast in the image indicates the difference in the heights of the structure. A height profile along the line AB denotes a thickness of ∼6 nm, corresponding to a thickness of around 10 layers.
![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Se = 1 mg
Se = 1 mg![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 600 mg), but thick-branched dendrite structures were observed at a low Se concentration (Mo
600 mg), but thick-branched dendrite structures were observed at a low Se concentration (Mo![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) Se = 1 mg
Se = 1 mg![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) :
:![[thin space (1/6-em)]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_2009.gif) 150 mg). In Fig. 10(a) and (b), a clear transition from the compact island to fractals at the edges is observed.
150 mg). In Fig. 10(a) and (b), a clear transition from the compact island to fractals at the edges is observed.
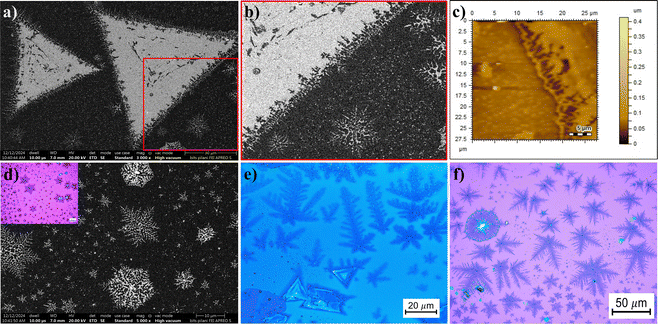 | ||
| Fig. 10 (a) FESEM image of a MoSe2 crystal with fractal edges. (b) Zoomed-in image of the area enclosed in a red square showing the fractals near the edges in Fig. 9(a). (c) AFM image showing the fractal edge of a triangular crystal. (d) FESEM images of snowflakes, inset contains a high-resolution OM image of the same. (e) and (f) High-resolution OM images of the as-grown MoSe2 dendrite structures. | ||
At increased flux of metal precursor, the dominant morphology is fractal due to surface diffusion prevailing over edge diffusion.62 The adatoms reaching the edge of growing triangular domains do not contribute to the lateral growth. They diffuse randomly, which leads to the formation of fractals. The edge diffusion is highly suppressed, but the incoming adatoms attach themselves to the domain edges predominantly via diffusion-limited aggregation (DLA).63 Adding NaCl as a seed promoter, there is an obvious increase in the metal flux because of the increase in volatile metal oxychlorides (MoOxCly). Thus, the formation of fractals along the edges of a compact triangular domain and that of isolated fractals are promoted.
The transition from triangular to truncated, and further to fractal and dendritic MoSe2 flakes, is attributed64,65 to accelerated directional growth of either a Mo- or Se-terminated edge under a Se-deficient or Mo-rich growth environment, respectively. Thus, different dendritic shapes are induced, including snowflakes. Dendritic structures are observed at a low Se concentration, mainly at the substrate–boat contact interface, which creates a confined space leading to a high flux of metal precursors.61,66 The abundance of MoO3−x vapour in the confined reaction space also leads to fractal edges surrounding the compact triangular flakes, as shown in the AFM image of Fig. 10(c). The fractal edges observed in our experiment could be understood to be driven by kinetics rather than thermodynamics. This is congruent with our earlier work on MoS2 dendrites.38 These dendrites develop as atoms and diffuse preferentially along specific directions, forming the characteristic “branches” of the structure. From Fig. 10(d), it can be observed that most of the dendrites align with the three crystallographic directions typical of snowflakes. The larger dendrites have a greater number of branches, as shown in Fig. 10(e) and (f). The anisotropic influence of neighbouring atoms, combined with the tendency of dendrites to grow only along lower-energy directions, causes their preferential growth along specific directions.
The formation of the spiral growth depends on the MoSe2 flux. At low MoSe2 flux, monolayer MoSe2 is formed, whereas, as the flux increases, both monolayer and spiral MoSe2 are obtained. At a high flux of MoSe2, thick spiral MoSe2 with screw dislocations is formed. A diffusion-limited growth mechanism causes the formation of a domain when it is growing. During this growth, one grain boundary can elevate over another when two edges encounter a lattice mismatch within the same domain.42 A line of unsaturated chalcogen dangling bonds is formed on the lifted edge. A screw dislocation appears at the end of this line, which favours the growth of spirals. The generation of screw dislocations is thus increased, if the probability of a misaligned meeting of two exposed edges is increased. These accidental overgrowths occur frequently when the 2D growth rate increases. The rapid growth of certain edges is thus favoured over slower ones, when the growth rate is high. The spiral growth is observed in the as-grown MoSe2 crystals on adding NaCl with amounts ≥1.3 mg at a growth temperature of 750 °C. The considerable increase in growth rate when adding salt promotes the formation of edge dislocations. As growth advances around the screw dislocation, the exposed edges trace the corners of the underlying layer edges. This leads to the formation of the spirals.
4. Conclusions
The controlled growth of diverse MoSe2 nanostructures synthesised using an APCVD was systematically investigated, with NaCl serving as a seed promoter. Key CVD growth parameters, including the optimal NaCl concentration, growth temperature, and chalcogen precursor amount, were optimised to grow unique morphologies such as nanoribbons, dendrites, snowflakes, and spirals. A morphological mapping of a clearly defined parameter space is proposed to grow the desired nanostructures. This study not only establishes precise conditions for the reproducible synthesis of these unique structures but also provides insights into their growth mechanisms. This comprehensive study can be extended to the controlled CVD growth of various other TMDC nanostructures to be used in various next-generation applications.Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.Acknowledgements
We would like to express our sincere gratitude to Dr Krishnendu Chatterjee for his invaluable contribution to the development of the QRYSTAL CVD. We sincerely thank Mr Sandeep Kumar for his assistance in synthesizing CVD MoSe2. Additionally, we extend our heartfelt thanks to Dr O. P. Thakur, Solid State Physics Laboratory (SSPL), DRDO, Timarpur, Delhi, for granting us access to their microscopy facility and to Dr Akhilesh Pandey, SSPL, DRDO, for providing the AFM facility. We thank Garima Gupta (SSPL, DRDO) for acquiring AFM data. We thank the SIF facility, BITS Pilani, and Pilani Campus, for providing FESEM, XPS and Raman facilities.References
- S. Zhang, Y. Hao, F. Gao, X. Wu, S. Hao, M. Qiu, X. Zheng, Y. Wei and G. Hao, Controllable growth of wafer-scale two-dimensional WS2 with outstanding optoelectronic properties, 2D Mater., 2023, 11(1), 015007 CrossRef.
- W. Yan, J. Wan, B. Zhao, Z. Zhang, L. Meng and X. A. Li, Controllable Synthesis of Large-Area MoSe2 Monolayer Films and Bilayer Crystals, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2024, 128, 58 CrossRef.
- W. Fu, M. John, T. D. Maddumapatabandi, F. Bussolotti, Y. S. Yau, M. Lin and K. E. Johnson Goh, Toward Edge Engineering of Two-Dimensional Layered Transition-Metal Dichalcogenides by Chemical Vapor Deposition, ACS Nano, 2023, 17(17), 16348–16368 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. D. Cain, F. Shi, J. Wu and V. P. Dravid, Growth Mechanism of Transition Metal Dichalcogenide Monolayers: The Role of Self-Seeding Fullerene Nuclei, ACS Nano, 2016, 10(5), 5440–5445 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- T. Chen, G. Hao, G. Wang, B. Li, L. Kou, H. Yang, X. Zheng and J. Zhong, Controlled growth of atomically thin MoSe2 films and nanoribbons by chemical vapor deposition, 2D Mater., 2019, 6(2), 025002 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Huang, H. Liu, B. Jin, M. Liu, Q. Zhang, L. Luo, S. Chu, S. Chu and R. Peng, Large-area snow-like MoSe2 monolayers: synthesis, growth mechanism, and efficient electrocatalyst application, Nanotechnology, 2017, 28(27), 275704 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. H. Chang, W. Zhang, Y. Zhu, Y. Han, J. Pu, J. K. Chang, W. T. Hsu, J. K. Huang, C. L. Hsu, M. H. Chiu, T. Takenobu, H. Li, C. I. Wu, W. H. Chang, A. T. S. Wee and L. J. Li, Monolayer MoSe2 grown by chemical vapor deposition for fast photodetection, ACS Nano, 2014, 8(8), 8582–8590 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- A. Eftekhari, Molybdenum diselenide (MoSe2) for energy storage, catalysis, and optoelectronics, Appl. Mater. Today, 2017, 8, 1–17 CrossRef.
- S. Li, Salt-assisted chemical vapor deposition of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides, iScience, 2021, 11(24), 103229 CrossRef PubMed.
- J. C. Shaw, H. Zhou, Y. Chen, N. O. Weiss, Y. Liu, Y. Huang and X. Duan, Chemical vapor deposition growth of monolayer MoSe2 nanosheets, Nano Res., 2014, 7, 511–517 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Lu, M. I. B. Utama, J. Lin, X. Gong, J. Zhang, Y. Zhao, S. T. Pantelides, J. Wang, Z. Dong, Z. Liu, W. Zhou and Q. Xiong, Large-area synthesis of monolayer and few-layer MoSe2 films on SiO2 substrates, Nano Lett., 2014, 14(5), 2419–2425 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Xia, X. Huang, L. Z. Liu, M. Wang, L. Wang, B. Huang, D. D. Zhu, J. J. Li, C. Z. Guc and X. M. Meng, CVD synthesis of large-area, highly crystalline MoSe2 atomic layers on diverse substrates and application to photodetectors, Nanoscale, 2014, 6(15), 8949–8955 RSC.
- Z. Chen, H. Liu, X. Chen, G. Chu, S. Chu and H. Zhang, Wafer-size and single-crystal MoSe2 atomically thin films grown on GaN substrate for light emission and harvesting, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2016, 8(31), 20267–20273 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Zhao, H. Lee, W. Choi, W. Fei and C. J. Lee, Large-area synthesis of monolayer MoSe2 films on SiO2/Si substrates by atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition, RSC Adv., 2017, 7(45), 27969–27973 RSC.
- H. Wang, D. Zhu, F. Jiang, P. Zhao, H. Wang, Z. Zhang, X. Chen and C. Jin, Revealing the microscopic CVD growth mechanism of MoSe2 and the role of hydrogen gas during the growth procedure, Nanotechnology, 2018, 29, 31 Search PubMed.
- T. Pham, K. Reidy, J. D. Thomsen, B. Wang, N. Deshmukh, M. A. Filler and F. M. Ross, Salt-assisted vapor-liquid-solid growth of 1D van der Waals, Materials, 2024, 36(24), 2309360 CAS.
- S. Yang, C. Wang, J. Wu, H. Yan, G. Wang, J. Feng, B. Zhang, D. Li, T. J. Booth, P. Bøggild, G. Yu and B. Luo, Self-relaxation vapor-liquid-solid growth of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides with loose interface, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2023, 613, 156019 CrossRef CAS.
- H. Guo, Y. Xu, H. Chen, Z. Wang, X. Mao, G. Zhou, J. Zhang and S. Wang, Synthesis of multiwall Boron Nitride (BN) nanotubes by a PVD method based on vapor-liquid-solid Growth, Materials, 2020, 13(4), 915 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Hacohen, R. Popovitz-Biro, E. Grunbaum, Y. Prior and R. Tenne, Vapor-liquid-solid growth of NiCl2 nanotubes via reactive gas laser ablation, Adv. Mater., 2002, 14(15), 1075–1078 CrossRef CAS.
- G. Shao, X. X. Xue, X. Zhou, J. Xu, Y. Jin, S. Qi, N. Liu, H. Duan, S. Wang, S. Li, M. Ouzounian, T. S. Hu, J. Luo, S. Liu and Y. Feng, Shape-engineered synthesis of atomically thin 1T-SnS2 catalyzed by potassium halides, ACS Nano, 2019, 13(7), 8265–8274 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. Schönherr, L. J. Collins-McIntyre, S. L. Zhang, P. Kusch, S. Reich, T. Giles, D. Daisenberger, D. Prabhakaran and T. Hesjedal, Vapour-liquid-solid growth of ternary Bi2Se2Te nanowires, Nanoscale Res. Lett., 2014, 9(1), 1–6 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. Li, S. Wang, D. M. Tang, W. Zhao, H. Xu, L. Chu, Y. Bando, D. Golberg and G. Eda, Halide-assisted atmospheric pressure growth of large WSe2 and WS2 monolayer crystals, Appl. Mater. Today, 2015, 1(1), 60–66 CrossRef.
- S. Li, Y. C. Lin, J. Hong, B. Gao, H. E. Lim and X. Yang, et al., Mixed-Salt Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition of Two-Dimensional Transition Metal Dichalcogenides, Chem. Mater., 2021, 33 CAS.
- H. Kim, D. Ovchinnikov, D. Deiana, D. Unuchek and A. Kis, Suppressing nucleation in metal-organic chemical vapor deposition of MoS2 monolayers by alkali metal halides, Nano Lett., 2017, 17(8), 5056–5063 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Zhou, J. Lin, X. Huang, Y. Zhou, Y. Chen, J. Xia, H. Wang, Y. Xie, H. Yu, J. Lei, D. Wu, F. Liu, Q. Fu, Q. Zeng, C. H. Hsu, C. Yang, L. Lu, T. Yu, Z. Shen, H. Lin, B. I. Yakobson, Q. Liu, K. Suenaga, G. Liu and Z. Liu, A library of atomically thin metal chalcogenides, Nature, 2018, 556, 355–359 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Li, W. Yan, Y. Lv, J. Leng, D. Zhang, C. O. Coileaín, C. P. Cullen, S. T. Lindner, G. S. Duesberg, J. Cho, M. Choi, B. S. Chun, Y. Zhao, C. Lv, S. K. Arora and H. C. Wu, Sub-millimeter size high mobility single crystal MoSe2 monolayers synthesized by NaCl-assisted chemical vapor deposition, RSC Adv., 2020, 10(3), 1580–1587 RSC.
- Q. Feng, M. Zhu, Y. Zhao, H. Liu, M. Li, J. Zheng, H. Xu and Y. Jiang, Chemical vapor deposition growth of sub-centimeter single crystal WSe2 monolayer by NaCl-assistant, Nanotechnology, 2019, 30, 3 Search PubMed.
- A. Singh, M. Moun, M. Sharma, A. Barman, A. Kumar Kapoor and R. Singh, NaCl-assisted substrate dependent 2D planar nucleated growth of MoS2, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2021, 538, 148201 CrossRef CAS.
- M. Bay, Y. Çelik, F. Ay and N. K. Perkgöz, Catalytic strategies for uniform monolayer MoSe2 growth in CVD processes, Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process., 2024, 180, 108551 CrossRef CAS.
- P. Cui, J. H. Choi, W. Chen, J. Zeng, C. K. Shih, Z. Li and Z. Zhang, Contrasting structural reconstructions, electronic properties, and magnetic orderings along different edges of zigzag transition metal dichalcogenide nanoribbons, Nano Lett., 2017, 17(2), 1097–1101 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Chen, P. Cui, X. Ren, C. Zhang, C. Jin, Z. Zhang and C. K. Shih, Fabrication of MoSe2 nanoribbons via an unusual morphological phase transition, Nat. Commun., 2017, 8(1), 1–9 CrossRef PubMed.
- S. M. Poh, S. J. R. Tan, X. Zhao, Z. Chen, I. Abdelwahab, D. Fu, H. Xu, Y. Bao, W. Zhou and K. P. Loh, Large area synthesis of 1D-MoSe2 using molecular beam epitaxy, Adv. Mater., 2017, 29(12), 1605641 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. Li, Z. Zhou, S. Zhang and Z. Chen, MoS2 nanoribbons: High stability and unusual electronic and magnetic properties, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130(49), 16739–16744 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Q. Zhou, S. Su, P. Cheng, X. Hu, X. Gao, Z. Zhang and J. M. Liu, Vertically conductive MoS2 pyramids with a high density of active edge sites for efficient hydrogen evolution, J. Mater. Chem. C, 2020, 8, 3017 RSC.
- X. Xu and L. Liu, MoS2 with Controlled thickness for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution, Nanoscale Res. Lett., 2021, 16(1), 1–10 CrossRef PubMed.
- Y. Zhang, K. Liu, F. Wang, T. A. Shifa, Y. Wen, F. Wang, K. Xu, Z. Wang, C. Jiang and J. He, Dendritic growth of monolayer ternary WS2(1−x)Se2x flakes for enhanced hydrogen evolution reaction, Nanoscale, 2017, 9(17), 5641–5647 RSC.
- J. Xie, H. Zhang, S. Li, R. Wang, X. Sun, M. Zhou, J. Zhou, X. W. Lou and Y. Xie, Defect-rich MoS2 ultrathin nanosheets with additional active edge sites for enhanced electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution, Adv. Mater., 2013, 25(40), 5807–5813 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. Tyagi, A. A. Tiwari, S. Dey and D. Sahdev, Chemical vapor deposition growth ofs large-area molybdenum disulphide (MoS2) dendrites, Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects, 2024, 40, 101380 CrossRef CAS.
- T. H. Ly, J. Zhao, H. Kim, G. H. Han, H. Nam and Y. H. Lee, Vertically Conductive MoS2 Spiral Pyramid, Adv. Mater., 2016, 28(35), 7723–7728 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- J. Ahn, S. Ha, J. Choi, D. I. Yeom and Y. Yoo, Large-area structure selective synthesis of symmetry-broken MoSe2 and their broadband nonlinear optical response, Adv. Opt. Mater., 2023, 11, 12 Search PubMed.
- D. Ouyang, X. Tong, S. Liu, J. Wang, Y. Zhao, R. Liu, X. Zhao, N. Zhang, F. Cao, Y. Liu, Y. Li, L. Li and T. Zhai, Superior nonlinear optical response in non-centrosymmetric stacking edge-rich spiral MoTe2 nanopyramids, Adv. Funct. Mater., 2022, 32(21), 2113052 CrossRef CAS.
- X. Fan, Y. Jiang, X. Zhuang, H. Liu, T. Xu, W. Zheng, P. Fan, H. Li, X. Wu, X. Zhu, Q. Zhang, H. Zhou, W. Hu, X. Wang, L. Sun, X. F. Duan and A. Pan, Broken symmetry induced strong nonlinear optical effects in spiral WS2 nanosheets, ACS Nano, 2017, 11(5), 4892–4898 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- M. J. Shearer, L. Samad, Y. Zhang, Y. Zhao, A. Puretzky, K. W. Eliceiri, J. C. Wright, R. J. Hamers and S. Jin, Complex and non-centrosymmetric stacking of layered metal dichalcogenide materials created by screw dislocations, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139(9), 3496–3504 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- QRYSTAL-CVD-1100 Chemical Vapour Deposition System Specification sheet.
- Quazar Technologies Pvt. Ltd, https://quazartech.com/.
- P. Soubelet, A. E. Bruchhausen, A. Fainstein, K. Nogajewski and C. Faugeras, Resonance effects in the Raman scattering of monolayer and few-layer MoSe2, Phys. Rev. B, 2016, 93, 15 CrossRef.
- P. Tonndorf, R. Schmidt, P. Böttger, X. Zhang, J. Börner, A. Liebig, M. Albrecht, C. Kloc, O. Gordan, D. R. T. Zahn, S. Michaelis de Vasconcellos and R. Bratschitsch, Photoluminescence emission and Raman response of monolayer MoS2, MoSe2 and WSe2, Opt. Express, 2013, 21(4), 4908 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- P. A. Markeev, E. Najafidehaghani, Z. Gan, K. Sotthewes, A. George, A. Turchanin and M. P. Jong, Energy-level alignment at interfaces between transition-metal dichalcogenide monolayers and metal electrodes studied with kelvin probe force microscopy, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2021, 125(24), 13551–13559 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Wang, G. Wang, X. Yang, H. Yang, M. Zhu, S. Zhang, G. Peng and Z. Li, Synthesis of monolayer MoSe2 with controlled nucleation via reverse-flow chemical vapor deposition, Nanomaterials, 2020, 10(1), 75 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- G. S. Papanai, K. R. Sahoo, G. B. Reshma, S. Gupta and B. K. Gupta, Role of processing parameters in CVD grown crystalline monolayer MoSe2, RSC Adv., 2022, 12(21), 13428–13439 RSC.
- M. Mobin, A. U. Malik and S. Ahmad, High-temperature interactions of metal oxides with NaCl, J. Less-Common Met., 1990, 160(1), 1–14 CrossRef CAS.
- D. A. Johnson, J. H. Levy, J. C. Taylor, A. B. Waugh and J. Brough, Purification of molybdenum: volatilisation processes using MoO3, Polyhedron, 1982, 1(5), 479–482 CrossRef CAS.
- X. R. Shi, J. Wang and K. Hermann, Theoretical cluster studies on the catalytic sulfidation of MoO3, J. Phys. Chem. C, 2010, 114(14), 6791–6801 CrossRef CAS.
- H. R. Rasouli, N. Mehmood, O. Çakiroǧlu and T. Serkan Kasirga, Real-time optical observation and control of atomically thin transition metal dichalcogenide synthesis, Nanoscale, 2019, 11(15), 7317–7323 RSC.
- L. Huang, Q. H. Thi, F. Zheng, X. Chen, Y. W. Chu, C. S. Lee, J. Zhao and T. H. Ly, Catalyzed Kinetic Growth in Two-Dimensional MoS2, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142(30), 13130–13135 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- C. González, J. P. B. Silva, A. S. Viana, K. Gwozdz and O. Conde, Shape-controlled monolayer MoSe2 flakes by chemical vapor deposition towards tuning the photoluminescence emission, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2022, 605, 154742 CrossRef.
- L. Chen, L. Zang, L. Chen, J. Wu, C. Jiang and J. Song, Study on the catalyst effect of NaCl on MoS2 growth in a chemical vapor deposition process, Cryst. Eng. Commun., 2021, 23(31), 5337 RSC.
- X. Zhang, Characterization of Layer Number of Two-Dimensional Transition Metal Diselenide Semiconducting Devices Using Si-Peak Analysis, Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng., 2019,(1), 7865698 CAS.
- Y. Sha, S. Xiao, X. Zhang, F. Qin and X. Gu, Layer-by-layer thinning of MoSe2 by soft and reactive plasma etching, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2017, 411, 182–188 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Li, Y. C. Lin, W. Zhao, J. Wu, Z. Wang, Z. Hu, Y. Shen, D. M. Tang, J. Wang, Q. Zhang, H. Zhu, L. Chu, W. Zhao, C. Liu, Z. Sun, T. Taniguchi, M. Osada, W. Chen, Q. H. Xu, A. T. S. Wee, K. Suenaga, F. Ding and G. Eda, Vapor-liquid-solid growth of monolayer MoS2 nanoribbons, Nat. Mater., 2018, 17, 535–542 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- R. R. Srivastava, S. Sarkar and A. Srivastava, Study of morphological evolution and growth mechanism of CVD grown 2D tin disulfide, Surf. Interfaces, 2023, 38, 102870 CrossRef CAS.
- J. Ren, B. Guo, Y. Feng and K. Yu, Few-layer MoS2 dendrites as a highly active humidity sensor, Phys. E, 2020, 116, 113782 CrossRef CAS.
- S. Chowdhury, A. Roy, I. Bodemann and S. K. Banerjee, Two-dimensional to three-dimensional growth of transition metal diselenides by chemical vapor deposition: interplay between fractal, dendritic, and compact Morphologies, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12(13), 15885–15892 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- Y. Nie, C. Liang, K. Zhang, R. Zhao, S. M. Eichfeld, P. R. Cha, L. Colombo, J. A. Robinson, R. M. Wallace and K. Cho, First-principles kinetic Monte Carlo study on the growth patterns of WSe2 monolayer, 2D Mater., 2016, 3(2), 25029 CrossRef.
- M. Suleman, S. Lee, M. Kim, V. H. Nguyen, M. Riaz, N. Nasir, S. Kumar, H. M. Park, J. Jung and Y. Seo, NaCl-Assisted temperature-dependent controllable growth of large-area MoS2 crystals using confined-space CVD, ACS Omega, 2022, 7(34), 30074–30086 CrossRef CAS PubMed.
- S. Zhou, L. Gan, D. Wang, H. Li and T. Zhai, Space-confined vapor deposition synthesis of two dimensional materials, Nano Res., 2018, 11, 2909–2931 CrossRef CAS.
Footnote |
| † Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d5ma00121h |
| This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry 2025 |